Thermostat
Das Thermostat-Beispiel zeigt, wie man je nach Fenstergröße unterschiedliche Designs implementieren kann.
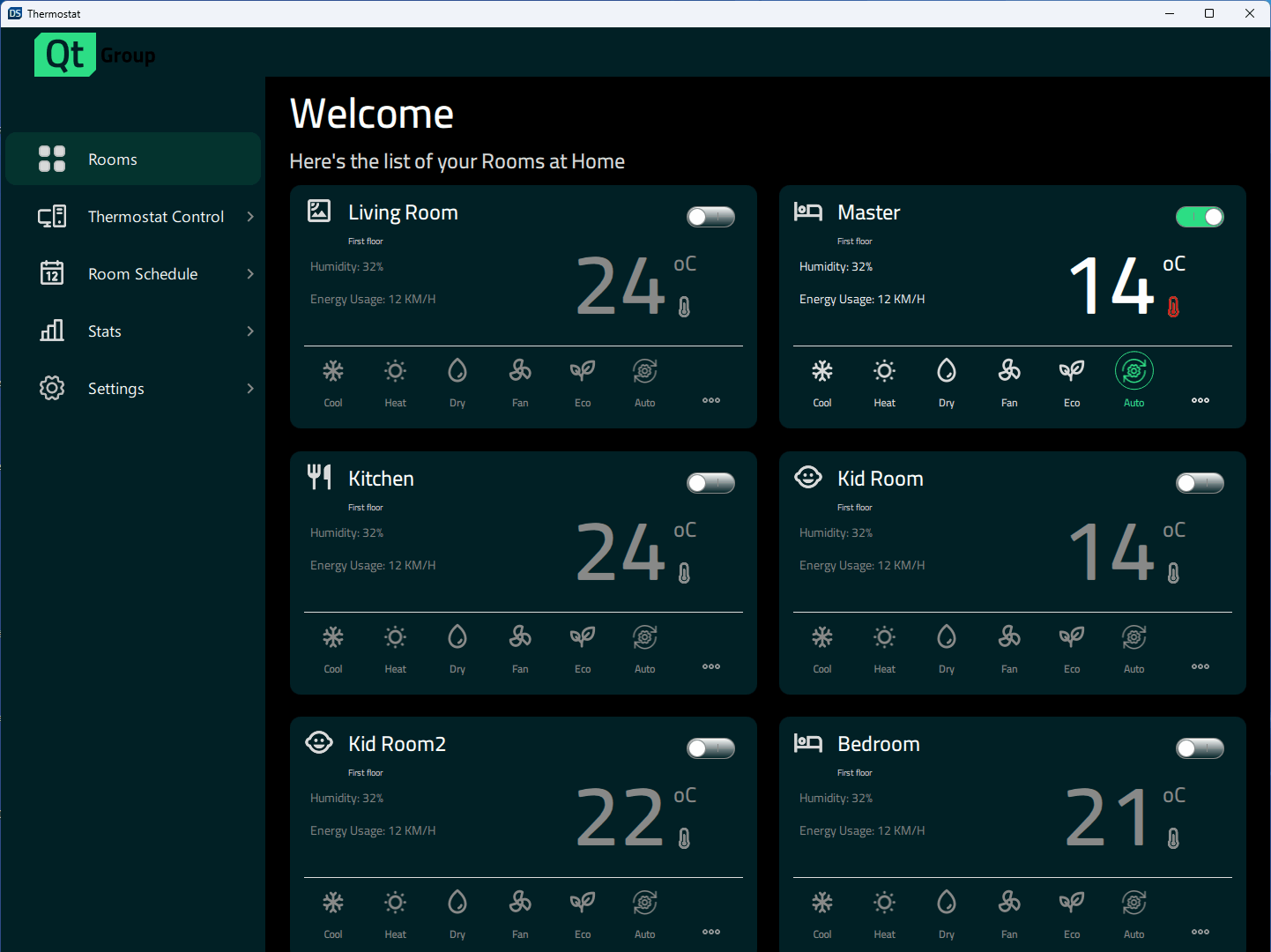
Eine Benutzeroberfläche für ein Heimthermostat, die zeigt, wie man in Qt Quick responsive Anwendungen erstellt, die von großen Desktop-Displays auf mobile und kleine eingebettete Displays skalieren.
