Android Service with BroadcastReceiver - Same Lib File
Demonstrates how to run an Android service in a separate process, and how to communicate with Qt using a BroadcastReceiver.
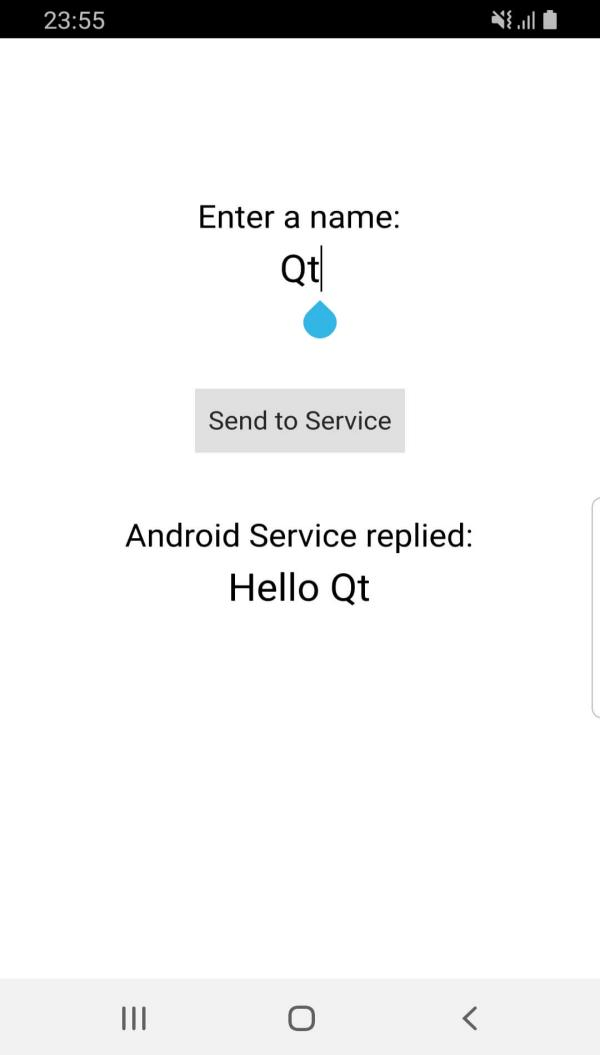
This example demonstrates how to create and run an Android service in its own process using the same main .so lib file, and then exchange data between QML/C++ and the Java service using a BroadcastReceiver.
When clicking the Send to Service button, the name entered in the QML view, Qt, in this case, is sent to the Android service. Then, the service replies back with a message Hello Qt which is printed in the QML view.
Running the Example
To run the example from Qt Creator, open the Welcome mode and select the example from Examples. For more information, visit Building and Running an Example.
Create the Service
When running the app's process, you can extend either QtService or Service. Extending QtService allows Qt to load all the necessary libraries to load Qt components correctly and call native methods on Android. However, here the service is running in the same process, and with the BroadcastReceiver you don't need native calls to exchange messages with Qt, so extending either class works.
Start by creating the Java service class. This is a normal Android Service that receives a name from QML and replies back with Hello <name>:
package org.qtproject.example.qtandroidservice;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;
import android.os.IBinder;
import org.qtproject.qt5.android.bindings.QtService;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
public class QtAndroidService extends QtService
{
private static final String TAG = "QtAndroidService";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG, "Creating Service");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.i(TAG, "Destroying Service");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
int ret = super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
String name = new String(intent.getByteArrayExtra("name"));
Intent sendToUiIntent = new Intent();
sendToUiIntent.setAction(ActivityUtils.BROADCAST_NAME_ACTION);
sendToUiIntent.putExtra("name", name);
Log.i(TAG, "Service sending broadcast");
sendBroadcast(sendToUiIntent);
return ret;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return super.onBind(intent);
}
}In the overwritten method onStartCommand(), the service receives a name from the calling intent, then sends a broadcast to the BroadcastReceiver, which in turn will call the native method sendToQt(String message). For more information on managing native calls in Qt, see Calling QML/C++ Functions from Java Code.
