Qt#
The Qt namespace contains miscellaneous identifiers used throughout the Qt library. More…
Synopsis#
Static functions#
def
beginPropertyUpdateGroup()def
bin(s)def
bom(s)def
center(s)def
dec(s)def
endPropertyUpdateGroup()def
endl(s)def
fixed(s)def
flush(s)def
forcepoint(s)def
forcesign(s)def
hex(s)def
left(s)def
lowercasebase(s)def
lowercasedigits(s)def
noforcepoint(s)def
noforcesign(s)def
noshowbase(s)def
oct(s)def
reset(s)def
right(s)def
scientific(s)def
showbase(s)def
uppercasebase(s)def
uppercasedigits(s)def
ws(s)
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.GlobalColor#
Qt’s predefined QColor objects:
Constant
Description
Qt.white
White (#ffffff)
Qt.black
Black (#000000)
Qt.red
Red (#ff0000)
Qt.darkRed
Dark red (#800000)
Qt.green
Green (#00ff00)
Qt.darkGreen
Dark green (#008000)
Qt.blue
Blue (#0000ff)
Qt.darkBlue
Dark blue (#000080)
Qt.cyan
Cyan (#00ffff)
Qt.darkCyan
Dark cyan (#008080)
Qt.magenta
Magenta (#ff00ff)
Qt.darkMagenta
Dark magenta (#800080)
Qt.yellow
Yellow (#ffff00)
Qt.darkYellow
Dark yellow (#808000)
Qt.gray
Gray (#a0a0a4)
Qt.darkGray
Dark gray (#808080)
Qt.lightGray
Light gray (#c0c0c0)
Qt.transparent
a transparent black value (i.e., QColor(0, 0, 0, 0))
Qt.color0
0 pixel value (for bitmaps)
Qt.color1
1 pixel value (for bitmaps)
See also
QColor
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ColorScheme#
Represents the appearance of an application’s theme, defined by QGuiApplication::palette().
Constant
Description
Qt.ColorScheme.Unknown
The appearance is unknown.
Qt.ColorScheme.Light
The background colors are lighter than the text color, i.e. the theme is light.
Qt.ColorScheme.Dark
The background colors are darker than the text color, i.e. the theme is dark.
New in version 6.5.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.MouseButton#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum type describes the different mouse buttons.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoButton
The button state does not refer to any button (see QMouseEvent::button()).
Qt.AllButtons
This value corresponds to a mask of all possible mouse buttons. Use to set the ‘acceptedButtons’ property of a MouseArea to accept ALL mouse buttons.
Qt.LeftButton
The left button is pressed, or an event refers to the left button. (The left button may be the right button on left-handed mice.)
Qt.RightButton
The right button.
Qt.MiddleButton
The middle button.
Qt.BackButton
The ‘Back’ button. (Typically present on the ‘thumb’ side of a mouse with extra buttons. This is NOT the tilt wheel.)
Qt.XButton1
The ‘Back’ Button.
Qt.ExtraButton1
The ‘Back’ Button.
Qt.ForwardButton
The ‘Forward’ Button. (Typically present beside the ‘Back’ button, and also pressed by the thumb.)
Qt.XButton2
The ‘Forward Button.
Qt.ExtraButton2
The ‘Forward’ Button.
Qt.TaskButton
The ‘Task’ Button.
Qt.ExtraButton3
The ‘Task’ Button.
Qt.ExtraButton4
The 7th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton5
The 8th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton6
The 9th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton7
The 10th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton8
The 11th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton9
The 12th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton10
The 13th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton11
The 14th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton12
The 15th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton13
The 16th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton14
The 17th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton15
The 18th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton16
The 19th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton17
The 20th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton18
The 21st non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton19
The 22nd non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton20
The 23rd non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton21
The 24th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton22
The 25th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton23
The 26th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Qt.ExtraButton24
The 27th non-wheel Mouse Button.
Note
Some models of multi-button mice are pre-configured with high-numbered Buttons emulating keyboard sequences, for use in specific games. In order for these Buttons to be seen as actual ‘Mouse Buttons’, the device must be re-configured (using the vendor’s configuration tool).
See also
KeyboardModifier Modifier
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.Orientation#
(inherits enum.Flag) This type is used to signify an object’s orientation.
Constant
Description
Qt.Horizontal
Qt.Vertical
Orientation is used with QScrollBar for example.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.FocusPolicy#
(inherits enum.IntFlag) This enum type defines the various policies a widget can have with respect to acquiring keyboard focus.
