Editable Tree Model Example¶
This example shows how to implement a simple item-based tree model that can be used with other classes the model/view framework.
The model supports editable items, custom headers, and the ability to insert and remove rows and columns. With these features, it is also possible to insert new child items, and this is shown in the supporting example code.
Overview¶
As described in the Model Subclassing Reference , models must provide implementations for the standard set of model functions: flags() , data() , headerData() , columnCount() , and rowCount() . In addition, hierarchical models, such as this one, need to provide implementations of index() and parent() .
An editable model needs to provide implementations of setData() and setHeaderData() , and must return a suitable combination of flags from its flags() function.
Since this example allows the dimensions of the model to be changed, we must also implement insertRows() , insertColumns() , removeRows() , and removeColumns() .
Design¶
As with the Simple Tree Model example, the model simply acts as a wrapper around a collection of instances of a TreeItem class. Each TreeItem is designed to hold data for a row of items in a tree view, so it contains a list of values corresponding to the data shown in each column.
Since QTreeView provides a row-oriented view onto a model, it is natural to choose a row-oriented design for data structures that will supply data via a model to this kind of view. Although this makes the tree model less flexible, and possibly less useful for use with more sophisticated views, it makes it less complex to design and easier to implement.
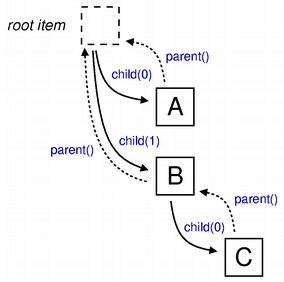
Relations between internal items
When designing a data structure for use with a custom model, it is useful to expose each item’s parent via a function like TreeItem::parent() because it will make writing the model’s own
parent()function easier. Similarly, a function like TreeItem::child() is helpful when implementing the model’sindex()function. As a result, eachTreeItemmaintains information about its parent and children, making it possible for us to traverse the tree structure.The diagram shows how
TreeIteminstances are connected via their parent() and child() functions.In the example shown, two top-level items, A and B, can be obtained from the root item by calling its child() function, and each of these items return the root node from their parent() functions, though this is only shown for item A.
Each TreeItem stores data for each column in the row it represents in its itemData private member (a list of QVariant objects). Since there is a one-to-one mapping between each column in the view and each entry in the list, we provide a simple data() function to read entries in the itemData list and a setData() function to allow them to be modified. As with other functions in the item, this simplifies the implemention of the model’s data() and setData() functions.
We place an item at the root of the tree of items. This root item corresponds to the null model index, QModelIndex() , that is used to represent the parent of a top-level item when handling model indexes. Although the root item does not have a visible representation in any of the standard views, we use its internal list of QVariant objects to store a list of strings that will be passed to views for use as horizontal header titles.
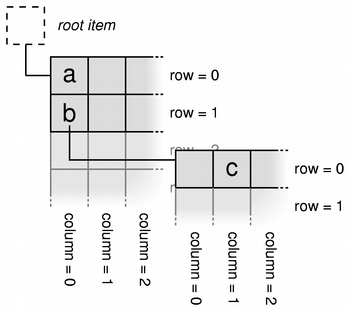
Accessing data via the model
In the case shown in the diagram, the piece of information represented by a can be obtained using the standard model/view API:
QVariant a = model->index(0, 0, QModelIndex()).data();Since each items holds pieces of data for each column in a given row, there can be many model indexes that map to the same
TreeItemobject. For example, the information represented by b can be obtained using the following code:QVariant b = model->index(1, 0, QModelIndex()).data();The same underlying
TreeItemwould be accessed to obtain information for the other model indexes in the same row as b.
In the model class, TreeModel, we relate TreeItem objects to model indexes by passing a pointer for each item when we create its corresponding model index with createIndex() in our index() and parent() implementations. We can retrieve pointers stored in this way by calling the internalPointer() function on the relevant model index - we create our own getItem() function to do the work for us, and call it from our data() and parent() implementations.
Storing pointers to items is convenient when we control how they are created and destroyed since we can assume that an address obtained from internalPointer() is a valid pointer. However, some models need to handle items that are obtained from other components in a system, and in many cases it is not possible to fully control how items are created or destroyed. In such situations, a pure pointer-based approach needs to be supplemented by safeguards to ensure that the model does not attempt to access items that have been deleted.
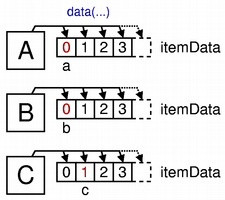
Storing information in the underlying data structure
Several pieces of data are stored as
QVariantobjects in theitemDatamember of eachTreeIteminstance.The diagram shows how pieces of information, represented by the labels a, b and c in the previous two diagrams, are stored in items A, B and C in the underlying data structure. Note that pieces of information from the same row in the model are all obtained from the same item. Each element in a list corresponds to a piece of information exposed by each column in a given row in the model.
