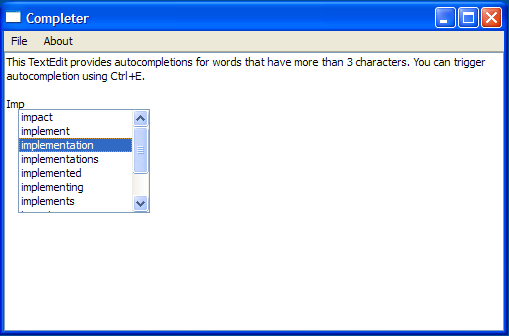
Custom Completer Example¶
The Custom Completer example shows how to provide string-completion facilities for an input widget based on data provided by a model. The completer pops up suggestions for possible words based on the first three characters input by the user and the user’s choice of word is inserted into the TextEdit using QTextCursor .
Setting Up The Resource File¶
The Custom Completer example requires a resource file, wordlist.txt, that has a list of words to help QCompleter complete words. This file contains the following:
<Code snippet "/tmp/snapshot-qt5full-6.2/qt5/qtbase/tools/customcompleter/customcompleter.qrc" not found>
TextEdit Class Definition¶
The TextEdit class is a subclass of QTextEdit with a custom insertCompletion() slot and it reimplements the keyPressEvent() and the focusInEvent() functions. TextEdit also contains a private function textUnderCursor() and a private instance of QCompleter , c.
class TextEdit(QTextEdit): Q_OBJECT # public TextEdit(QWidget parent = None) ~TextEdit() def setCompleter(c): completer = QCompleter() protected: def keyPressEvent(e): def focusInEvent(e): slots: = private() def insertCompletion(completion): # private textUnderCursor = QString() # private c = None()
TextEdit Class Implementation¶
The constructor for TextEdit constructs a TextEdit with a parent and initializes c. The instructions to use the completer is displayed on the TextEdit object, using the setPlainText() function.
def __init__(self, parent): QTextEdit.__init__(self, parent) setPlainText(tr("This TextEdit provides autocompletions for words that have more than" " 3 characters. You can trigger autocompletion using ") + QKeySequence("Ctrl+E").toString(QKeySequence.NativeText))
In addition, TextEdit also includes a default destructor:
TextEdit::~TextEdit()
The setCompleter() function accepts a completer and sets it up. We use if (c) to check if c has been initialized. If it has been initialized, the disconnect() function is invoked to disconnect the signal from the slot. This is to ensure that no previous completer object is still connected to the slot.
def setCompleter(self, completer): if (c) c.disconnect(self) c = completer if (not c) return c.setWidget(self) c.setCompletionMode(QCompleter.PopupCompletion) c.setCaseSensitivity(Qt.CaseInsensitive) QObject.connect(c, QOverload<QString >.of(QCompleter.activated), self, TextEdit::insertCompletion)
We then instantiate c with completer and set it as TextEdit's widget. The completion mode and case sensitivity are also set and then we connect the activated() signal to the insertCompletion() slot.
The completer() function is a getter function that returns c.
TextEdit::completer = QCompleter() return c
The completer pops up the options available, based on the contents of wordlist.txt, but the text cursor is responsible for filling in the missing characters, according to the user’s choice of word.
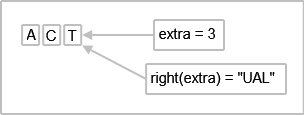
Suppose the user inputs “ACT” and accepts the completer’s suggestion of “ACTUAL”. The completion string is then sent to insertCompletion() by the completer’s activated() signal.
The insertCompletion() function is responsible for completing the word using a QTextCursor object, tc. It validates to ensure that the completer’s widget is TextEdit before using tc to insert the extra characters to complete the word.
def insertCompletion(self, completion): if (c.widget() != self) return tc = textCursor() extra = completion.length() - c.completionPrefix().length() tc.movePosition(QTextCursor.Left) tc.movePosition(QTextCursor.EndOfWord) tc.insertText(completion.right(extra)) setTextCursor(tc)
The figure below illustrates this process:
completion.length() = 6
c->completionPrefix().length()=3
The difference between these two values is extra, which is 3. This means that the last three characters from the right, “U”, “A”, and “L”, will be inserted by tc.
The textUnderCursor() function uses a QTextCursor , tc, to select a word under the cursor and return it.
def textUnderCursor(self): tc = textCursor() tc.select(QTextCursor.WordUnderCursor) return tc.selectedText()
The TextEdit class reimplements focusInEvent() function, which is an event handler used to receive keyboard focus events for the widget.
def focusInEvent(self, e): if (c) c.setWidget(self) QTextEdit.focusInEvent(e)
The keyPressEvent() is reimplemented to ignore key events like Key_Enter , Key_Return , Key_Escape , Key_Tab , and Key_Backtab so the completer can handle them.