Constant
Description
Qt.TabFocus
the widget accepts focus by tabbing.
Qt.ClickFocus
the widget accepts focus by clicking.
Qt.StrongFocus
the widget accepts focus by both tabbing and clicking. On macOS this will also be indicate that the widget accepts tab focus when in ‘Text/List focus mode’.
Qt.WheelFocus
like Qt::StrongFocus plus the widget accepts focus by using the mouse wheel.
Qt.NoFocus
the widget does not accept focus.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TabFocusBehavior#
This enum type provides different focus behaviors for tab navigation.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoTabFocus
iterate nothing.
Qt.TabFocusTextControls
iterate text controls and widgets.
Qt.TabFocusListControls
iterate list controls and widgets.
Qt.TabFocusAllControls
iterate all controls and widgets.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.SortOrder#
This enum describes how the items in a widget are sorted.
Constant
Description
Qt.AscendingOrder
The items are sorted ascending e.g. starts with ‘AAA’ ends with ‘ZZZ’ in Latin-1 locales
Qt.DescendingOrder
The items are sorted descending e.g. starts with ‘ZZZ’ ends with ‘AAA’ in Latin-1 locales
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.SplitBehaviorFlags#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum specifies how the split() functions should behave with respect to empty strings.
Constant
Description
Qt.KeepEmptyParts
If a field is empty, keep it in the result.
Qt.SkipEmptyParts
If a field is empty, don’t include it in the result.
See also
split()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TileRule#
This enum describes how to repeat or stretch the parts of an image when drawing.
Constant
Description
Qt.StretchTile
Scale the image to fit to the available area.
Qt.RepeatTile
Repeat the image until there is no more space. May crop the last image.
Qt.RoundTile
Similar to Repeat, but scales the image down to ensure that the last tile is not cropped.
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.AlignmentFlag#
(inherits enum.IntFlag) This enum type is used to describe alignment. It contains horizontal and vertical flags that can be combined to produce the required effect.
The TextElideMode enum can also be used in many situations to fine-tune the appearance of aligned text.
The horizontal flags are:
Constant
Description
Qt.AlignLeft
Aligns with the left edge.
Qt.AlignRight
Aligns with the right edge.
Qt.AlignHCenter
Centers horizontally in the available space.
Qt.AlignJustify
Justifies the text in the available space.
The vertical flags are:
Constant
Description
Qt.AlignTop
Aligns with the top.
Qt.AlignBottom
Aligns with the bottom.
Qt.AlignVCenter
Centers vertically in the available space.
Qt.AlignBaseline
Aligns with the baseline.
You can use only one of the horizontal flags at a time. There is one two-dimensional flag:
Constant
Description
Qt.AlignCenter
Centers in both dimensions.
You can use at most one horizontal and one vertical flag at a time. Qt::AlignCenter counts as both horizontal and vertical.
Three enum values are useful in applications that can be run in right-to-left mode:
Constant
Description
Qt.AlignAbsolute
If the widget’s layout direction is
RightToLeft(instead ofLeftToRight, the default), Qt::AlignLeft refers to the right edge and Qt::AlignRight to the left edge. This is normally the desired behavior. If you want Qt::AlignLeft to always mean “left” and Qt::AlignRight to always mean “right”, combine the flag with Qt::AlignAbsolute.Qt.AlignLeading
Synonym for Qt::AlignLeft.
Qt.AlignTrailing
Synonym for Qt::AlignRight.
Masks:
Constant
Description
Qt.AlignHorizontal_Mask
Qt.AlignVertical_Mask
Conflicting combinations of flags have undefined meanings.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TextFlag#
(inherits enum.IntFlag) This enum type is used to define some modifier flags. Some of these flags only make sense in the context of printing:
Constant
Description
Qt.TextSingleLine
Treats all whitespace as spaces and prints just one line.
Qt.TextDontClip
If it’s impossible to stay within the given bounds, it prints outside.
Qt.TextExpandTabs
Makes the U+0009 (ASCII tab) character move to the next tab stop.
Qt.TextShowMnemonic
Displays the string “&P” as P For an ampersand, use “&&”.
Qt.TextWordWrap
Breaks lines at appropriate points, e.g. at word boundaries.
Qt.TextWrapAnywhere
Breaks lines anywhere, even within words.
