QDial¶
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
def
initStyleOption(option)def
notchSize()def
notchTarget()def
notchesVisible()def
setNotchTarget(target)def
wrapping()
Slots¶
def
setNotchesVisible(visible)def
setWrapping(on)
Detailed Description¶
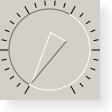
QDialis used when the user needs to control a value within a program-definable range, and the range either wraps around (for example, with angles measured from 0 to 359 degrees) or the dialog layout needs a square widget.Since
QDialinherits fromQAbstractSlider, the dial behaves in a similar way to aslider. Whenwrapping()is false (the default setting) there is no real difference between a slider and a dial. They both share the same signals, slots and member functions. Which one you use depends on the expectations of your users and on the type of application.The dial initially emits
valueChanged()signals continuously while the slider is being moved; you can make it emit the signal less often by disabling thetrackingproperty. ThesliderMoved()signal is emitted continuously even when tracking is disabled.The dial also emits
sliderPressed()andsliderReleased()signals when the mouse button is pressed and released. Note that the dial’s value can change without these signals being emitted since the keyboard and wheel can also be used to change the value.Unlike the slider,
QDialattempts to draw a “nice” number of notches rather than one per line step. If possible, the number of notches drawn is one per line step, but if there aren’t enough pixels to draw every one,QDialwill skip notches to try and draw a uniform set (e.g. by drawing every second or third notch).Like the slider, the dial makes the
QAbstractSliderfunctionsetValue()available as a slot.The dial’s keyboard interface is fairly simple: The left/up and right/down arrow keys adjust the dial’s
valueby the definedsingleStep, Page Up and Page Down by the definedpageStep, and the Home and End keys set the value to the definedminimumandmaximumvalues.If you are using the mouse wheel to adjust the dial, the increment value is determined by the lesser value of
wheelScrollLinesmultipled bysingleStep, andpageStep.
-
class
QDial([parent=None])¶ - param parent
Constructs a dial.
The
parentargument is sent to theQAbstractSliderconstructor.
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.initStyleOption(option)¶ - Parameters
option –
QStyleOptionSlider
Initialize
optionwith the values from thisQDial. This method is useful for subclasses when they need aQStyleOptionSlider, but don’t want to fill in all the information themselves.See also
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.notchSize()¶ - Return type
int
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.notchTarget()¶ - Return type
qreal
See also
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.notchesVisible()¶ - Return type
bool
See also
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.setNotchTarget(target)¶ - Parameters
target –
double
See also
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.setNotchesVisible(visible)¶ - Parameters
visible –
bool
See also
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.setWrapping(on)¶ - Parameters
on –
bool
See also
-
PySide2.QtWidgets.QDial.wrapping()¶ - Return type
bool
See also
© 2018 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.