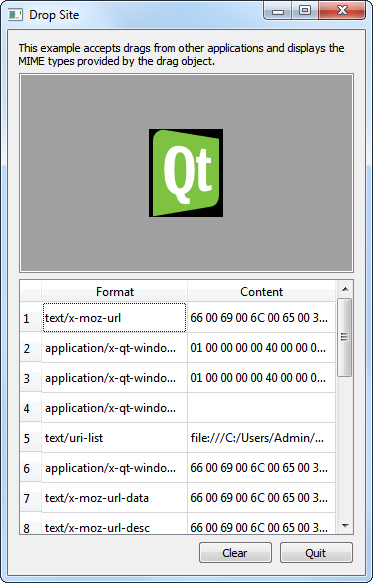
Drop Site Example¶
The example shows how to distinguish the various MIME formats available in a drag and drop operation.
The Drop Site example accepts drops from other applications, and displays the MIME formats provided by the drag object.
There are two classes, DropArea and DropSiteWindow, and a main() function in this example. A DropArea object is instantiated in DropSiteWindow; a DropSiteWindow object is then invoked in the main() function.
DropArea Class Definition¶
The DropArea class is a subclass of QLabel with a public slot, clear(), and a changed() signal.
class DropArea(QLabel): Q_OBJECT # public DropArea = explicit(QWidget parent = None) slots: = public() def clear(): signals: def changed(None):
In addition, DropArea also contains a private instance of QLabel and reimplementations of four QWidget event handlers:
dragEnterEvent()
dragMoveEvent()
dragLeaveEvent()
dropEvent()
These event handlers are further explained in the implementation of the DropArea class.
protected: def dragEnterEvent(event): def dragMoveEvent(event): def dragLeaveEvent(event): def dropEvent(event): # private label = QLabel()
DropArea Class Implementation¶
In the DropArea constructor, we set the minimum size to 200x200 pixels, the frame style to both Sunken and StyledPanel , and we align its contents to the center.
def __init__(self, parent): QLabel.__init__(self, parent) setMinimumSize(200, 200) setFrameStyle(QFrame.Sunken | QFrame.StyledPanel) setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter) setAcceptDrops(True) setAutoFillBackground(True) clear()
Also, we enable drop events in DropArea by setting the acceptDrops property to true. Then, we enable the autoFillBackground property and invoke the clear() function.
The dragEnterEvent() event handler is called when a drag is in progress and the mouse enters the DropArea object. For the DropSite example, when the mouse enters DropArea, we set its text to “<drop content>” and highlight its background.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:dragEnterEvent() function" not found>
Then, we invoke acceptProposedAction() on event, setting the drop action to the one proposed. Lastly, we emit the changed() signal, with the data that was dropped and its MIME type information as a parameter.
For dragMoveEvent() , we just accept the proposed QDragMoveEvent object, event, with acceptProposedAction() .
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:dragMoveEvent() function" not found>
The DropArea class’s implementation of dropEvent() extracts the event's mime data and displays it accordingly.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:dropEvent() function part1" not found>
The mimeData object can contain one of the following objects: an image, HTML text, Markdown text, plain text, or a list of URLs.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:dropEvent() function part2" not found>
If
mimeDatacontains an image, we display it inDropAreawithsetPixmap().If
mimeDatacontains HTML, we display it withsetText()and setDropArea's text format asRichText.If
mimeDatacontains Markdown, we display it withsetText()and setDropArea's text format asMarkdownText.If
mimeDatacontains plain text, we display it withsetText()and setDropArea's text format asPlainText. In the event thatmimeDatacontains URLs, we iterate through the list of URLs to display them on individual lines.If
mimeDatacontains other types of objects, we setDropArea's text, withsetText()to “Cannot display data” to inform the user.
We then set DropArea's backgroundRole to Dark and we accept event's proposed action.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:dropEvent() function part3" not found>
The dragLeaveEvent() event handler is called when a drag is in progress and the mouse leaves the widget.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:dragLeaveEvent() function" not found>
For DropArea's implementation, we clear invoke clear() and then accept the proposed event.
The clear() function sets the text in DropArea to “<drop content>” and sets the backgroundRole to Dark . Lastly, it emits the changed() signal.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/droparea.cpp:clear() function" not found>
DropSiteWindow Class Definition¶
The DropSiteWindow class contains a constructor and a public slot, updateFormatsTable().
class DropSiteWindow(QWidget): Q_OBJECT # public DropSiteWindow() slots: = public() def updateFormatsTable(mimeData): def copy(): # private dropArea = DropArea() abstractLabel = QLabel() formatsTable = QTableWidget() clearButton = QPushButton() copyButton = QPushButton() quitButton = QPushButton() buttonBox = QDialogButtonBox()
The class also contains a private instance of DropArea, dropArea, QLabel , abstractLabel, QTableWidget , formatsTable, QDialogButtonBox , buttonBox, and two QPushButton objects, clearButton and quitButton.