Qt.TextHideMnemonic
Same as Qt::TextShowMnemonic but doesn’t draw the underlines.
Qt.TextDontPrint
Treat this text as “hidden” and don’t print it.
Qt.TextIncludeTrailingSpaces
When this option is set, QTextLine::naturalTextWidth() and QTextLine::naturalTextRect() will return a value that includes the width of trailing spaces in the text; otherwise this width is excluded.
Qt.TextJustificationForced
Ensures that text lines are justified.
You can use as many modifier flags as you want, except that Qt::TextSingleLine and Qt::TextWordWrap cannot be combined.
Flags that are inappropriate for a given use are generally ignored.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TextElideMode#
This enum specifies where the ellipsis should appear when displaying texts that don’t fit:
Constant
Description
Qt.ElideLeft
The ellipsis should appear at the beginning of the text.
Qt.ElideRight
The ellipsis should appear at the end of the text.
Qt.ElideMiddle
The ellipsis should appear in the middle of the text.
Qt.ElideNone
Ellipsis should NOT appear in the text. When passed to functions such as QFontMetrics::elidedText(), this will cause the full string to return unless the text contains multi-length variants. Elision in this case must be done by clipping to the component width.
Qt::ElideMiddle is normally the most appropriate choice for URLs (e.g., “ http://bugreports.qt…/QTWEBSITE-13/ “), whereas Qt::ElideRight is appropriate for other strings (e.g., “ Deploying Applications on Ma… “).
See also
AlignmentFlagelideMode
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.WhiteSpaceMode#
This enum describes the types of whitespace mode that are used by the QTextDocument class to meet the requirements of different kinds of textual information.
Constant
Description
Qt.WhiteSpaceNormal
The whitespace mode used to display normal word wrapped text in paragraphs.
Qt.WhiteSpacePre
A preformatted text mode in which whitespace is reproduced exactly.
Qt.WhiteSpaceNoWrap
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.HitTestAccuracy#
This enum contains the types of accuracy that can be used by the QTextDocument class when testing for mouse clicks on text documents.
Constant
Description
Qt.ExactHit
The point at which input occurred must coincide exactly with input-sensitive parts of the document.
Qt.FuzzyHit
The point at which input occurred can lie close to input-sensitive parts of the document.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.WindowType#
(inherits enum.IntFlag) This enum type is used to specify various window-system properties for the widget. They are fairly unusual but necessary in a few cases. Some of these flags depend on whether the underlying window manager supports them.
The main types are
Constant
Description
Qt.Widget
This is the default type for QWidget. Widgets of this type are child widgets if they have a parent, and independent windows if they have no parent. See also Qt::Window and Qt::SubWindow.
Qt.Window
Indicates that the widget is a window, usually with a window system frame and a title bar, irrespective of whether the widget has a parent or not. Note that it is not possible to unset this flag if the widget does not have a parent.
Qt.Dialog
Indicates that the widget is a window that should be decorated as a dialog (i.e., typically no maximize or minimize buttons in the title bar). This is the default type for QDialog. If you want to use it as a modal dialog, it should be launched from another window, or have a parent and used with the QWidget::windowModality property. If you make it modal, the dialog will prevent other top-level windows in the application from getting any input. We refer to a top-level window that has a parent as a secondary window.
Qt.Sheet
Indicates that the window is a sheet on macOS. Since using a sheet implies window modality, the recommended way is to use QWidget::setWindowModality(), or QDialog::open(), instead.
Qt.Drawer
Indicates that the widget is a drawer on macOS. This feature is obsolete. Setting the flag has no effect.
Qt.Popup
Indicates that the widget is a pop-up top-level window, i.e. that it is modal, but has a window system frame appropriate for pop-up menus.
Qt.Tool
Indicates that the widget is a tool window. A tool window is often a small window with a smaller than usual title bar and decoration, typically used for collections of tool buttons. If there is a parent, the tool window will always be kept on top of it. If there isn’t a parent, you may consider using Qt::WindowStaysOnTopHint as well. If the window system supports it, a tool window can be decorated with a somewhat lighter frame. It can also be combined with Qt::FramelessWindowHint. On macOS, tool windows correspond to the NSPanel class of windows. This means that the window lives on a level above normal windows making it impossible to put a normal window on top of it. By default, tool windows will disappear when the application is inactive. This can be controlled by the
WA_MacAlwaysShowToolWindowattribute.Qt.ToolTip
Indicates that the widget is a tooltip. This is used internally to implement tooltips.
