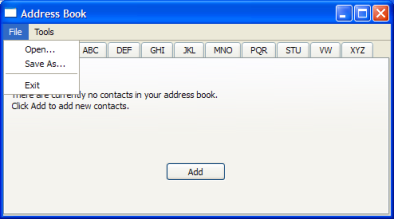
Address Book Example¶
The address book example shows how to use proxy models to display different views onto data from a single model.
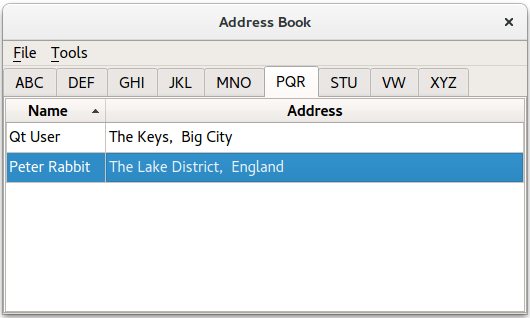
This example provides an address book that allows contacts to be grouped alphabetically into 9 groups: ABC, DEF, GHI, … , VW, …, XYZ. This is achieved by using multiple views on the same model, each of which is filtered using an instance of the
QSortFilterProxyModelclass.
Overview¶
The address book contains 5 classes:
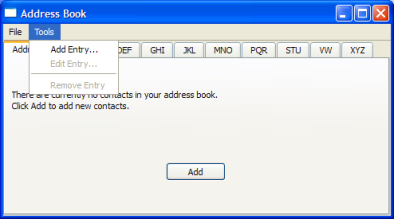
MainWindow,AddressWidget,TableModel,NewAddressTabandAddDialog. TheMainWindowclass usesAddressWidgetas its central widget and provides File and Tools menus.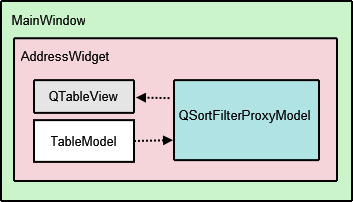
The
AddressWidgetclass is aQTabWidgetsubclass that is used to manipulate the 10 tabs displayed in the example: the 9 alphabet group tabs and an instance ofNewAddressTab. TheNewAddressTabclass is a subclass ofQWidgetthat is only used whenever the address book is empty, prompting the user to add some contacts.AddressWidgetalso interacts with an instance ofTableModelto add, edit and remove entries to the address book.
TableModelis a subclass ofQAbstractTableModelthat provides the standard model/view API to access data. It holds a list of added contacts. However, this data is not all visible in a single tab. Instead,QTableViewis used to provide 9 different views of the same data, according to the alphabet groups.
QSortFilterProxyModelis the class responsible for filtering the contacts for each group of contacts. Each proxy model uses aQRegExpto filter out contacts that do not belong in the corresponding alphabetical group. TheAddDialogclass is used to obtain information from the user for the address book. ThisQDialogsubclass is instantiated byNewAddressTabto add contacts, and byAddressWidgetto add and edit contacts.We begin by looking at the
TableModelimplementation.
TableModel Class Definition¶
The
TableModelclass provides standard API to access data in its list of contacts by subclassingQAbstractTableModel. The basic functions that must be implemented in order to do so are:rowCount(),columnCount(),data(),headerData(). For TableModel to be editable, it has to provide implementationsinsertRows(),removeRows(),setData()andflags()functions.struct Contact { QString name; QString address; bool operator==(const Contact &other) const { return name == other.name && address == other.address; } }; inline QDataStream &operator<<(QDataStream &stream, const Contact &contact) { return stream << contact.name << contact.address; } inline QDataStream &operator>>(QDataStream &stream, Contact &contact) { return stream >> contact.name >> contact.address; } class TableModel : public QAbstractTableModel { Q_OBJECT public: TableModel(QObject *parent = nullptr); TableModel(const QVector<Contact> &contacts, QObject *parent = nullptr); int rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const override; int columnCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const override; QVariant data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const override; QVariant headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation, int role) const override; Qt::ItemFlags flags(const QModelIndex &index) const override; bool setData(const QModelIndex &index, const QVariant &value, int role = Qt::EditRole) override; bool insertRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &index = QModelIndex()) override; bool removeRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &index = QModelIndex()) override; const QVector<Contact> &getContacts() const; private: QVector<Contact> contacts; };Two constructors are used, a default constructor which uses
TableModel‘s ownQVector<Contact>and one that takesQVector<Contact>as an argument, for convenience.
