Qt Widgets - Application Example¶
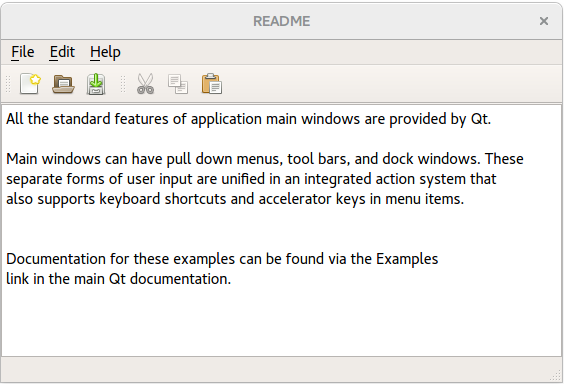
The Application example shows how to implement a standard widget application with menus, toolbars, and a status bar. The example itself is a simple text editor program built around QPlainTextEdit .
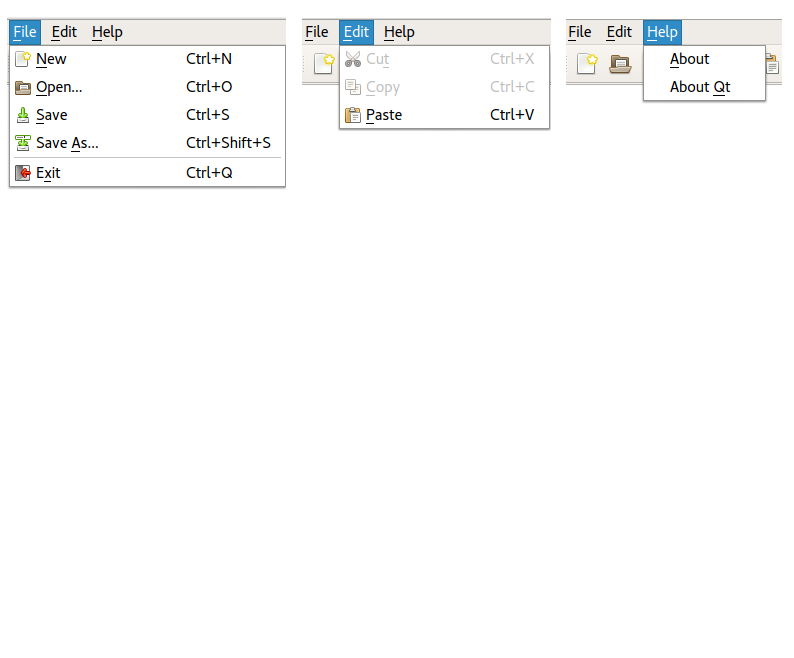
Nearly all of the code for the Application example is in the MainWindow class, which inherits QMainWindow . QMainWindow provides the framework for windows that have menus, toolbars, dock windows, and a status bar. The application provides File, Edit, and Help entries in the menu bar, with the following popup menus:
The status bar at the bottom of the main window shows a description of the menu item or toolbar button under the cursor.
To keep the example simple, recently opened files aren’t shown in the File menu, even though this feature is desired in 90% of applications. Furthermore, this example can only load one file at a time. The SDI and MDI examples show how to lift these restrictions and how to implement recently opened files handling.
MainWindow Class Definition¶
Here’s the class definition:
class MainWindow(QMainWindow): Q_OBJECT # public MainWindow() def loadFile(fileName): protected: def closeEvent(event): slots: = private() def newFile(): def open(): save = bool() saveAs = bool() def about(): def documentWasModified(): #ifndef QT_NO_SESSIONMANAGER def commitData(): #endif # private def createActions(): def createStatusBar(): def readSettings(): def writeSettings(): maybeSave = bool() saveFile = bool(QString fileName) def setCurrentFile(fileName): strippedName = QString(QString fullFileName) textEdit = QPlainTextEdit() curFile = QString()
The public API is restricted to the constructor. In the protected section, we reimplement closeEvent() to detect when the user attempts to close the window, and warn the user about unsaved changes. In the private slots section, we declare slots that correspond to menu entries, as well as a mysterious documentWasModified() slot. Finally, in the private section of the class, we have various members that will be explained in due time.