Qt.SplashScreen
Indicates that the window is a splash screen. This is the default type for QSplashScreen.
Qt.SubWindow
Indicates that this widget is a sub-window, such as a QMdiSubWindow widget.
Qt.ForeignWindow
Indicates that this window object is a handle representing a native platform window created by another process or by manually using native code.
Qt.CoverWindow
Indicates that the window represents a cover window, which is shown when the application is minimized on some platforms.
There are also a number of flags which you can use to customize the appearance of top-level windows. These have no effect on other windows:
Constant
Description
Qt.MSWindowsFixedSizeDialogHint
Gives the window a thin dialog border on Windows. This style is traditionally used for fixed-size dialogs.
Note
The use of this flag is not recommended in multi-monitor environments. This is because the system will enforce that the window maintains its native size when moving it across screens. This is particularly undesirable when using monitors with different resolutions.
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
Qt.MSWindowsOwnDC |
Gives the window its own display context on Windows. |
Qt.BypassWindowManagerHint |
This flag can be used to indicate to the platform plugin that “all” window manager protocols should be disabled. This flag will behave different depending on what operating system the application is running on and what window manager is running. The flag can be used to get a native window with no configuration set. |
Qt.X11BypassWindowManagerHint |
Bypass the window manager completely. This results in a borderless window that is not managed at all (i.e., no keyboard input unless you call QWidget::activateWindow() manually). |
Qt.FramelessWindowHint |
Produces a borderless window. |
On X11, the result of the flag is dependent on the window manager and its ability to understand Motif and/or NETWM hints. Most existing modern window managers can handle this.
Note
If the window manager relies on the frame to interactively manipulate the window, the user can no longer move or resize the window via the window system, but this side effect should not be relied on. To produce a fixed size window that can not be resized, please set QWindow::setMinimumSize() and QWindow::setMaximumSize() to the same size.
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
Qt.NoDropShadowWindowHint |
Disables window drop shadow on supporting platforms. |
The CustomizeWindowHint flag is used to enable customization of the window controls. This flag must be set to allow the WindowTitleHint, WindowSystemMenuHint, WindowMinimizeButtonHint, WindowMaximizeButtonHint and WindowCloseButtonHint flags to be changed.
Constant
Description
Qt.CustomizeWindowHint
Turns off the default window title hints.
Qt.WindowTitleHint
Gives the window a title bar.
Qt.WindowSystemMenuHint
Adds a window system menu, and possibly a close button (for example on Mac). If you need to hide or show a close button, it is more portable to use
WindowCloseButtonHint.Qt.WindowMinimizeButtonHint
Adds a minimize button. On some platforms this implies Qt::WindowSystemMenuHint for it to work.
Qt.WindowMaximizeButtonHint
Adds a maximize button. On some platforms this implies Qt::WindowSystemMenuHint for it to work.
Qt.WindowMinMaxButtonsHint
Adds a minimize and a maximize button. On some platforms this implies Qt::WindowSystemMenuHint for it to work.
Qt.WindowCloseButtonHint
Adds a close button. On some platforms this implies Qt::WindowSystemMenuHint for it to work.
Qt.WindowContextHelpButtonHint
Adds a context help button to dialogs. On some platforms this implies Qt::WindowSystemMenuHint for it to work.
Qt.MacWindowToolBarButtonHint
On macOS adds a tool bar button (i.e., the oblong button that is on the top right of windows that have toolbars).
Qt.WindowFullscreenButtonHint
On macOS adds a fullscreen button.
Qt.BypassGraphicsProxyWidget
Prevents the window and its children from automatically embedding themselves into a QGraphicsProxyWidget if the parent widget is already embedded. You can set this flag if you want your widget to always be a toplevel widget on the desktop, regardless of whether the parent widget is embedded in a scene or not.
Qt.WindowShadeButtonHint
Adds a shade button in place of the minimize button if the underlying window manager supports it.
Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint
Informs the window system that the window should stay on top of all other windows. Note that on some window managers on X11 you also have to pass Qt::X11BypassWindowManagerHint for this flag to work correctly.
Qt.WindowStaysOnBottomHint
Informs the window system that the window should stay on bottom of all other windows.
Note
On X11, this hint will work only in window managers that support _NET_WM_STATE_BELOW atom. If a window always on the bottom has a parent, the parent will also be left on the bottom. This window hint is currently not implemented for macOS.
Note
On Windows, this will work only for frameless or full-screen windows.