TableModel Class Implementation¶
We implement the two constructors as defined in the header file. The second constructor initializes the list of contacts in the model, with the parameter value.
TableModel::TableModel(QObject *parent) : QAbstractTableModel(parent) { } TableModel::TableModel(const QVector<Contact> &contacts, QObject *parent) : QAbstractTableModel(parent), contacts(contacts) { }The
rowCount()andcolumnCount()functions return the dimensions of the model. Whereas,rowCount()‘s value will vary depending on the number of contacts added to the address book,columnCount()‘s value is always 2 because we only need space for the Name and Address columns.int TableModel::rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const { return parent.isValid() ? 0 : contacts.size(); } int TableModel::columnCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const { return parent.isValid() ? 0 : 2; }The
data()function returns either a Name or Address , based on the contents of the model index supplied. The row number stored in the model index is used to reference an item in the list of contacts. Selection is handled by theQItemSelectionModel, which will be explained withAddressWidget.QVariant TableModel::data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const { if (!index.isValid()) return QVariant(); if (index.row() >= contacts.size() || index.row() < 0) return QVariant(); if (role == Qt::DisplayRole) { const auto &contact = contacts.at(index.row()); switch (index.column()) { case 0: return contact.name; case 1: return contact.address; default: break; } } return QVariant(); }The
headerData()function displays the table’s header, Name and Address . If you require numbered entries for your address book, you can use a vertical header which we have hidden in this example (see theAddressWidgetimplementation).QVariant TableModel::headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation, int role) const { if (role != Qt::DisplayRole) return QVariant(); if (orientation == Qt::Horizontal) { switch (section) { case 0: return tr("Name"); case 1: return tr("Address"); default: break; } } return QVariant(); }The
insertRows()function is called before new data is added, otherwise the data will not be displayed. ThebeginInsertRows()andendInsertRows()functions are called to ensure all connected views are aware of the changes.bool TableModel::insertRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &index) { Q_UNUSED(index); beginInsertRows(QModelIndex(), position, position + rows - 1); for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) contacts.insert(position, { QString(), QString() }); endInsertRows(); return true; }The
removeRows()function is called to remove data. Again,beginRemoveRows()andendRemoveRows()are called to ensure all connected views are aware of the changes.bool TableModel::removeRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &index) { Q_UNUSED(index); beginRemoveRows(QModelIndex(), position, position + rows - 1); for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) contacts.removeAt(position); endRemoveRows(); return true; }The
setData()function is the function that inserts data into the table, item by item and not row by row. This means that to fill a row in the address book,setData()must be called twice, as each row has 2 columns. It is important to emit thedataChanged()signal as it tells all connected views to update their displays.bool TableModel::setData(const QModelIndex &index, const QVariant &value, int role) { if (index.isValid() && role == Qt::EditRole) { const int row = index.row(); auto contact = contacts.value(row); switch (index.column()) { case 0: contact.name = value.toString(); break; case 1: contact.address = value.toString(); break; default: return false; } contacts.replace(row, contact); emit dataChanged(index, index, {Qt::DisplayRole, Qt::EditRole}); return true; } return false; }The
flags()function returns the item flags for the given index.Qt::ItemFlags TableModel::flags(const QModelIndex &index) const { if (!index.isValid()) return Qt::ItemIsEnabled; return QAbstractTableModel::flags(index) | Qt::ItemIsEditable; }We set the
ItemIsEditableflag because we want to allow theTableModelto be edited. Although for this example we don’t use the editing features of theQTableViewobject, we enable them here so that we can reuse the model in other programs.The last function in
TableModel,getContacts()returns theQVector<Contact> object that holds all the contacts in the address book. We use this function later to obtain the list of contacts to check for existing entries, write the contacts to a file and read them back. Further explanation is given withAddressWidget.const QVector<Contact> &TableModel::getContacts() const { return contacts; }
AddressWidget Class Definition¶
The
AddressWidgetclass is technically the main class involved in this example as it provides functions to add, edit and remove contacts, to save the contacts to a file and to load them from a file.class AddressWidget : public QTabWidget { Q_OBJECT public: AddressWidget(QWidget *parent = nullptr); void readFromFile(const QString &fileName); void writeToFile(const QString &fileName); public slots: void showAddEntryDialog(); void addEntry(const QString &name, const QString &address); void editEntry(); void removeEntry(); signals: void selectionChanged (const QItemSelection &selected); private: void setupTabs(); TableModel *table; NewAddressTab *newAddressTab; };
AddressWidgetextendsQTabWidgetin order to hold 10 tabs (NewAddressTaband the 9 alphabet group tabs) and also manipulatestable, theTableModelobject,proxyModel, theQSortFilterProxyModelobject that we use to filter the entries, andtableView, theQTableViewobject.
