PySide6.QtCore.QLineF¶
- class QLineF¶
The
QLineFclass provides a two-dimensional vector using floating point precision. More…Synopsis¶
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
__reduce__()def
__repr__()def
angle()def
angleTo()def
center()def
dx()def
dy()def
intersects()def
isNull()def
length()def
normalVector()def
__ne__()def
__mul__()def
__eq__()def
p1()def
p2()def
pointAt()def
setAngle()def
setLength()def
setLine()def
setP1()def
setP2()def
setPoints()def
toLine()def
toTuple()def
translate()def
translated()def
unitVector()def
x1()def
x2()def
y1()def
y2()
Static functions¶
def
fromPolar()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
A
QLineFdescribes a finite length line (or line segment) on a two-dimensional surface.QLineFdefines the start and end points of the line using floating point accuracy for coordinates. Use thetoLine()function to retrieve an integer-based copy of this line.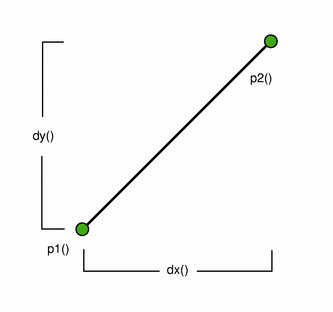
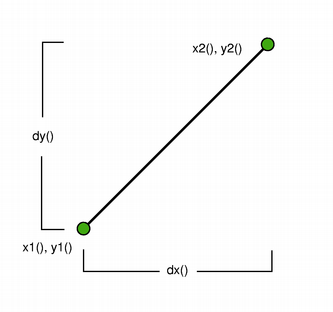
The positions of the line’s start and end points can be retrieved using the
p1(),x1(),y1(),p2(),x2(), andy2()functions. Thedx()anddy()functions return the horizontal and vertical components of the line, respectively.The line’s length can be retrieved using the
length()function, and altered using thesetLength()function. Similarly,angle()andsetAngle()are respectively used for retrieving and altering the angle of the line. Use theisNull()function to determine whether theQLineFrepresents a valid line or a null line.The
intersects()function determines theIntersectionTypefor this line and a given line, while theangleTo()function returns the angle between the lines. In addition, theunitVector()function returns a line that has the same starting point as this line, but with a length of only 1, while thenormalVector()function returns a line that is perpendicular to this line with the same starting point and length.Finally, the line can be translated a given offset using the
translate()function, and can be traversed using thepointAt()function.Constraints¶
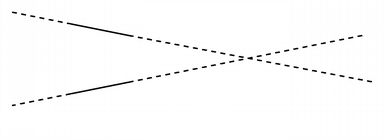
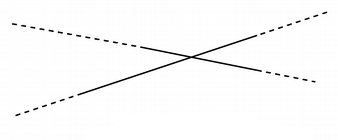
QLineis limited to the minimum and maximum values for theinttype. Operations on aQLinethat could potentially result in values outside this range will result in undefined behavior.- class IntersectionType¶
Describes the intersection between two lines.
QLineF::UnboundedIntersection
QLineF::BoundedIntersection
Constant
Description
QLineF.NoIntersection
Indicates that the lines do not intersect; i.e. they are parallel.
QLineF.UnboundedIntersection
The two lines intersect, but not within the range defined by their lengths. This will be the case if the lines are not parallel. intersect() will also return this value if the intersect point is within the start and end point of only one of the lines.
QLineF.BoundedIntersection
The two lines intersect with each other within the start and end points of each line.
See also
- __init__()¶
Constructs a null line.
- __init__(line)
- Parameters:
line –
QLine
Construct a
QLineFobject from the given integer-basedline.Constructs a line object that represents the line between
p1andp2.- __init__(x1, y1, x2, y2)
- Parameters:
x1 – float
y1 – float
x2 – float
y2 – float
Constructs a line object that represents the line between (
x1,y1) and (x2,y2).- __reduce__()¶
- Return type:
str
- __repr__()¶
- Return type:
str
- angle()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the angle of the line in degrees.