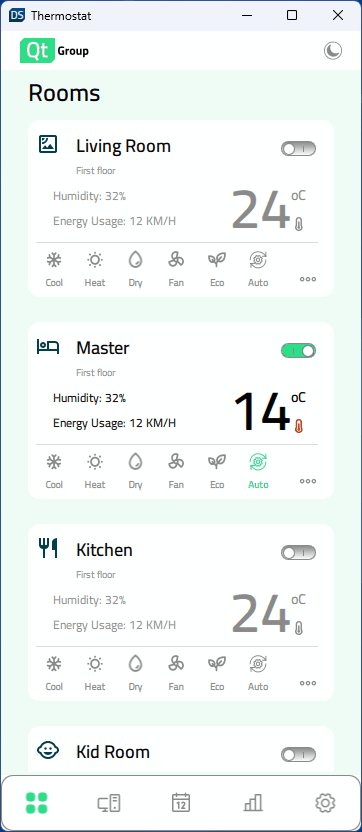
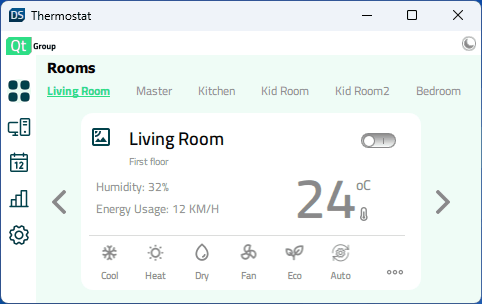
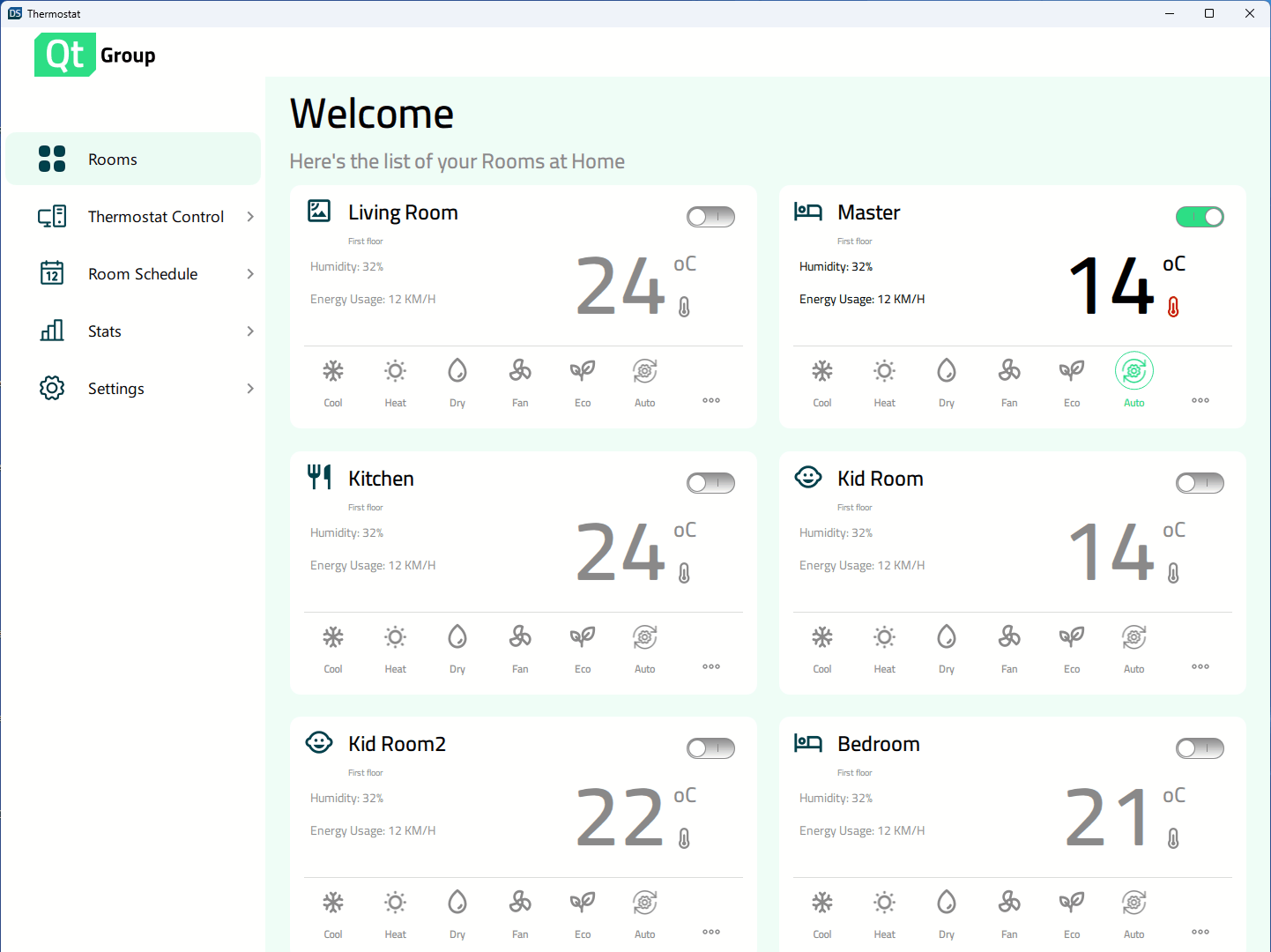

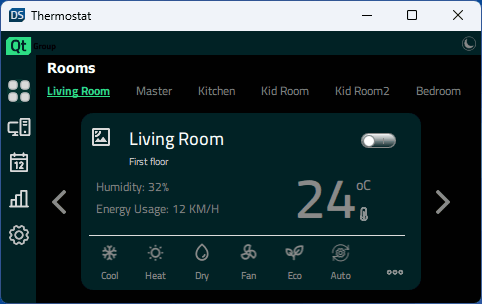
Ausführen des Beispiels
Zum Ausführen des Beispiels von Qt Creatorauszuführen, öffnen Sie den Modus Welcome und wählen Sie das Beispiel aus Examples aus. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Qt Creator: Tutorial: Erstellen und Ausführen.