AddressWidget Class Implementation¶
The
AddressWidgetconstructor accepts a parent widget and instantiatesNewAddressTab,TableModelandQSortFilterProxyModel. TheNewAddressTabobject, which is used to indicate that the address book is empty, is added and the rest of the 9 tabs are set up withsetupTabs().AddressWidget::AddressWidget(QWidget *parent) : QTabWidget(parent), table(new TableModel(this)), newAddressTab(new NewAddressTab(this)) { connect(newAddressTab, &NewAddressTab::sendDetails, this, &AddressWidget::addEntry); addTab(newAddressTab, tr("Address Book")); setupTabs(); }The
setupTabs()function is used to set up the 9 alphabet group tabs, table views and proxy models inAddressWidget. Each proxy model in turn is set to filter contact names according to the relevant alphabet group using acase-insensitiveQRegExpobject. The table views are also sorted in ascending order using the corresponding proxy model’ssort()function.Each table view’s
selectionModeis set toSingleSelectionandselectionBehavioris set toSelectRows, allowing the user to select all the items in one row at the same time. EachQTableViewobject is automatically given aQItemSelectionModelthat keeps track of the selected indexes.void AddressWidget::setupTabs() { const auto groups = { "ABC", "DEF", "GHI", "JKL", "MNO", "PQR", "STU", "VW", "XYZ" }; for (const QString &str : groups) { const auto regExp = QRegularExpression(QString("^[%1].*").arg(str), QRegularExpression::CaseInsensitiveOption); auto proxyModel = new QSortFilterProxyModel(this); proxyModel->setSourceModel(table); proxyModel->setFilterRegularExpression(regExp); proxyModel->setFilterKeyColumn(0); QTableView *tableView = new QTableView; tableView->setModel(proxyModel); tableView->setSelectionBehavior(QAbstractItemView::SelectRows); tableView->horizontalHeader()->setStretchLastSection(true); tableView->verticalHeader()->hide(); tableView->setEditTriggers(QAbstractItemView::NoEditTriggers); tableView->setSelectionMode(QAbstractItemView::SingleSelection); tableView->setSortingEnabled(true); connect(tableView->selectionModel(), &QItemSelectionModel::selectionChanged, this, &AddressWidget::selectionChanged); connect(this, &QTabWidget::currentChanged, this, [this, tableView](int tabIndex) { if (widget(tabIndex) == tableView) emit selectionChanged(tableView->selectionModel()->selection()); }); addTab(tableView, str); } }The
QItemSelectionModelclass provides aselectionChangedsignal that is connected toAddressWidget‘sselectionChanged()signal. We also connectcurrentChanged()signal to the lambda expression which emitsAddressWidget‘sselectionChanged()as well. These connections are necessary to enable the Edit Entry… and Remove Entry actions inMainWindow‘s Tools menu. It is further explained inMainWindow‘s implementation.Each table view in the address book is added as a tab to the
QTabWidgetwith the relevant label, obtained from theQStringListof groups.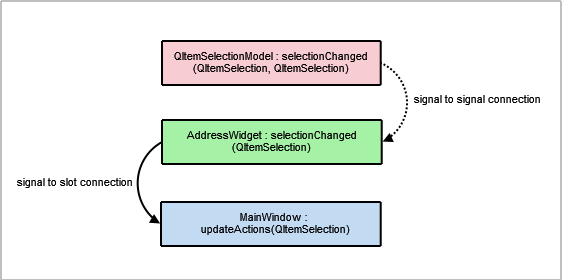
We provide two
addEntry()functions: One which is intended to be used to accept user input, and the other which performs the actual task of adding new entries to the address book. We divide the responsibility of adding entries into two parts to allownewAddressTabto insert data without having to popup a dialog.The first
addEntry()function is a slot connected to theMainWindow‘s Add Entry… action. This function creates anAddDialogobject and then calls the secondaddEntry()function to actually add the contact totable.void AddressWidget::showAddEntryDialog() { AddDialog aDialog; if (aDialog.exec()) addEntry(aDialog.name(), aDialog.address()); }Basic validation is done in the second
addEntry()function to prevent duplicate entries in the address book. As mentioned withTableModel, this is part of the reason why we require the getter methodgetContacts().void AddressWidget::addEntry(const QString &name, const QString &address) { if (!table->getContacts().contains({ name, address })) { table->insertRows(0, 1, QModelIndex()); QModelIndex index = table->index(0, 0, QModelIndex()); table->setData(index, name, Qt::EditRole); index = table->index(0, 1, QModelIndex()); table->setData(index, address, Qt::EditRole); removeTab(indexOf(newAddressTab)); } else { QMessageBox::information(this, tr("Duplicate Name"), tr("The name \"%1\" already exists.").arg(name)); } }If the model does not already contain an entry with the same name, we call
setData()to insert the name and address into the first and second columns. Otherwise, we display aQMessageBoxto inform the user.Note
The
newAddressTabis removed once a contact is added as the address book is no longer empty.Editing an entry is a way to update the contact’s address only, as the example does not allow the user to change the name of an existing contact.