DropSiteWindow Class Implementation¶
In the constructor of DropSiteWindow, we instantiate abstractLabel and set its wordWrap property to true. We also call the adjustSize() function to adjust abstractLabel's size according to its contents.
def __init__(self): abstractLabel = QLabel(tr("This example accepts drags from other " "applications and displays the MIME types " "provided by the drag object.")) abstractLabel.setWordWrap(True) abstractLabel.adjustSize()
Then we instantiate dropArea and connect its changed() signal to DropSiteWindow's updateFormatsTable() slot.
dropArea = DropArea connect(dropArea, DropArea::changed, self, DropSiteWindow::updateFormatsTable)
We now set up the QTableWidget object, formatsTable. Its horizontal header is set using a QStringList object, labels. The number of columms are set to two and the table is not editable. Also, the formatTable's horizontal header is formatted to ensure that its second column stretches to occupy additional space available.
labels = QStringList() labels << tr("Format") << tr("Content") formatsTable = QTableWidget formatsTable.setColumnCount(2) formatsTable.setEditTriggers(QAbstractItemView.NoEditTriggers) formatsTable.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(labels) formatsTable.horizontalHeader().setStretchLastSection(True)
Three QPushButton objects, clearButton, copyButton, and quitButton, are instantiated and added to buttonBox - a QDialogButtonBox object. We use QDialogButtonBox here to ensure that the push buttons are presented in a layout that conforms to the platform’s style.
clearButton = QPushButton(tr("Clear")) copyButton = QPushButton(tr("Copy")) quitButton = QPushButton(tr("Quit")) buttonBox = QDialogButtonBox buttonBox.addButton(clearButton, QDialogButtonBox.ActionRole) buttonBox.addButton(copyButton, QDialogButtonBox.ActionRole) #if !QT_CONFIG(clipboard) copyButton.setVisible(False) #endif buttonBox.addButton(quitButton, QDialogButtonBox.RejectRole) connect(quitButton, QAbstractButton.clicked, self, QWidget.close) connect(clearButton, QAbstractButton.clicked, dropArea, DropArea.clear) connect(copyButton, QAbstractButton.clicked, self, DropSiteWindow.copy)
The clicked() signals for copyButton, clearButton, and quitButton are connected to copy(), clear() and close() , respectively.
For the layout, we use a QVBoxLayout , mainLayout, to arrange our widgets vertically. We also set the window title to “Drop Site” and the minimum size to 350x500 pixels.
mainLayout = QVBoxLayout(self) mainLayout.addWidget(abstractLabel) mainLayout.addWidget(dropArea) mainLayout.addWidget(formatsTable) mainLayout.addWidget(buttonBox) setWindowTitle(tr("Drop Site")) setMinimumSize(350, 500)
We move on to the updateFormatsTable() function. This function updates the formatsTable, displaying the MIME formats of the object dropped onto the DropArea object. First, we set QTableWidget ‘s rowCount property to 0. Then, we validate to ensure that the QMimeData object passed in is a valid object.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/dropsitewindow.cpp:updateFormatsTable() part1" not found>
Once we are sure that mimeData is valid, we iterate through its supported formats.
Note
The formats() function returns a QStringList object, containing all the formats supported by the mimeData.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/dropsitewindow.cpp:updateFormatsTable() part2" not found>
Within each iteration, we create a QTableWidgetItem , formatItem and we set its flags to ItemIsEnabled , and its text alignment to AlignTop and AlignLeft .
A QString object, text, is customized to display data according to the contents of format. We invoke QString ‘s simplified() function on text, to obtain a string that has no additional space before, after or in between words.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/dropsitewindow.cpp:updateFormatsTable() part3" not found>
If format contains a list of URLs, we iterate through them, using spaces to separate them. On the other hand, if format contains an image, we display the data by converting the text to hexadecimal.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/dropsitewindow.cpp:updateFormatsTable() part4" not found>
Once text has been customized to contain the appropriate data, we insert both format and text into formatsTable with setItem() . Lastly, we invoke resizeColumnToContents() on formatsTable's first column.
The main() Function¶
Within the main() function, we instantiate DropSiteWindow and invoke its show() function.
<Code snippet "draganddrop/dropsite/main.cpp:main() function" not found>
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.