Since the TreeModel implementation has been designed for use with QTreeView , we have added a restriction on the way it uses TreeItem instances: each item must expose the same number of columns of data. This makes viewing the model consistent, allowing us to use the root item to determine the number of columns for any given row, and only adds the requirement that we create items containing enough data for the total number of columns. As a result, inserting and removing columns are time-consuming operations because we need to traverse the entire tree to modify every item.
An alternative approach would be to design the TreeModel class so that it truncates or expands the list of data in individual TreeItem instances as items of data are modified. However, this “lazy” resizing approach would only allow us to insert and remove columns at the end of each row and would not allow columns to be inserted or removed at arbitrary positions in each row.
Relating items using model indexes
As with the Simple Tree Model example, the
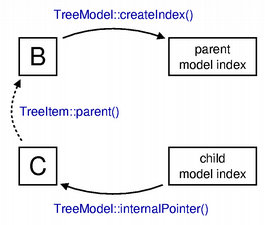
TreeModelneeds to be able to take a model index, find the correspondingTreeItem, and return model indexes that correspond to its parents and children.In the diagram, we show how the model’s parent() implementation obtains the model index corresponding to the parent of an item supplied by the caller, using the items shown in a previous diagram .
A pointer to item C is obtained from the corresponding model index using the
internalPointer()function. The pointer was stored internally in the index when it was created. Since the child contains a pointer to its parent, we use its parent() function to obtain a pointer to item B. The parent model index is created using thecreateIndex()function, passing the pointer to item B as the internal pointer.
TreeItem Class Definition¶
The TreeItem class provides simple items that contain several pieces of data, including information about their parent and child items:
class TreeItem(): # public TreeItem = explicit(QList data, TreeItem parent = None) ~TreeItem() child = TreeItem(int number) childCount = int() columnCount = int() data = QVariant(int column) insertChildren = bool(int position, int count, int columns) insertColumns = bool(int position, int columns) parent = TreeItem() removeChildren = bool(int position, int count) removeColumns = bool(int position, int columns) childNumber = int() setData = bool(int column, QVariant value) # private *> = QList<TreeItem() itemData = QList() parentItem = TreeItem()
We have designed the API to be similar to that provided by QAbstractItemModel by giving each item functions to return the number of columns of information, read and write data, and insert and remove columns. However, we make the relationship between items explicit by providing functions to deal with “children” rather than “rows”.
Each item contains a list of pointers to child items, a pointer to its parent item, and a list of QVariant objects that correspond to information held in columns in a given row in the model.
TreeItem Class Implementation¶
Each TreeItem is constructed with a list of data and an optional parent item:
def __init__(self, data, parent): self.itemData = data self.parentItem = parent {}
Initially, each item has no children. These are added to the item’s internal childItems member using the insertChildren() function described later.
The destructor ensures that each child added to the item is deleted when the item itself is deleted:
TreeItem::~TreeItem() qDeleteAll(childItems)
Since each item stores a pointer to its parent, the parent() function is trivial:
TreeItem::parent = TreeItem() return parentItem
Three functions provide information about the children of an item. child() returns a specific child from the internal list of children:
TreeItem::child = TreeItem(int number) if (number < 0 or number >= childItems.size()) return None return childItems.at(number)
The childCount() function returns the total number of children:
def childCount(self): return childItems.count()
The childNumber() function is used to determine the index of the child in its parent’s list of children. It accesses the parent’s childItems member directly to obtain this information:
def childNumber(self): if (parentItem) return parentItem.childItems.indexOf(TreeItem(self)) return 0
The root item has no parent item; for this item, we return zero to be consistent with the other items.
The columnCount() function simply returns the number of elements in the internal itemData list of QVariant objects:
def columnCount(self): return itemData.count()
Data is retrieved using the data() function, which accesses the appropriate element in the itemData list:
def data(self, int column): if (column < 0 or column >= itemData.size()) def QVariant(): return itemData.at(column)
Data is set using the setData() function, which only stores values in the itemData list for valid list indexes, corresponding to column values in the model:
def setData(self, int column, QVariant value): if (column < 0 or column >= itemData.size()) return False itemData[column] = value return True
To make implementation of the model easier, we return true to indicate that the data was set successfully.
Editable models often need to be resizable, enabling rows and columns to be inserted and removed. The insertion of rows beneath a given model index in the model leads to the insertion of new child items in the corresponding item, handled by the insertChildren() function:
def insertChildren(self, int position, int count, int columns): if (position < 0 or position > childItems.size()) return False for row in range(0, count): data = QList(columns) item = TreeItem(data, self) childItems.insert(position, item) return True
This ensures that new items are created with the required number of columns and inserted at a valid position in the internal childItems list. Items are removed with the removeChildren() function:
def removeChildren(self, int position, int count): if (position < 0 or position + count > childItems.size()) return False for row in range(0, count): del childItems.takeAt(position) return True
As discussed above, the functions for inserting and removing columns are used differently to those for inserting and removing child items because they are expected to be called on every item in the tree. We do this by recursively calling this function on each child of the item:
def insertColumns(self, int position, int columns): if (position < 0 or position > itemData.size()) return False for column in range(0, columns): itemData.insert(position, QVariant()) for child in qAsConst(childItems): child.insertColumns(position, columns) return True
TreeModel Class Definition¶
The TreeModel class provides an implementation of the QAbstractItemModel class, exposing the necessary interface for a model that can be edited and resized.