Firstly, we obtain the active tab’s
QTableViewobject usingcurrentWidget(). Then we extract theselectionModelfrom thetableViewto obtain the selected indexes.void AddressWidget::editEntry() { QTableView *temp = static_cast<QTableView*>(currentWidget()); QSortFilterProxyModel *proxy = static_cast<QSortFilterProxyModel*>(temp->model()); QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel = temp->selectionModel(); const QModelIndexList indexes = selectionModel->selectedRows(); QString name; QString address; int row = -1; for (const QModelIndex &index : indexes) { row = proxy->mapToSource(index).row(); QModelIndex nameIndex = table->index(row, 0, QModelIndex()); QVariant varName = table->data(nameIndex, Qt::DisplayRole); name = varName.toString(); QModelIndex addressIndex = table->index(row, 1, QModelIndex()); QVariant varAddr = table->data(addressIndex, Qt::DisplayRole); address = varAddr.toString(); }Next we extract data from the row the user intends to edit. This data is displayed in an instance of
AddDialogwith a different window title. Thetableis only updated if changes have been made to data inaDialog.AddDialog aDialog; aDialog.setWindowTitle(tr("Edit a Contact")); aDialog.editAddress(name, address); if (aDialog.exec()) { const QString newAddress = aDialog.address(); if (newAddress != address) { const QModelIndex index = table->index(row, 1, QModelIndex()); table->setData(index, newAddress, Qt::EditRole); } } }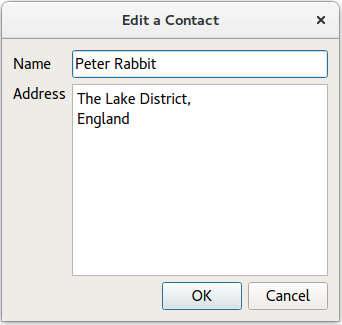
Entries are removed using the
removeEntry()function. The selected row is removed by accessing it through theQItemSelectionModelobject,selectionModel. ThenewAddressTabis re-added to theAddressWidgetonly if the user removes all the contacts in the address book.void AddressWidget::removeEntry() { QTableView *temp = static_cast<QTableView*>(currentWidget()); QSortFilterProxyModel *proxy = static_cast<QSortFilterProxyModel*>(temp->model()); QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel = temp->selectionModel(); const QModelIndexList indexes = selectionModel->selectedRows(); for (QModelIndex index : indexes) { int row = proxy->mapToSource(index).row(); table->removeRows(row, 1, QModelIndex()); } if (table->rowCount(QModelIndex()) == 0) insertTab(0, newAddressTab, tr("Address Book")); }The
writeToFile()function is used to save a file containing all the contacts in the address book. The file is saved in a custom.datformat. The contents of the list of contacts are written tofileusingQDataStream. If the file cannot be opened, aQMessageBoxis displayed with the related error message.void AddressWidget::writeToFile(const QString &fileName) { QFile file(fileName); if (!file.open(QIODevice::WriteOnly)) { QMessageBox::information(this, tr("Unable to open file"), file.errorString()); return; } QDataStream out(&file); out << table->getContacts(); }The
readFromFile()function loads a file containing all the contacts in the address book, previously saved usingwriteToFile().QDataStreamis used to read the contents of a.datfile into a list of contacts and each of these is added usingaddEntry().void AddressWidget::readFromFile(const QString &fileName) { QFile file(fileName); if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly)) { QMessageBox::information(this, tr("Unable to open file"), file.errorString()); return; } QVector<Contact> contacts; QDataStream in(&file); in >> contacts; if (contacts.isEmpty()) { QMessageBox::information(this, tr("No contacts in file"), tr("The file you are attempting to open contains no contacts.")); } else { for (const auto &contact: qAsConst(contacts)) addEntry(contact.name, contact.address); } }
NewAddressTab Class Definition¶
The