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
Qt.WindowTransparentForInput |
Informs the window system that this window is used only for output (displaying something) and does not take input. Therefore input events should pass through as if it wasn’t there. |
Qt.WindowOverridesSystemGestures |
Informs the window system that this window implements its own set of gestures and that system level gestures, like for instance three-finger desktop switching, should be disabled. |
Qt.WindowDoesNotAcceptFocus |
Informs the window system that this window should not receive the input focus. |
Qt.MaximizeUsingFullscreenGeometryHint |
Informs the window system that when maximizing the window it should use as much of the available screen geometry as possible, including areas that may be covered by system UI such as status bars or application launchers. This may result in the window being placed under these system UIs, but does not guarantee it, depending on whether or not the platform supports it. When the flag is enabled the user is responsible for taking QScreen::availableGeometry() into account, so that any UI elements in the application that require user interaction are not covered by system UI. |
Qt.WindowType_Mask |
A mask for extracting the window type part of the window flags. |
See also
windowFlagsWindow Flags Example
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.WindowState#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum type is used to specify the current state of a top-level window.
The states are
Constant
Description
Qt.WindowNoState
The window has no state set (in normal state).
Qt.WindowMinimized
The window is minimized (i.e. iconified).
Qt.WindowMaximized
The window is maximized with a frame around it.
Qt.WindowFullScreen
The window fills the entire screen without any frame around it.
Qt.WindowActive
The window is the active window, i.e. it has keyboard focus.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ApplicationState#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum type is used to specify the current state of the application.
The states are
Constant
Description
Qt.ApplicationSuspended
The application is about to suspend. When entering this state, the application should save its state, cease all activities, and be prepared for code execution to stop. While suspended, the application can be killed at any time without further warnings (e.g. when low memory forces the OS to purge suspended applications).
Qt.ApplicationHidden
The application is hidden and runs in the background. This is the normal state for applications that need to do background processing, like playing music, while the user interacts with other applications. The application should free up all graphical resources when entering this state.
Qt.ApplicationInactive
The application is visible, but not selected to be in front. On desktop platforms, this typically means that the user activated another application. On mobile platforms, it is more common to enter this state when the OS is interrupting the user with e.g. incoming calls or SMS-messages. While in this state, consider reducing CPU-intensive tasks.
Qt.ApplicationActive
The application is visible and selected to be in front.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ScreenOrientation#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum type specifies the various orientations a screen might have.
Constant
Description
Qt.PrimaryOrientation
The display’s primary orientation.
Qt.LandscapeOrientation
Landscape orientation, display width is greater than display height.
Qt.PortraitOrientation
Portrait orientation, display height is greater than display width, rotated 90 degree clockwise relative to landscape.
Qt.InvertedLandscapeOrientation
Inverted landscape orientation, rotated 180 degrees relative to landscape.
Qt.InvertedPortraitOrientation
Inverted portrait orientation, rotated 180 degrees relative to portrait.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.WidgetAttribute#
This enum type is used to specify various widget attributes. Attributes are set and cleared with QWidget::setAttribute(), and queried with QWidget::testAttribute(), although some have special convenience functions which are mentioned below.
Constant
Description
Qt.WA_AcceptDrops
Allows data from drag and drop operations to be dropped onto the widget (see QWidget::setAcceptDrops()).
Qt.WA_AlwaysShowToolTips
Enables tooltips for inactive windows.
Qt.WA_CustomWhatsThis
Indicates that the widget wants to continue operating normally in “What’s This?” mode. This is set by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_DeleteOnClose
Makes Qt delete this widget when the widget has accepted the close event (see QWidget::closeEvent()).
Qt.WA_Disabled
Indicates that the widget is disabled, i.e. it does not receive any mouse or keyboard events. There is also a getter functions QWidget::isEnabled(). This is set/cleared by the Qt kernel.
Qt.WA_DontShowOnScreen
Indicates that the widget is hidden or is not a part of the viewable Desktop.
Qt.WA_ForceDisabled
Indicates that the widget is explicitly disabled, i.e. it will remain disabled even when all its ancestors are set to the enabled state. This implies WA_Disabled. This is set/cleared by QWidget::setEnabled() and QWidget::setDisabled().
Qt.WA_ForceUpdatesDisabled
Indicates that updates are explicitly disabled for the widget; i.e. it will remain disabled even when all its ancestors are set to the updates-enabled state. This implies WA_UpdatesDisabled. This is set/cleared by QWidget::setUpdatesEnabled().