If there is an active completer, we cannot process the shortcut, Ctrl+E.
def keyPressEvent(self, e): if (c and c.popup().isVisible()) { # The following keys are forwarded by the completer to the widget switch (e.key()) { Qt.Key_Enter: = case() Qt.Key_Return: = case() Qt.Key_Escape: = case() Qt.Key_Tab: = case() Qt.Key_Backtab: = case() e.ignore() return # let the completer do default behavior default: break isShortcut = (e.modifiers().testFlag(Qt.ControlModifier) and e.key() == Qt.Key_E) # CTRL+E if (not c or not isShortcut) // do not process the shortcut when we have a completer QTextEdit.keyPressEvent(e)
We also handle other modifiers and shortcuts for which we do not want the completer to respond to.
ctrlOrShift = e.modifiers().testFlag(Qt.ControlModifier) or e.modifiers().testFlag(Qt.ShiftModifier) if (not c or (ctrlOrShift and e.text().isEmpty())) return QString eow("~not @#$%^*()_+{}|:\"<>?,./'[]\\-="); # end of word hasModifier = (e.modifiers() != Qt.NoModifier) and !ctrlOrShift completionPrefix = textUnderCursor() if (not isShortcut and (hasModifier or e.text().isEmpty()or completionPrefix.length() < 3 or eow.contains(e.text().right(1)))) { c.popup().hide() return if (completionPrefix != c.completionPrefix()) { c.setCompletionPrefix(completionPrefix) c.popup().setCurrentIndex(c.completionModel().index(0, 0)) cr = cursorRect() cr.setWidth(c.popup().sizeHintForColumn(0) + c.popup().verticalScrollBar().sizeHint().width()) c.complete(cr) # popup it up!
Finally, we pop up the completer.
MainWindow Class Definition¶
The MainWindow class is a subclass of QMainWindow and implements a private slot, about(). This class also has two private functions, createMenu() and modelFromFile() as well as private instances of QCompleter and TextEdit.
class MainWindow(QMainWindow): Q_OBJECT # public MainWindow(QWidget parent = None) slots: = private() def about(): # private def createMenu(): modelFromFile = QAbstractItemModel(QString fileName) completer = None() completingTextEdit = TextEdit()
MainWindow Class Implementation¶
The constructor constructs a MainWindow with a parent and initializes the completer. It also instantiates a TextEdit and sets its completer. A QStringListModel , obtained from modelFromFile(), is used to populate the completer. The MainWindow's central widget is set to TextEdit and its size is set to 500 x 300.
def __init__(self, parent): QMainWindow.__init__(self, parent) createMenu() completingTextEdit = TextEdit completer = QCompleter(self) completer.setModel(modelFromFile(":/resources/wordlist.txt")) completer.setModelSorting(QCompleter.CaseInsensitivelySortedModel) completer.setCaseSensitivity(Qt.CaseInsensitive) completer.setWrapAround(False) completingTextEdit.setCompleter(completer) setCentralWidget(completingTextEdit) resize(500, 300) setWindowTitle(tr("Completer"))
The createMenu() function creates the necessary QAction objects needed for the “File” and “Help” menu and their triggered() signals are connected to the quit(), about(), and aboutQt() slots respectively.
def createMenu(self): exitAction = QAction(tr("Exit"), self) aboutAct = QAction(tr("About"), self) aboutQtAct = QAction(tr("About Qt"), self) connect(exitAction, QAction.triggered, qApp, QApplication.quit) connect(aboutAct, QAction.triggered, self, MainWindow.about) connect(aboutQtAct, QAction.triggered, qApp, QApplication.aboutQt) fileMenu = menuBar().addMenu(tr("File")) fileMenu.addAction(exitAction) helpMenu = menuBar().addMenu(tr("About")) helpMenu.addAction(aboutAct) helpMenu.addAction(aboutQtAct)
The modelFromFile() function accepts a fileName and attempts to extract the contents of this file into a QStringListModel . We display the WaitCursor when we are populating the QStringList , words, and restore the mouse cursor when we are done.
MainWindow::modelFromFile = QAbstractItemModel(QString fileName) file = QFile(fileName) if (not file.open(QFile.ReadOnly)) def QStringListModel(completer): #ifndef QT_NO_CURSOR QGuiApplication.setOverrideCursor(QCursor(Qt.WaitCursor)) #endif words = QStringList() while (not file.atEnd()) { line = file.readLine() if (not line.isEmpty()) words << QString.fromUtf8(line.trimmed()) #ifndef QT_NO_CURSOR QGuiApplication.restoreOverrideCursor() #endif def QStringListModel(words,completer):
The about() function provides a brief description about the Custom Completer example.
def about(self): QMessageBox.about(self, tr("About"), tr("This example demonstrates the " "different features of the QCompleter class."))
`` main()``
Function¶
The main() function instantiates MainWindow and invokes the show() function.
if __name__ == "__main__": Q_INIT_RESOURCE(customcompleter) app = QApplication([]) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec())
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.