NewAddressTabclass provides an informative tab telling the user that the address book is empty. It appears and disappears according to the contents of the address book, as mentioned inAddressWidget‘s implementation.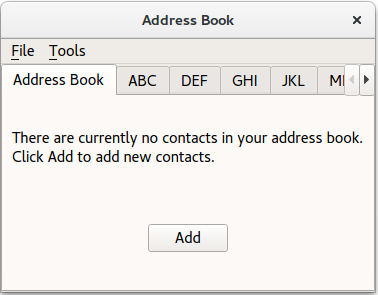
The
NewAddressTabclass extendsQWidgetand contains aQLabelandQPushButton.class NewAddressTab : public QWidget { Q_OBJECT public: NewAddressTab(QWidget *parent = nullptr); public slots: void addEntry(); signals: void sendDetails(const QString &name, const QString &address); };
NewAddressTab Class Implementation¶
The constructor instantiates the
addButton,descriptionLabeland connects theaddButton‘s signal to theaddEntry()slot.NewAddressTab::NewAddressTab(QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent) { auto descriptionLabel = new QLabel(tr("There are currently no contacts in your address book. " "\nClick Add to add new contacts.")); auto addButton = new QPushButton(tr("Add")); connect(addButton, &QAbstractButton::clicked, this, &NewAddressTab::addEntry); auto mainLayout = new QVBoxLayout; mainLayout->addWidget(descriptionLabel); mainLayout->addWidget(addButton, 0, Qt::AlignCenter); setLayout(mainLayout); }The
addEntry()function is similar toAddressWidget‘saddEntry()in the sense that both functions instantiate anAddDialogobject. Data from the dialog is extracted and sent toAddressWidget‘saddEntry()slot by emitting thesendDetails()signal.void NewAddressTab::addEntry() { AddDialog aDialog; if (aDialog.exec()) emit sendDetails(aDialog.name(), aDialog.address()); }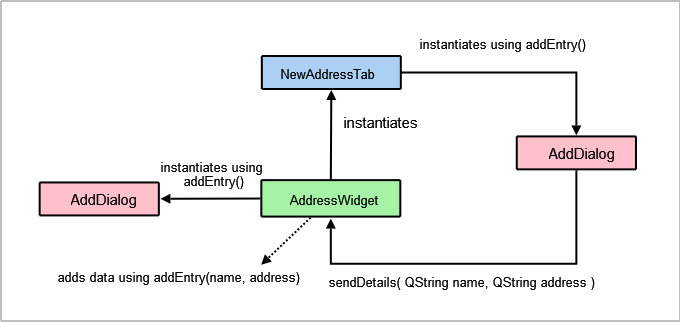
AddDialog Class Definition¶
The
AddDialogclass extendsQDialogand provides the user with aQLineEditand aQTextEditto input data into the address book.class AddDialog : public QDialog { Q_OBJECT public: AddDialog(QWidget *parent = nullptr); QString name() const; QString address() const; void editAddress(const QString &name, const QString &address); private: QLineEdit *nameText; QTextEdit *addressText; };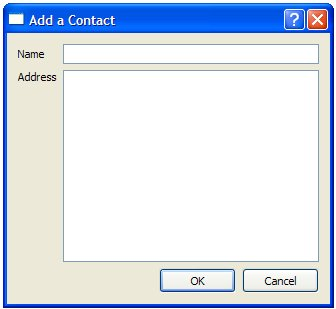
AddDialog Class Implementation¶
The
AddDialog‘s constructor sets up the user interface, creating the necessary widgets and placing them into layouts.AddDialog::AddDialog(QWidget *parent) : QDialog(parent), nameText(new QLineEdit), addressText(new QTextEdit) { auto nameLabel = new QLabel(tr("Name")); auto addressLabel = new QLabel(tr("Address")); auto okButton = new QPushButton(tr("OK")); auto cancelButton = new QPushButton(tr("Cancel")); auto gLayout = new QGridLayout; gLayout->setColumnStretch(1, 2); gLayout->addWidget(nameLabel, 0, 0); gLayout->addWidget(nameText, 0, 1); gLayout->addWidget(addressLabel, 1, 0, Qt::AlignLeft|Qt::AlignTop); gLayout->addWidget(addressText, 1, 1, Qt::AlignLeft); auto buttonLayout = new QHBoxLayout; buttonLayout->addWidget(okButton); buttonLayout->addWidget(cancelButton); gLayout->addLayout(buttonLayout, 2, 1, Qt::AlignRight); auto mainLayout = new QVBoxLayout; mainLayout->addLayout(gLayout); setLayout(mainLayout); connect(okButton, &QAbstractButton::clicked, this, &QDialog::accept); connect(cancelButton, &QAbstractButton::clicked, this, &QDialog::reject); setWindowTitle(tr("Add a Contact")); } QString AddDialog::name() const { return nameText->text(); } QString AddDialog::address() const { return addressText->toPlainText(); } void AddDialog::editAddress(const QString &name, const QString &address) { nameText->setReadOnly(true); nameText->setText(name); addressText->setPlainText(address); }To give the dialog the desired behavior, we connect the OK and Cancel buttons to the dialog’s
accept()andreject()slots. Since the dialog only acts as a container for name and address information, we do not need to implement any other functions for it.