MainWindow Class Implementation¶
from PySide6 import QtWidgets from mainwindow import *
We start by including <QtWidgets>, a header file that contains the definition of all classes in the Qt Core, Qt GUI and Qt Widgets modules. This saves us from the trouble of having to include every class individually. We also include mainwindow.h.
You might wonder why we don’t include <QtWidgets> in mainwindow.h and be done with it. The reason is that including such a large header from another header file can rapidly degrade performances. Here, it wouldn’t do any harm, but it’s still generally a good idea to include only the header files that are strictly necessary from another header file.
def __init__(self): self.textEdit = QPlainTextEdit setCentralWidget(textEdit) createActions() createStatusBar() readSettings() connect(textEdit.document(), QTextDocument.contentsChanged, self, MainWindow::documentWasModified) #ifndef QT_NO_SESSIONMANAGER connect(qApp, QGuiApplication.commitDataRequest, self, MainWindow::commitData) #endif setCurrentFile(QString()) setUnifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac(True)
In the constructor, we start by creating a QPlainTextEdit widget as a child of the main window (the this object). Then we call setCentralWidget() to tell that this is going to be the widget that occupies the central area of the main window, between the toolbars and the status bar.
Then we call createActions() and createStatusBar(), two private functions that set up the user interface. After that, we call readSettings() to restore the user’s preferences.
We establish a signal-slot connection between the QPlainTextEdit ‘s document object and our documentWasModified() slot. Whenever the user modifies the text in the QPlainTextEdit , we want to update the title bar to show that the file was modified.
At the end, we set the window title using the private setCurrentFile() function. We’ll come back to this later.
def closeEvent(self, event): if (maybeSave()) { writeSettings() event.accept() else: event.ignore()
When the user attempts to close the window, we call the private function maybeSave() to give the user the possibility to save pending changes. The function returns true if the user wants the application to close; otherwise, it returns false. In the first case, we save the user’s preferences to disk and accept the close event; in the second case, we ignore the close event, meaning that the application will stay up and running as if nothing happened.
def newFile(self): if (maybeSave()) { textEdit.clear() setCurrentFile(QString())
The newFile() slot is invoked when the user selects File|New from the menu. We call maybeSave() to save any pending changes and if the user accepts to go on, we clear the QPlainTextEdit and call the private function setCurrentFile() to update the window title and clear the windowModified flag.
def open(self): if (maybeSave()) { fileName = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self) if (not fileName.isEmpty()) loadFile(fileName)
The open() slot is invoked when the user clicks File|Open. We pop up a QFileDialog asking the user to choose a file. If the user chooses a file (i.e., fileName is not an empty string), we call the private function loadFile() to actually load the file.
def save(self): if (curFile.isEmpty()) { def saveAs(): else: def saveFile(curFile):
The save() slot is invoked when the user clicks File|Save. If the user hasn’t provided a name for the file yet, we call saveAs(); otherwise, we call the private function saveFile() to actually save the file.
def saveAs(self): dialog = QFileDialog(self) dialog.setWindowModality(Qt.WindowModal) dialog.setAcceptMode(QFileDialog.AcceptSave) if (dialog.exec() != QDialog.Accepted) return False def saveFile(dialog.selectedFiles().first()):
In saveAs(), we start by popping up a QFileDialog asking the user to provide a name. If the user clicks Cancel, the returned file name is empty, and we do nothing.
def about(self): QMessageBox.about(self, tr("About Application"), tr("The <b>Application</b> example demonstrates how to " "write modern GUI applications using Qt, with a menu bar, " "toolbars, and a status bar."))