Reaktionsfähiges Design
Die Anwendung unterstützt eine Vielzahl von Anzeigegrößen. Sie kann dynamisch skaliert werden, wenn der Benutzer die Fenstergröße ändert, oder die Anwendung wählt die richtigen Größen auf der Grundlage der verfügbaren Anzeige auf mobilen Zielgeräten aus. Constants.qml enthält Eigenschaften, die die Anzeigegröße angeben und steuern, welches Layout gerade verwendet wird:
property bool isBigDesktopLayout: layout === Constants.Layout.Desktop property bool isSmallDesktopLayout: layout === Constants.Layout.SmallDesktop property bool isMobileLayout: layout === Constants.Layout.Mobile property bool isSmallLayout: layout === Constants.Layout.Small
In App.qml werden die Eigenschaften beim Start der Anwendung an die Höhe und Breite des Fensters gebunden:
Component.onCompleted: { Constants.layout = Qt.binding(() => { let tall = window.height >= window.width if (window.width >= 1440 && window.height >= 520) return Constants.Layout.Desktop if (window.width >= 1024 && window.height >= 768) return Constants.Layout.SmallDesktop if (tall || (window.width >= 600 && window.height >= 380)) return Constants.Layout.Mobile return Constants.Layout.Small }) }
Die Zustände werden dann verwendet, um die Eigenschaften der Komponenten zu steuern, wie Breite, Höhe, fontSize, Position und Layout (Spalte oder Zeile).
states: [ State { name: "bigDesktopLayout" when: Constants.isBigDesktopLayout PropertyChanges { target: statistics leftPadding: 53 rightPadding: 53 topPadding: 23 bottomPadding: 43 } PropertyChanges { target: scrollView isBackgroundVisible: false delegateWidth: 350 delegateHeight: 182 statisticsChartWidth: grid.width statisticsChartHeight: 647 } PropertyChanges { target: grid width: 1100 } }, State { name: "smallDesktopLayout" when: Constants.isSmallDesktopLayout PropertyChanges { target: statistics leftPadding: 53 rightPadding: 53 topPadding: 23 bottomPadding: 43 } PropertyChanges { target: scrollView isBackgroundVisible: false delegateWidth: 290 delegateHeight: 182 statisticsChartWidth: grid.width statisticsChartHeight: 541 } PropertyChanges { target: grid width: 918 } }, State { name: "mobileLayout" when: Constants.isMobileLayout PropertyChanges { target: statistics leftPadding: 0 rightPadding: 0 topPadding: 0 bottomPadding: 0 } PropertyChanges { target: scrollView isBackgroundVisible: false delegateWidth: 327 delegateHeight: 110 statisticsChartWidth: 346 statisticsChartHeight: 383 } }, State { name: "smallLayout" when: Constants.isSmallLayout PropertyChanges { target: statistics leftPadding: 0 rightPadding: 0 topPadding: 0 bottomPadding: 0 } PropertyChanges { target: scrollView isBackgroundVisible: true delegateWidth: 332 delegateHeight: 90 statisticsChartWidth: 420 statisticsChartHeight: 240 } } ]
Quelldateien
Siehe auch Alle Qt Beispiele und Qt Quick Beispiele und Tutorials.
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