The return value will be in the range of values from 0.0 up to but not including 360.0. The angles are measured counter-clockwise from a point on the x-axis to the right of the origin (x > 0).
See also
Returns the angle (in degrees) from this line to the given
line, taking the direction of the lines into account. If the lines do notintersectwithin their range, it is the intersection point of the extended lines that serves as origin (seeUnboundedIntersection).The returned value represents the number of degrees you need to add to this line to make it have the same angle as the given
line, going counter-clockwise.See also
Returns the center point of this line. This is equivalent to 0.5 *
p1()+ 0.5 *p2().- dx()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the horizontal component of the line’s vector.
- dy()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the vertical component of the line’s vector.
Returns a
QLineFwith the givenlengthandangle.The first point of the line will be on the origin.
Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
Returns a value indicating whether or not this line intersects with the given
line.The actual intersection point is extracted to
intersectionPoint(if the pointer is valid). If the lines are parallel, the intersection point is undefined.- isNull()¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the line does not have distinct start and end points; otherwise returnsfalse. The start and end points are considered distinct ifqFuzzyCompare()can distinguish them in at least one coordinate.Note
Due to the use of fuzzy comparison, isNull() may return
truefor lines whoselength()is not zero.See also
qFuzzyCompare()length()- length()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the length of the line.
See also
Returns a line that is perpendicular to this line with the same starting point and length.
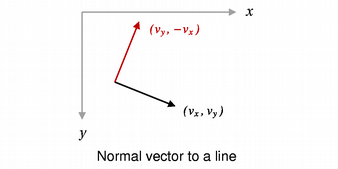
See also
- __ne__(rhs)
- Parameters:
rhs –
QLineF- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the linelhsis not the same as linerhs.A line is different from another line if their start or end points differ, or the internal order of the points is different.
- __mul__(m)¶
- Parameters:
m –
QTransform- Return type:
- __eq__(rhs)
- Parameters:
rhs –
QLineF- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the linelhsis the same as linerhs.A line is identical to another line if the start and end points are identical, and the internal order of the points is the same.
Returns the line’s start point.
Returns the line’s end point.
Returns the point at the position specified by finite parameter
t. The function returns the line’s start point if t = 0, and its end point if t = 1.- setAngle(angle)¶
- Parameters:
angle – float
Sets the angle of the line to the given
angle(in degrees). This will change the position of the second point of the line such that the line has the given angle.Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
See also
- setLength(len)¶
- Parameters:
len – float
Sets the length of the line to the given finite
length.QLineFwill move the end point -p2()- of the line to give the line its new length, unlesslength()was previously zero, in which case no scaling is attempted.See also
- setLine(x1, y1, x2, y2)¶
- Parameters:
x1 – float
y1 – float
x2 – float
y2 – float
Sets this line to the start in
x1,y1and end inx2,y2.Sets the starting point of this line to
p1.Sets the end point of this line to
p2.Sets the start point of this line to
p1and the end point of this line top2.Returns an integer-based copy of this line.
Note that the returned line’s start and end points are rounded to the nearest integer.
See also
QLineF()toLineF()- toTuple()¶
- Return type:
object
Translates this line by the given
offset.- translate(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – float
dy – float
This is an overloaded function.
Translates this line the distance specified by
dxanddy.Returns this line translated by the given
offset.- translated(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – float
dy – float
- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Returns this line translated the distance specified by
dxanddy.Returns the unit vector for this line, i.e a line starting at the same point as this line with a length of 1.0, provided the line is non-null.
See also
- x1()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the x-coordinate of the line’s start point.
See also
- x2()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the x-coordinate of the line’s end point.
See also
- y1()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the y-coordinate of the line’s start point.
See also
- y2()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the y-coordinate of the line’s end point.
See also