The application’s About box is done using one statement, using the about() static function and relying on its support for an HTML subset.
The tr() call around the literal string marks the string for translation. It is a good habit to call tr() on all user-visible strings, in case you later decide to translate your application to other languages. The Internationalization with Qt overview covers tr() in more detail.
def documentWasModified(self): setWindowModified(textEdit.document().isModified())
The documentWasModified() slot is invoked each time the text in the QPlainTextEdit changes because of user edits. We call setWindowModified() to make the title bar show that the file was modified. How this is done varies on each platform.
def createActions(self): fileMenu = menuBar().addMenu(tr("File")) fileToolBar = addToolBar(tr("File")) newIcon = QIcon.fromTheme("document-new", QIcon(":/images/new.png")) newAct = QAction(newIcon, tr("New"), self) newAct.setShortcuts(QKeySequence.New) newAct.setStatusTip(tr("Create a file")) connect(newAct, QAction.triggered, self, MainWindow.newFile) fileMenu.addAction(newAct) fileToolBar.addAction(newAct) openIcon = QIcon.fromTheme("document-open", QIcon(":/images/open.png")) openAct = QAction(openIcon, tr("Open..."), self) openAct.setShortcuts(QKeySequence.Open) openAct.setStatusTip(tr("Open an existing file")) connect(openAct, QAction.triggered, self, MainWindow.open) fileMenu.addAction(openAct) fileToolBar.addAction(openAct) ... aboutQtAct = helpMenu.addAction(tr("About Qt"), qApp, QApplication.aboutQt) aboutQtAct.setStatusTip(tr("Show the Qt library's About box"))
The createActions() private function, which is called from the MainWindow constructor, creates QAction s and populates the menus and two toolbars. The code is very repetitive, so we show only the actions corresponding to File|New, File|Open, and Help|About Qt.
A QAction is an object that represents one user action, such as saving a file or invoking a dialog. An action can be put in a QMenu or a QToolBar , or both, or in any other widget that reimplements actionEvent() .
An action has a text that is shown in the menu, an icon, a shortcut key, a tooltip, a status tip (shown in the status bar), a “What’s This?” text, and more. It emits a triggered() signal whenever the user invokes the action (e.g., by clicking the associated menu item or toolbar button).
Instances of QAction can be created by passing a parent QObject or by using one of the convenience functions of QMenu , QMenuBar or QToolBar . We create the actions that are in a menu as well as in a toolbar parented on the window to prevent ownership issues. For actions that are only in the menu, we use the convenience function addAction() , which allows us to pass text, icon and the target object and its slot member function.
Creating toolbars is very similar to creating menus. The same actions that we put in the menus can be reused in the toolbars. After creating the action, we add it to the toolbar using addAction() .
The code above contains one more idiom that must be explained. For some of the actions, we specify an icon as a QIcon to the QAction constructor. We use fromTheme() to obtain the correct standard icon from the underlying window system. If that fails due to the platform not supporting it, we pass a file name as fallback. Here, the file name starts with :. Such file names aren’t ordinary file names, but rather path in the executable’s stored resources. We’ll come back to this when we review the application.qrc file that’s part of the project.
#ifndef QT_NO_CLIPBOARD cutAct.setEnabled(False) copyAct.setEnabled(False) connect(textEdit, QPlainTextEdit.copyAvailable, cutAct, QAction.setEnabled) connect(textEdit, QPlainTextEdit.copyAvailable, copyAct, QAction.setEnabled) #endif // !QT_NO_CLIPBOARD
The Edit|Cut and Edit|Copy actions must be available only when the QPlainTextEdit contains selected text. We disable them by default and connect the copyAvailable() signal to the setEnabled() slot, ensuring that the actions are disabled when the text editor has no selection.