Manage the AndroidManifest.xml File
To use the service, it must be declared in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<service android:process=":qt_service" android:name=".QtAndroidService">
<!-- Application arguments -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.arguments" android:value="-service"/>
<!-- Application arguments -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.lib_name" android:value="-- %%INSERT_APP_LIB_NAME%% --"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.qt_sources_resource_id" android:resource="@array/qt_sources"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.repository" android:value="default"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.qt_libs_resource_id" android:resource="@array/qt_libs"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.bundled_libs_resource_id" android:resource="@array/bundled_libs"/>
<!-- Deploy Qt libs as part of package -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.bundle_local_qt_libs" android:value="-- %%BUNDLE_LOCAL_QT_LIBS%% --"/>
<!-- Run with local libs -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.use_local_qt_libs" android:value="-- %%USE_LOCAL_QT_LIBS%% --"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.libs_prefix" android:value="/data/local/tmp/qt/"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.load_local_libs_resource_id" android:resource="@array/load_local_libs"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.load_local_jars" android:value="-- %%INSERT_LOCAL_JARS%% --"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.app.static_init_classes" android:value="-- %%INSERT_INIT_CLASSES%% --"/>
<!-- Run with local libs -->
<!-- Background running -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.background_running" android:value="true"/>
<!-- Background running -->
</service>Start the Service
Since the service is run using the same .so lib file with different arguments for the service, you must handle the arguments. For the main application use:
if (argc <= 1) {
Then take the following steps:
- Register the native method
- Create the BroadcastReceiver in a custom Java class:
package org.qtproject.example.qtandroidservice; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.IntentFilter; public class ActivityUtils { private static native void sendToQt(String message); private static final String TAG = "ActivityUtils"; public static final String BROADCAST_NAME_ACTION = "org.qtproject.example.qtandroidservice.broadcast.name"; public void registerServiceBroadcastReceiver(Context context) { IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter(); intentFilter.addAction(BROADCAST_NAME_ACTION); context.registerReceiver(serviceMessageReceiver, intentFilter); Log.i(TAG, "Registered broadcast receiver"); } private BroadcastReceiver serviceMessageReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { Log.i(TAG, "In OnReceive broadcast receiver"); if (BROADCAST_NAME_ACTION.equals(intent.getAction())) { String name = intent.getStringExtra("name"); Log.i(TAG, "Service received name: " + name); String message = "Hello " + name; sendToQt(message); Log.i(TAG, "Service sent back message: " + message); } } }; } - Register the BroadcastReceiver:
void QtAndroidService::registerBroadcastReceiver() { QAndroidJniEnvironment env; jclass javaClass = env.findClass("org/qtproject/example/qtandroidservice/ActivityUtils"); QAndroidJniObject classObject(javaClass); classObject.callMethod<void>("registerServiceBroadcastReceiver", "(Landroid/content/Context;)V", QtAndroid::androidContext().object()); }
- Call the startService() method, as follows:
void QtAndroidService::sendToService(const QString &name) { QAndroidIntent serviceIntent(QtAndroid::androidActivity().object(), "org/qtproject/example/qtandroidservice/QtAndroidService"); serviceIntent.putExtra("name", name.toUtf8()); QAndroidJniObject result = QtAndroid::androidActivity().callObjectMethod( "startService", "(Landroid/content/Intent;)Landroid/content/ComponentName;", serviceIntent.handle().object()); }
This function is used to start the Service. If the service is already running, it will only send the names without starting a new service instance.
- Then, you have to add the necessary Connections, as described in Qt JNI Messenger Example.
Handle the service argument as follows:
} else if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "-service") == 0) { qWarning() << "Service starting with BroadcastReceiver from same .so file"; QAndroidService app(argc, argv); return app.exec();
See also Android Service with BroadcastReceiver, Android Services, Qt for Android, and Qt Android Extras.
© 2024 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