Qt.WA_Hover
Forces Qt to generate paint events when the mouse enters or leaves the widget. This feature is typically used when implementing custom styles.
Qt.WA_InputMethodEnabled
Enables input methods for Asian languages. Must be set when creating custom text editing widgets.
Qt.WA_KeyboardFocusChange
Set on a toplevel window when the users changes focus with the keyboard (tab, backtab, or shortcut).
Qt.WA_KeyCompression
Enables key event compression if set, and disables it if not set. By default key compression is off, so widgets receive one key press event for each key press (or more, since autorepeat is usually on). If you turn it on and your program doesn’t keep up with key input, Qt may try to compress key events so that more than one character can be processed in each event. For example, a word processor widget might receive 2, 3 or more characters in each QKeyEvent::text(), if the layout recalculation takes too long for the CPU. If a widget supports multiple character unicode input, it is always safe to turn the compression on. Qt performs key event compression only for printable characters.
Modifierkeys, cursor movement keys, function keys and miscellaneous action keys (e.g. Escape, Enter, Backspace, PrintScreen) will stop key event compression, even if there are more compressible key events available. Platforms other than Mac and X11 do not support this compression, in which case turning it on will have no effect. This is set/cleared by the widget’s author.Qt.WA_LayoutOnEntireRect
Indicates that the widget wants QLayout to operate on the entire QWidget::rect(), not only on QWidget::contentsRect(). This is set by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_LayoutUsesWidgetRect
Ignore the layout item rect from the style when laying out this widget with QLayout.
Qt.WA_MacOpaqueSizeGrip
Indicates that the native size grip should be opaque instead of transparent (the default). This attribute is only applicable to macOS and is set by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_MacShowFocusRect
Indicates that this widget should get a QFocusFrame around it. Some widgets draw their own focus halo regardless of this attribute. Not that the QWidget::focusPolicy also plays the main role in whether something is given focus or not, this only controls whether or not this gets the focus frame. This attribute is only applicable to macOS.
Qt.WA_MacNormalSize
Indicates the widget should have the normal size for widgets in macOS. This attribute is only applicable to macOS.
Qt.WA_MacSmallSize
Indicates the widget should have the small size for widgets in macOS. This attribute is only applicable to macOS.
Qt.WA_MacMiniSize
Indicates the widget should have the mini size for widgets in macOS. This attribute is only applicable to macOS.
Qt.WA_Mapped
Indicates that the widget is mapped on screen. This is set/cleared by the Qt kernel.
Qt.WA_MouseNoMask
Makes the widget receive mouse events for the entire widget regardless of the currently set mask, overriding QWidget::setMask(). This is not applicable for top-level windows.
Qt.WA_MouseTracking
Indicates that the widget has mouse tracking enabled. See QWidget::mouseTracking.
Qt.WA_Moved
Indicates that the widget has an explicit position. This is set/cleared by QWidget::move() and by QWidget::setGeometry().
Qt.WA_NoChildEventsForParent
Indicates that the widget does not want ChildAdded or ChildRemoved events sent to its parent. This is rarely necessary but can help to avoid automatic insertion widgets like splitters and layouts. This is set by a widget’s author.
Qt.WA_NoChildEventsFromChildren
Indicates that the widget does not want to receive ChildAdded or ChildRemoved events sent from its children. This is set by a widget’s author.
Qt.WA_NoMouseReplay
Used for pop-up widgets. Indicates that the most recent mouse press event should not be replayed when the pop-up widget closes. The flag is set by the widget’s author and cleared by the Qt kernel every time the widget receives a new mouse event.
Qt.WA_NoMousePropagation
Prohibits mouse events from being propagated to the widget’s parent. This attribute is disabled by default.
Qt.WA_TransparentForMouseEvents
When enabled, this attribute disables the delivery of mouse events to the widget and its children. Mouse events are delivered to other widgets as if the widget and its children were not present in the widget hierarchy; mouse clicks and other events effectively “pass through” them. This attribute is disabled by default.