Just before we create the Help menu, we call addSeparator() . This has no effect for most widget styles (e.g., Windows and macOS styles), but for some styles this makes sure that Help is pushed to the right side of the menu bar.
def createStatusBar(self): statusBar().showMessage(tr("Ready"))
statusBar() returns a pointer to the main window’s QStatusBar widget. Like with menuBar() , the widget is automatically created the first time the function is called.
def readSettings(self): settings = QSettings(QCoreApplication.organizationName(), QCoreApplication.applicationName()) geometry = settings.value("geometry", QByteArray()).toByteArray() if (geometry.isEmpty()) { availableGeometry = screen().availableGeometry() resize(availableGeometry.width() / 3, availableGeometry.height() / 2) move((availableGeometry.width() - width()) / 2, (availableGeometry.height() - height()) / 2) else: restoreGeometry(geometry)
The readSettings() function is called from the constructor to load the user’s preferences and other application settings. The QSettings class provides a high-level interface for storing settings permanently on disk. On Windows, it uses the (in)famous Windows registry; on macOS, it uses the native XML-based CFPreferences API; on Unix/X11, it uses text files.
The QSettings constructor takes arguments that identify your company and the name of the product. This ensures that the settings for different applications are kept separately.
We use value() to extract the value of the geometry setting. The second argument to value() is optional and specifies a default value for the setting if there exists none. This value is used the first time the application is run.
We use saveGeometry() and Widget::restoreGeometry() to save the position. They use an opaque QByteArray to store screen number, geometry and window state.
def writeSettings(self): settings = QSettings(QCoreApplication.organizationName(), QCoreApplication.applicationName()) settings.setValue("geometry", saveGeometry())
The writeSettings() function is called from closeEvent(). Writing settings is similar to reading them, except simpler. The arguments to the QSettings constructor must be the same as in readSettings().
def maybeSave(self): if (not textEdit.document().isModified()) return True QMessageBox.StandardButton ret = QMessageBox.warning(self, tr("Application"), tr("The document has been modified.\n" "Do you want to save your changes?"), QMessageBox.Save | QMessageBox.Discard | QMessageBox.Cancel) switch (ret) { QMessageBox.Save: = case() def save(): QMessageBox.Cancel: = case() return False default: break return True
The maybeSave() function is called to save pending changes. If there are pending changes, it pops up a QMessageBox giving the user to save the document. The options are Yes , No , and Cancel . The Yes button is made the default button (the button that is invoked when the user presses Return) using the Default flag; the Cancel button is made the escape button (the button that is invoked when the user presses Esc) using the Escape flag.
The maybeSave() function returns true in all cases, except when the user clicks Cancel or saving the file fails. The caller must check the return value and stop whatever it was doing if the return value is false.
def loadFile(self, fileName): file = QFile(fileName) if (not file.open(QFile.ReadOnly | QFile.Text)) { QMessageBox.warning(self, tr("Application"), tr("Cannot read file %1:\n%2.") .arg(QDir.toNativeSeparators(fileName), file.errorString())) return in = QTextStream(file) #ifndef QT_NO_CURSOR QGuiApplication.setOverrideCursor(Qt.WaitCursor) #endif textEdit.setPlainText(in.readAll()) #ifndef QT_NO_CURSOR QGuiApplication.restoreOverrideCursor() #endif setCurrentFile(fileName) statusBar().showMessage(tr("File loaded"), 2000)
In loadFile(), we use QFile and QTextStream to read in the data. The QFile object provides access to the bytes stored in a file.
We start by opening the file in read-only mode. The QFile::Text flag indicates that the file is a text file, not a binary file. On Unix and macOS, this makes no difference, but on Windows, it ensures that the “\r\n” end-of-line sequence is converted to “\n” when reading.
If we successfully opened the file, we use a QTextStream object to read in the data. QTextStream automatically converts the 8-bit data into a Unicode QString and supports various encodings. If no encoding is specified, QTextStream assumes the file is encoded in UTF-8.
Since the call to readAll() might take some time, we set the cursor to be WaitCursor for the entire application while it goes on.
