Qt Quick 3D Physics - Cannon Example
Demonstrates how to spawn physical objects.
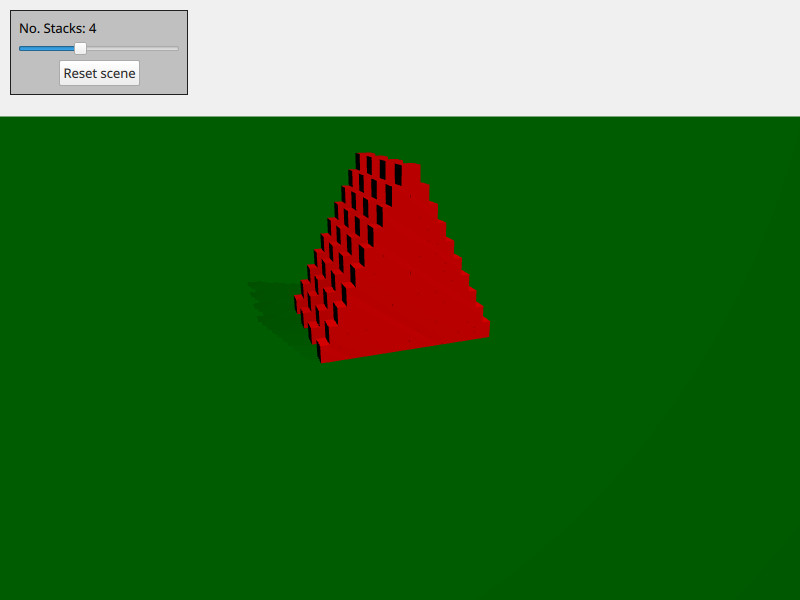
This example demonstrates how to create and delete physical objects on demand. The scene consists of a number of stacks of boxes. You can move around by using WASD and the mouse and shoot a ball by pressing space.
The scene is setup with the usual Qt Quick 3D objects like view, camera and light:
PerspectiveCamera { id: camera position: Qt.vector3d(-4000, 5000, 10000) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-20, -20, 0) clipFar: 200000 clipNear: 100 } DirectionalLight { eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-45, 45, 0) castsShadow: true brightness: 1 shadowMapQuality: Light.ShadowMapQualityVeryHigh shadowMapFar: camera.clipFar shadowFactor: 50 csmNumSplits: 2 csmSplit1: 0.1 csmSplit2: 0.3 softShadowQuality: Light.PCF4 }
We also add a static floor:
StaticRigidBody { eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-90, 0, 0) collisionShapes: PlaneShape {} Model { source: "#Rectangle" scale: Qt.vector3d(2000, 2000, 1) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } castsShadows: false receivesShadows: true } }
We create a Node we use as the spawner of objects and put inside our view:
Node { id: shapeSpawner property var instancesBoxes: [] property var instancesSpheres: [] property int stackCount: 0 property var boxComponent: Qt.createComponent("Box.qml") property var sphereComponent: Qt.createComponent("Sphere.qml") function createStack(stackZ, numStacks) { let size = 10 let extents = 400 for (var i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (var j = 0; j < size - i; j++) { let x = j * 2 - size + i let y = i * 2 + 1 let z = 5 * (stackZ - numStacks) let center = Qt.vector3d(x, y, z).times(0.5 * extents) let box = boxComponent.incubateObject(shapeSpawner, { "position": center, "xyzExtents": extents }) instancesBoxes.push(box) } } } function createBall(position, forward) { var diameter = 600 var speed = 20000 let settings = { "position": position, "sphereDiameter": diameter } let sphere = sphereComponent.createObject(shapeSpawner, settings) sphere.setLinearVelocity(forward.times(speed)) instancesSpheres.push(sphere) if (sphere === null) { console.log("Error creating object") } } function reset() { // Only run method if previous stack has been created fully for (var i = 0; i < instancesBoxes.length; i++) if (!instancesBoxes[i].object) return instancesSpheres.forEach(sphere => { sphere.collisionShapes = [] sphere.destroy() }) instancesBoxes.forEach(box => { box.object.collisionShapes = [] box.object.destroy() }) instancesSpheres = [] instancesBoxes = [] for (var stackI = 0; stackI < stackSlider.value; stackI++) { shapeSpawner.createStack(stackI, stackSlider.value) } } }
We have three methods: createStack for creating a stack, createBall for creating a ball with velocity and reset for resetting the scene. The actual box and sphere that is spawn is stored in their own qml files (box.qml and sphere.qml).
Files:
© 2026 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