Qt.WA_NoSystemBackground
Indicates that the widget has no background, i.e. when the widget receives paint events, the background is not automatically repainted. Note: Unlike WA_OpaquePaintEvent, newly exposed areas are never filled with the background (e.g., after showing a window for the first time the user can see “through” it until the application processes the paint events). This flag is set or cleared by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_OpaquePaintEvent
Indicates that the widget paints all its pixels when it receives a paint event. Thus, it is not required for operations like updating, resizing, scrolling and focus changes to erase the widget before generating paint events. The use of WA_OpaquePaintEvent provides a small optimization by helping to reduce flicker on systems that do not support double buffering and avoiding computational cycles necessary to erase the background prior to painting. Note: Unlike WA_NoSystemBackground, WA_OpaquePaintEvent makes an effort to avoid transparent window backgrounds. This flag is set or cleared by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_OutsideWSRange
Indicates that the widget is outside the valid range of the window system’s coordinate system. A widget outside the valid range cannot be mapped on screen. This is set/cleared by the Qt kernel.
Qt.WA_PaintOnScreen
Indicates that the widget wants to draw directly onto the screen. Widgets with this attribute set do not participate in composition management, i.e. they cannot be semi-transparent or shine through semi-transparent overlapping widgets. Note: This flag is only supported on X11 and it disables double buffering. On Qt for Embedded Linux, the flag only works when set on a top-level widget and it relies on support from the active screen driver. This flag is set or cleared by the widget’s author. To render outside of Qt’s paint system, e.g., if you require native painting primitives, you need to reimplement QWidget::paintEngine() to return 0 and set this flag.
Qt.WA_PaintUnclipped
Makes all painters operating on this widget unclipped. Children of this widget or other widgets in front of it do not clip the area the painter can paint on. This flag is only supported for widgets with the WA_PaintOnScreen flag set. The preferred way to do this in a cross platform way is to create a transparent widget that lies in front of the other widgets.
Qt.WA_PendingMoveEvent
Indicates that a move event is pending, e.g., when a hidden widget was moved. This flag is set or cleared by the Qt kernel.
Qt.WA_PendingResizeEvent
Indicates that a resize event is pending, e.g., when a hidden widget was resized. This flag is set or cleared by the Qt kernel.
Qt.WA_QuitOnClose
Indicates that the widget should be taken into account when deciding whether to quit the application when the last window is closed. This behavior can be modified with the QGuiApplication::quitOnLastWindowClosed property. By default this attribute is set for all widgets of type
Window.Qt.WA_Resized
Indicates that the widget has an explicit size. This flag is set or cleared by QWidget::resize() and QWidget::setGeometry().
Qt.WA_RightToLeft
Indicates that the layout direction for the widget is right to left.
Qt.WA_SetCursor
Indicates that the widget has a cursor of its own. This flag is set or cleared by QWidget::setCursor() and QWidget::unsetCursor().
Qt.WA_SetFont
Indicates that the widget has a font of its own. This flag is set or cleared by QWidget::setFont().
Qt.WA_SetPalette
Indicates that the widget has a palette of its own. This flag is set or cleared by QWidget::setPalette().
Qt.WA_SetStyle
Indicates that the widget has a style of its own. This flag is set or cleared by QWidget::setStyle().
Qt.WA_ShowModal
This attribute has been deprecated. Use QWidget::windowModality instead.
Qt.WA_StaticContents
Indicates that the widget contents are north-west aligned and static. On resize, such a widget will receive paint events only for parts of itself that are newly visible. This flag is set or cleared by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_StyleSheet
Indicates that the widget is styled using a style sheet. WA_StyleSheet is set whenever a widget is subject to a style sheet, even if the style sheet did not affect the widget appearance.
Qt.WA_StyleSheetTarget
Indicates that the widget appearance was modified by a style sheet. WA_StyleSheet will also be set. This value was introduced in Qt 5.12.
Qt.WA_TabletTracking
Indicates that the widget has tablet tracking enabled. See QWidget::tabletTracking.
Qt.WA_TranslucentBackground
Indicates that the widget should have a translucent background, i.e., any non-opaque regions of the widgets will be translucent because the widget will have an alpha channel. Setting this flag causes WA_NoSystemBackground to be set. On Windows the widget also needs the
FramelessWindowHintwindow flag to be set. This flag is set or cleared by the widget’s author. As of Qt 5.0, toggling this attribute after the widget has been shown is not uniformly supported across platforms. When translucent background is desired, set the attribute early when creating the widget, and avoid altering it afterwards.Qt.WA_UnderMouse
Indicates that the widget is under the mouse cursor. The value is not updated correctly during drag and drop operations. There is also a getter function, QWidget::underMouse(). This flag is set or cleared by the Qt kernel.
Qt.WA_UpdatesDisabled
Indicates that updates are blocked (including the system background). This flag is set or cleared by the Qt kernel. Warning: This flag must never be set or cleared by the widget’s author.