class TreeModel(QAbstractItemModel): Q_OBJECT # public TreeModel(QStringList headers, QString data, parent = None) ~TreeModel()
The constructor and destructor are specific to this model.
data = QVariant(QModelIndex index, int role) headerData(int = QVariant() role = Qt.DisplayRole) override() index(int = QModelIndex() QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex()) override parent = QModelIndex(QModelIndex index) rowCount = int(QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex()) columnCount = int(QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex())
Read-only tree models only need to provide the above functions. The following public functions provide support for editing and resizing:
Qt.ItemFlags flags(QModelIndex index) override setData(QModelIndex = bool() role = Qt.EditRole) override() setHeaderData(int = bool() QVariant value, int role = Qt.EditRole) override insertColumns(int = bool() QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex()) override removeColumns(int = bool() QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex()) override insertRows(int = bool() QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex()) override removeRows(int = bool() QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex()) override # private def setupModelData(lines, parent): getItem = TreeItem(QModelIndex index) rootItem = TreeItem()
To simplify this example, the data exposed by the model is organized into a data structure by the model’s setupModelData() function. Many real world models will not process the raw data at all, but simply work with an existing data structure or library API.
TreeModel Class Implementation¶
The constructor creates a root item and initializes it with the header data supplied:
def __init__(self, headers, data, parent): QAbstractItemModel.__init__(self, parent) rootData = QList() for header in headers: rootData << header rootItem = TreeItem(rootData) setupModelData(data.split('\n'), rootItem)
We call the internal setupModelData() function to convert the textual data supplied to a data structure we can use with the model. Other models may be initialized with a ready-made data structure, or use an API from a library that maintains its own data.
The destructor only has to delete the root item, which will cause all child items to be recursively deleted.
TreeModel::~TreeModel() del rootItem
Since the model’s interface to the other model/view components is based on model indexes, and since the internal data structure is item-based, many of the functions implemented by the model need to be able to convert any given model index to its corresponding item. For convenience and consistency, we have defined a getItem() function to perform this repetitive task:
TreeModel::getItem = TreeItem(QModelIndex index) if (index.isValid()) { item = TreeItem(index.internalPointer()) if (item) return item return rootItem
Each model index passed to this function should correspond to a valid item in memory. If the index is invalid, or its internal pointer does not refer to a valid item, the root item is returned instead.
The model’s rowCount() implementation is simple: it first uses the getItem() function to obtain the relevant item; then it returns the number of children it contains:
def rowCount(self, QModelIndex parent): if (parent.isValid() and parent.column() > 0) return 0 parentItem = getItem(parent) return parentItem if parentItem.childCount() else 0
By contrast, the columnCount() implementation does not need to look for a particular item because all items are defined to have the same number of columns associated with them.
def columnCount(self, QModelIndex parent): Q_UNUSED(parent) return rootItem.columnCount()
As a result, the number of columns can be obtained directly from the root item.
To enable items to be edited and selected, the flags() function needs to be implemented so that it returns a combination of flags that includes the ItemIsEditable and ItemIsSelectable flags as well as ItemIsEnabled :
Qt.ItemFlags TreeModel.flags(QModelIndex index) if (not index.isValid()) return Qt.NoItemFlags return Qt.ItemIsEditable | QAbstractItemModel.flags(index)
The model needs to be able to generate model indexes to allow other components to request data and information about its structure. This task is performed by the index() function, which is used to obtain model indexes corresponding to children of a given parent item:
def index(self, int row, int column, QModelIndex parent): if (parent.isValid() and parent.column() != 0) def QModelIndex():
In this model, we only return model indexes for child items if the parent index is invalid (corresponding to the root item) or if it has a zero column number.
We use the custom getItem() function to obtain a TreeItem instance that corresponds to the model index supplied, and request its child item that corresponds to the specified row.
parentItem = getItem(parent) if (not parentItem) def QModelIndex(): childItem = parentItem.child(row) if (childItem) def createIndex(row,column,childItem): def QModelIndex():
Since each item contains information for an entire row of data, we create a model index to uniquely identify it by calling createIndex() it with the row and column numbers and a pointer to the item. In the data() function, we will use the item pointer and column number to access the data associated with the model index; in this model, the row number is not needed to identify data.
The parent() function supplies model indexes for parents of items by finding the corresponding item for a given model index, using its parent() function to obtain its parent item, then creating a model index to represent the parent. (See the above diagram ).
def parent(self, QModelIndex index): if (not index.isValid()) def QModelIndex(): childItem = getItem(index) parentItem = childItem if childItem.parent() else None if (parentItem == rootItem or not parentItem) def QModelIndex(): def createIndex(parentItem.childNumber(),0,parentItem):
Items without parents, including the root item, are handled by returning a null model index. Otherwise, a model index is created and returned as in the index() function, with a suitable row number, but with a zero column number to be consistent with the scheme used in the index() implementation.
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.