QTextTable¶
The QTextTable class represents a table in a QTextDocument . More…
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
def
appendColumns(count)def
appendRows(count)def
cellAt(c)def
cellAt(position)def
cellAt(row, col)def
columns()def
format()def
insertColumns(pos, num)def
insertRows(pos, num)def
mergeCells(cursor)def
mergeCells(row, col, numRows, numCols)def
removeColumns(pos, num)def
removeRows(pos, num)def
resize(rows, cols)def
rowEnd(c)def
rowStart(c)def
rows()def
setFormat(format)def
splitCell(row, col, numRows, numCols)
Detailed Description¶
A table is a group of cells ordered into rows and columns. Each table contains at least one row and one column. Each cell contains a block, and is surrounded by a frame.
Tables are usually created and inserted into a document with the insertTable() function. For example, we can insert a table with three rows and two columns at the current cursor position in an editor using the following lines of code:
cursor = QTextCursor(editor.textCursor()) cursor.movePosition(QTextCursor.Start) table = cursor.insertTable(rows, columns, tableFormat)
The table format is either defined when the table is created or changed later with setFormat() .
The table currently being edited by the cursor is found with currentTable() . This allows its format or dimensions to be changed after it has been inserted into a document.
A table’s size can be changed with resize() , or by using insertRows() , insertColumns() , removeRows() , or removeColumns() . Use cellAt() to retrieve table cells.
The starting and ending positions of table rows can be found by moving a cursor within a table, and using the rowStart() and rowEnd() functions to obtain cursors at the start and end of each row.
Rows and columns within a QTextTable can be merged and split using the mergeCells() and splitCell() functions. However, only cells that span multiple rows or columns can be split. (Merging or splitting does not increase or decrease the number of rows and columns.)
Note that if you have merged multiple columns and rows into one cell, you will not be able to split the merged cell into new cells spanning over more than one row or column. To be able to split cells spanning over several rows and columns you need to do this over several iterations.
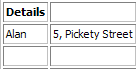
Suppose we have a 2x3 table of names and addresses. To merge both columns in the first row we invoke
mergeCells()withrow= 0,column= 0,numRows= 1 andnumColumns= 2.table.mergeCells(0, 0, 1, 2)
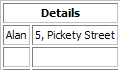
This gives us the following table. To split the first row of the table back into two cells, we invoke the
splitCell()function withnumRowsandnumCols= 1.table.splitCell(0, 0, 1, 1)
This results in the original table.
See also
- class PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable(doc)¶
- Parameters
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.appendColumns(count)¶
- Parameters
count – int
Appends count columns at the right side of the table.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.appendRows(count)¶
- Parameters
count – int
Appends count rows at the bottom of the table.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.cellAt(c)¶
- Parameters
- Return type
This is an overloaded function.
Returns the table cell containing the given cursor.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.cellAt(position)
- Parameters
position – int
- Return type
This is an overloaded function.
Returns the table cell that contains the character at the given position in the document.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.cellAt(row, col)
- Parameters
row – int
col – int
- Return type
Returns the table cell at the given row and column in the table.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.columns()¶
- Return type
int
Returns the number of columns in the table.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.format()¶
- Return type
Returns the table’s format.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.insertColumns(pos, num)¶
- Parameters
pos – int
num – int
Inserts a number of columns before the column with the specified index.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.insertRows(pos, num)¶
- Parameters
pos – int
num – int
Inserts a number of rows before the row with the specified index.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.mergeCells(cursor)¶
- Parameters
cursor –
PySide6.QtGui.QTextCursor
This is an overloaded function.
Merges the cells selected by the provided cursor.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.mergeCells(row, col, numRows, numCols)
- Parameters
row – int
col – int
numRows – int
numCols – int
Merges the cell at the specified row and column with the adjacent cells into one cell. The new cell will span numRows rows and numCols columns. This method does nothing if numRows or numCols is less than the current number of rows or columns spanned by the cell.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.removeColumns(pos, num)¶
- Parameters
pos – int
num – int
Removes a number of columns starting with the column at the specified index.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.removeRows(pos, num)¶
- Parameters
pos – int
num – int
Removes a number of rows starting with the row at the specified index.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.resize(rows, cols)¶
- Parameters
rows – int
cols – int
Resizes the table to contain the required number of rows and columns.
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.rowEnd(c)¶
- Parameters
- Return type
Returns a cursor pointing to the end of the row that contains the given cursor.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.rowStart(c)¶
- Parameters
- Return type
Returns a cursor pointing to the start of the row that contains the given cursor.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.rows()¶
- Return type
int
Returns the number of rows in the table.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.setFormat(format)¶
- Parameters
format –
PySide6.QtGui.QTextTableFormat
Sets the table’s format.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QTextTable.splitCell(row, col, numRows, numCols)¶
- Parameters
row – int
col – int
numRows – int
numCols – int
Splits the specified cell at row and column into an array of multiple cells with dimensions specified by numRows and numCols.
Note
It is only possible to split cells that span multiple rows or columns, such as rows that have been merged using mergeCells() .
See also
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.