PySide6.QtSensors.QAccelerometerReading¶
- class QAccelerometerReading¶
The
QAccelerometerReadingclass reports on linear acceleration along the X, Y and Z axes. More…Synopsis¶
Properties¶
Methods¶
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
QAccelerometerReading Units¶
The scale of the values is meters per second squared. The axes are arranged as follows.
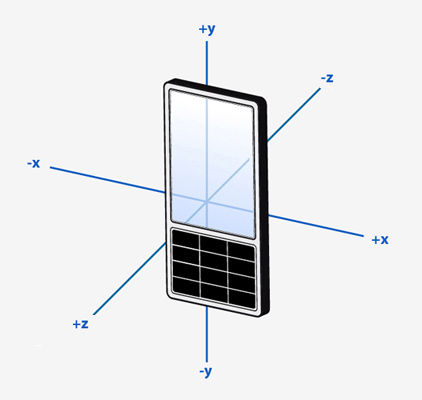
A monoblock device sitting at rest, face up on a desk will experience a force of approximately 9.8 on the Z axis (ie. towards the roof). This is the proper acceleration the device experiences relative to freefall.
Note
Properties can be used directly when
from __feature__ import true_propertyis used or via accessor functions otherwise.- property xᅟ: float¶
This property holds the acceleration on the X axis..
The scale of the values is meters per second squared.
See also
QAccelerometerReading Units- Access functions:
- property yᅟ: float¶
This property holds the acceleration on the Y axis..
The scale of the values is meters per second squared.
See also
QAccelerometerReading Units- Access functions:
- property zᅟ: float¶
This property holds the acceleration on the Z axis..
The scale of the values is meters per second squared.
See also
QAccelerometerReading Units- Access functions:
- setX(x)¶
- Parameters:
x – float
Sets the acceleration on the X axis to
x.See also
- setY(y)¶
- Parameters:
y – float
Sets the acceleration on the Y axis to
y.See also
- setZ(z)¶
- Parameters:
z – float
Sets the acceleration on the Z axis to
z.See also
Getter of property
xᅟ.Getter of property
yᅟ.Getter of property
zᅟ.