At the end, we call the private setCurrentFile() function, which we’ll cover in a moment, and we display the string “File loaded” in the status bar for 2 seconds (2000 milliseconds).
def saveFile(self, QString fileName): errorMessage = QString() QGuiApplication.setOverrideCursor(Qt.WaitCursor) file = QSaveFile(fileName) if (file.open(QFile.WriteOnly | QFile.Text)) { out = QTextStream(file) out << textEdit.toPlainText() if (not file.commit()) { errorMessage = tr("Cannot write file %1:\n%2.") .arg(QDir.toNativeSeparators(fileName), file.errorString()) else: errorMessage = tr("Cannot open file %1 for writing:\n%2.") .arg(QDir.toNativeSeparators(fileName), file.errorString()) QGuiApplication.restoreOverrideCursor() if (not errorMessage.isEmpty()) { QMessageBox.warning(self, tr("Application"), errorMessage) return False setCurrentFile(fileName) statusBar().showMessage(tr("File saved"), 2000) return True
Saving a file is similar to loading one. We use QSaveFile to ensure all data are safely written and existing files are not damaged should writing fail. We use the QFile::Text flag to make sure that on Windows, “\n” is converted into “\r\n” to conform to the Windows convention.
def setCurrentFile(self, fileName): curFile = fileName textEdit.document().setModified(False) setWindowModified(False) shownName = curFile if (curFile.isEmpty()) shownName = "untitled.txt" setWindowFilePath(shownName)
The setCurrentFile() function is called to reset the state of a few variables when a file is loaded or saved, or when the user starts editing a new file (in which case fileName is empty). We update the curFile variable, clear the modified flag and the associated QWidget:windowModified flag, and update the window title to contain the new file name (or untitled.txt).
The strippedName() function call around curFile in the setWindowTitle() call shortens the file name to exclude the path. Here’s the function:
def strippedName(self, QString fullFileName): def QFileInfo(fullFileName).fileName():
The main() Function¶
The main() function for this application is typical of applications that contain one main window:
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication from PySide6.QtCore import QCommandLineParser from PySide6.QtCore import QCommandLineOption from mainwindow import * if __name__ == "__main__": Q_INIT_RESOURCE(application) app = QApplication([]) QCoreApplication.setOrganizationName("QtProject") QCoreApplication.setApplicationName("Application Example") QCoreApplication.setApplicationVersion(QT_VERSION_STR) parser = QCommandLineParser() parser.setApplicationDescription(QCoreApplication.applicationName()) parser.addHelpOption() parser.addVersionOption() parser.addPositionalArgument("file", "The file to open.") parser.process(app) mainWin = MainWindow() if (not parser.positionalArguments().isEmpty()) mainWin.loadFile(parser.positionalArguments().first()) mainWin.show() sys.exit(app.exec())
The main function uses QCommandLineParser to check whether some file argument was passed to the application and loads it via MainWindow::loadFile().
The Resource File¶
As you will probably recall, for some of the actions, we specified icons with file names starting with : and mentioned that such file names aren’t ordinary file names, but path in the executable’s stored resources. These resources are compiled
The resources associated with an application are specified in a .qrc file, an XML-based file format that lists files on the disk. Here’s the application.qrc file that’s used by the Application example:
<Code snippet "/tmp/snapshot-qt5full-6.2/qt5/qtbase/mainwindows/application/application.qrc" not found>
The .png files listed in the application.qrc file are files that are part of the Application example’s source tree. Paths are relative to the directory where the application.qrc file is located (the mainwindows/application directory).
The resource file must be mentioned in the application.pro file so that qmake knows about it:
<Code snippet "mainwindows/application/application.pro:0" not found>
qmake will produce make rules to generate a file called qrc_application.cpp that is linked into the application. This file contains all the data for the images and other resources as static C++ arrays of compressed binary data. See The Qt Resource System for more information about resources.
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.