QGradient¶
Inherited by: QConicalGradient, QLinearGradient, QRadialGradient
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
def
__eq__(gradient)def
__ne__(other)def
coordinateMode()def
interpolationMode()def
setColorAt(pos, color)def
setCoordinateMode(mode)def
setInterpolationMode(mode)def
setSpread(spread)def
setStops(stops)def
spread()def
stops()def
type()
Detailed Description¶
Qt currently supports three types of gradient fills:
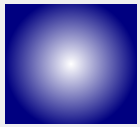
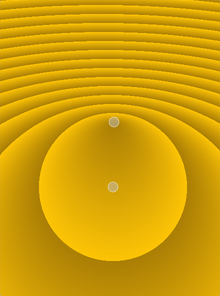
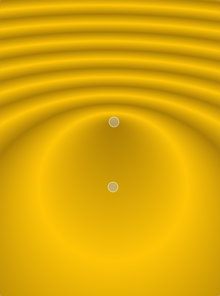
Linear gradients interpolate colors between start and end points.
Simple radial gradients interpolate colors between a focal point and end points on a circle surrounding it.
Extended radial gradients interpolate colors between a center and a focal circle.
Conical gradients interpolate colors around a center point.
A gradient’s type can be retrieved using the
type()function. Each of the types is represented by a subclass ofQGradient:
The colors in a gradient are defined using stop points of the
QGradientStoptype; i.e., a position and a color. Use thesetColorAt()function to define a single stop point. Alternatively, use thesetStops()function to define several stop points in one go. Note that the latter function replaces the current set of stop points.It is the gradient’s complete set of stop points (accessible through the
stops()function) that describes how the gradient area should be filled. If no stop points have been specified, a gradient of black at 0 to white at 1 is used.A diagonal linear gradient from black at (100, 100) to white at (200, 200) could be specified like this:
linearGrad = QLinearGradient(QPointF(100, 100), QPointF(200, 200)) linearGrad.setColorAt(0, Qt.black) linearGrad.setColorAt(1, Qt.white)A gradient can have an arbitrary number of stop points. The following would create a radial gradient starting with red in the center, blue and then green on the edges:
radialGrad = QRadialGradient(QPointF(100, 100), 100) radialGrad.setColorAt(0, Qt.red) radialGrad.setColorAt(0.5, Qt.blue) radialGrad.setColorAt(1, Qt.green)It is possible to repeat or reflect the gradient outside its area by specifiying the
spread methodusing thesetSpread()function. The default is to pad the outside area with the color at the closest stop point. The currently setspread methodcan be retrieved using thespread()function. TheSpreadenum defines three different methods:
PadSpread
RepeatSpread
ReflectSpreadNote that the
setSpread()function only has effect for linear and radial gradients. The reason is that the conical gradient is closed by definition, i.e. the conical gradient fills the entire circle from 0 - 360 degrees, while the boundary of a radial or a linear gradient can be specified through its radius or final stop points, respectively.The gradient coordinates can be specified in logical coordinates, relative to device coordinates, or relative to object bounding box coordinates. The
coordinate modecan be set using thesetCoordinateMode()function. The default isLogicalMode, where the gradient coordinates are specified in the same way as the object coordinates. To retrieve the currently setcoordinate modeusecoordinateMode().See also
-
class
QGradient¶ QGradient(arg__1)
QGradient(QGradient)
- param arg__1
Preset- param QGradient
Constructs a gradient based on a predefined
preset.The coordinate mode of the resulting gradient is
ObjectMode, allowing the preset to be applied to arbitrary object sizes.
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.Type¶ Specifies the type of gradient.
Constant
Description
QGradient.LinearGradient
Interpolates colors between start and end points (
QLinearGradient).QGradient.RadialGradient
Interpolate colors between a focal point and end points on a circle surrounding it (
QRadialGradient).QGradient.ConicalGradient
Interpolate colors around a center point (
QConicalGradient).QGradient.NoGradient
No gradient is used.
See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.Spread¶ Specifies how the area outside the gradient area should be filled.
Constant
Description
QGradient.PadSpread
The area is filled with the closest stop color. This is the default.
QGradient.RepeatSpread
The gradient is repeated outside the gradient area.
QGradient.ReflectSpread
The gradient is reflected outside the gradient area.
See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.CoordinateMode¶ This enum specifies how gradient coordinates map to the paint device on which the gradient is used.
Constant
Description
QGradient.LogicalMode
This is the default mode. The gradient coordinates are specified logical space just like the object coordinates.
QGradient.ObjectMode
In this mode the gradient coordinates are relative to the bounding rectangle of the object being drawn, with (0,0) in the top left corner, and (1,1) in the bottom right corner of the object’s bounding rectangle. This value was added in Qt 5.12.
QGradient.StretchToDeviceMode
In this mode the gradient coordinates are relative to the bounding rectangle of the paint device, with (0,0) in the top left corner, and (1,1) in the bottom right corner of the paint device.
QGradient.ObjectBoundingMode
This mode is the same as , except that the {
transform()} {brush transform}, if any, is applied relative to the logical space instead of the object space. This enum value is deprecated and should not be used in new code.
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.InterpolationMode¶ Constant
Description
QGradient.ComponentInterpolation
The color components and the alpha component are independently linearly interpolated.
QGradient.ColorInterpolation
The colors are linearly interpolated in premultiplied color space.
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.Preset¶ This enum specifies a set of predefined presets for
QGradient, based on the gradients from https://webgradients.com/.
New in version 5.12.
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.coordinateMode()¶ - Return type
Returns the coordinate mode of this gradient. The default mode is
LogicalMode.See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.interpolationMode()¶ - Return type
Returns the interpolation mode of this gradient. The default mode is .
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.__ne__(other)¶ - Parameters
other –
QGradient- Return type
bool
Returns
trueif the gradient is the same as the othergradientspecified; otherwise returnsfalse.See also
operator==()
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.__eq__(gradient)¶ - Parameters
gradient –
QGradient- Return type
bool
Returns
trueif the gradient is the same as the othergradientspecified; otherwise returnsfalse.See also
operator!=()
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.setColorAt(pos, color)¶ - Parameters
pos –
qrealcolor –
QColor
Creates a stop point at the given
positionwith the givencolor. The givenpositionmust be in the range 0 to 1.See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.setCoordinateMode(mode)¶ - Parameters
mode –
CoordinateMode
Sets the coordinate mode of this gradient to
mode. The default mode isLogicalMode.See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.setInterpolationMode(mode)¶ - Parameters
mode –
InterpolationMode
Sets the interpolation mode of this gradient to
mode. The default mode is .
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.setSpread(spread)¶ - Parameters
spread –
Spread
Specifies the spread
methodthat should be used for this gradient.Note that this function only has effect for linear and radial gradients.
See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.setStops(stops)¶ - Parameters
stops –
Replaces the current set of stop points with the given
stopPoints. The positions of the points must be in the range 0 to 1, and must be sorted with the lowest point first.See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.spread()¶ - Return type
Returns the spread method use by this gradient. The default is
PadSpread.See also
-
PySide2.QtGui.QGradient.stops()¶ - Return type
Returns the stop points for this gradient.
If no stop points have been specified, a gradient of black at 0 to white at 1 is used.
See also
© 2018 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.