MainWindow Class Definition¶
The
MainWindowclass extendsQMainWindowand implements the menus and actions necessary to manipulate the address book.
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow { Q_OBJECT public: MainWindow(); private slots: void updateActions(const QItemSelection &selection); void openFile(); void saveFile(); private: void createMenus(); AddressWidget *addressWidget; QAction *editAct; QAction *removeAct; };The
MainWindowclass uses anAddressWidgetas its central widget and provides the File menu with Open, Close and Exit actions, as well as the Tools menu with Add Entry…, Edit Entry… and Remove Entry actions.
MainWindow Class Implementation¶
The constructor for
MainWindowinstantiates AddressWidget, sets it as its central widget and calls thecreateMenus()function.MainWindow::MainWindow() : QMainWindow(), addressWidget(new AddressWidget) { setCentralWidget(addressWidget); createMenus(); setWindowTitle(tr("Address Book")); }The
createMenus()function sets up the File and Tools menus, connecting the actions to their respective slots. Both the Edit Entry… and Remove Entry actions are disabled by default as such actions cannot be carried out on an empty address book. They are only enabled when one or more contacts are added.void MainWindow::createMenus() { QMenu *fileMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&File")); QAction *openAct = new QAction(tr("&Open..."), this); fileMenu->addAction(openAct); connect(openAct, &QAction::triggered, this, &MainWindow::openFile); ... editAct = new QAction(tr("&Edit Entry..."), this); editAct->setEnabled(false); toolMenu->addAction(editAct); connect(editAct, &QAction::triggered, addressWidget, &AddressWidget::editEntry); toolMenu->addSeparator(); removeAct = new QAction(tr("&Remove Entry"), this); removeAct->setEnabled(false); toolMenu->addAction(removeAct); connect(removeAct, &QAction::triggered, addressWidget, &AddressWidget::removeEntry); connect(addressWidget, &AddressWidget::selectionChanged, this, &MainWindow::updateActions); }Apart from connecting all the actions’ signals to their respective slots, we also connect
AddressWidget‘sselectionChanged()signal to itsupdateActions()slot.The
openFile()function allows the user to choose a file with theopen file dialog. The chosen file has to be a custom.datfile that contains address book contacts. This function is a slot connected toopenActin the File menu.void MainWindow::openFile() { QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this); if (!fileName.isEmpty()) addressWidget->readFromFile(fileName); }The
saveFile()function allows the user to save a file with thesave file dialog. This function is a slot connected tosaveActin the File menu.void MainWindow::saveFile() { QString fileName = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this); if (!fileName.isEmpty()) addressWidget->writeToFile(fileName); }The
updateActions()function enables and disables Edit Entry… and Remove Entry depending on the contents of the address book. If the address book is empty, these actions are disabled; otherwise, they are enabled. This function is a slot is connected to theAddressWidget‘sselectionChanged()signal.void MainWindow::updateActions(const QItemSelection &selection) { QModelIndexList indexes = selection.indexes(); if (!indexes.isEmpty()) { removeAct->setEnabled(true); editAct->setEnabled(true); } else { removeAct->setEnabled(false); editAct->setEnabled(false); } }
main() Function¶
The main function for the address book instantiates
QApplicationand opens aMainWindowbefore running the event loop.int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { #ifdef Q_OS_ANDROID QApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling); #endif QApplication app(argc, argv); MainWindow mw; mw.show(); return app.exec(); }
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.