Qt.WA_WindowModified
Indicates that the window is marked as modified. On some platforms this flag will do nothing, on others (including macOS and Windows) the window will take a modified appearance. This flag is set or cleared by QWidget::setWindowModified().
Qt.WA_WindowPropagation
Makes a toplevel window inherit font, palette and locale from its parent.
Qt.WA_MacAlwaysShowToolWindow
On macOS, show the tool window even when the application is not active. By default, all tool windows are hidden when the application is inactive.
Qt.WA_SetLocale
Indicates the locale should be taken into consideration in the widget.
Qt.WA_StyledBackground
Indicates the widget should be drawn using a styled background.
Qt.WA_ShowWithoutActivating
Show the widget without making it active.
Qt.WA_NativeWindow
Indicates that a native window is created for the widget. Enabling this flag will also force a native window for the widget’s ancestors unless Qt::WA_DontCreateNativeAncestors is set.
Qt.WA_DontCreateNativeAncestors
Indicates that the widget’s ancestors are kept non-native even though the widget itself is native.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeDesktop
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_DESKTOP to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeDock
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_DOCK to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeToolBar
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_TOOLBAR to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for QToolBar.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeMenu
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_MENU to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for QMenu when torn-off.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeUtility
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_UTILITY to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for the
Toolwindow type.Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeSplash
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_SPLASH to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for the
SplashScreenwindow type.Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeDialog
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_DIALOG to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for the
DialogandSheetwindow types.Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeDropDownMenu
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_DROPDOWN_MENU to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for QMenu objects added to a QMenuBar.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypePopupMenu
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_POPUP_MENU to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for QMenu.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeToolTip
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_TOOLTIP to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for the
ToolTipwindow type.Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeNotification
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_NOTIFICATION to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeCombo
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_COMBO to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute for the QComboBox pop-up.
Qt.WA_X11NetWmWindowTypeDND
Adds _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_DND to the window’s _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE X11 window property. See http://standards.freedesktop.org/wm-spec/ for more details. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms. Note: Qt automatically sets this attribute on the feedback widget used during a drag.
Qt.WA_AcceptTouchEvents
Allows touch events (see QTouchEvent) to be sent to the widget. Must be set on all widgets that can handle touch events. Without this attribute set, events from a touch device will be sent as mouse events.
Qt.WA_TouchPadAcceptSingleTouchEvents
Allows touchpad single touch events to be sent to the widget.
Qt.WA_X11DoNotAcceptFocus
Asks the window manager to not give focus to this top level window. This attribute has no effect on non-X11 platforms.
Qt.WA_AlwaysStackOnTop
Forces QOpenGLWidget and QQuickWidget to be drawn last, on top of other widgets. Ignored for other type of widgets. Setting this attribute breaks the stacking order, but allows having a semi-transparent OpenGL widget with other widgets visible underneath. It is strongly recommended to call update() on the widget’s top-level window after enabling or disabling this attribute.
Qt.WA_ContentsMarginsRespectsSafeArea
A QWidget respects the safe area margins of a window by incorporating the margins into its contents’ margins by default. This means, that a QLayout will use the content area of a widget for its layout, unless the Qt::WA_LayoutOnEntireRect attribute is set. This along with a contents margin of 0 can be used on the actual layout, to allow for example a background image to underlay the status bar and other system areas on an iOS device, while still allowing child widgets of that background to be inset based on the safe area.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ApplicationAttribute#
This enum describes attributes that change the behavior of application-wide features. These are enabled and disabled using QCoreApplication::setAttribute(), and can be tested for with QCoreApplication::testAttribute().
Constant
Description
Qt.AA_DontShowIconsInMenus
Actions with the Icon property won’t be shown in any menus unless specifically set by the QAction::iconVisibleInMenu property. Menus that are currently open or menus already created in the native macOS menubar may not pick up a change in this attribute. Changes in the QAction::iconVisibleInMenu property will always be picked up.
Qt.AA_DontShowShortcutsInContextMenus
Actions with the Shortcut property won’t be shown in any shortcut menus unless specifically set by the QAction::shortcutVisibleInContextMenu property. This value was added in Qt 5.10, and is by default based on the value reported by QStyleHints::showShortcutsInContextMenus(). To override the default behavior, set the style hint before
QCoreApplicationhas been instantiated, or set this attribute afterQCoreApplicationhas been instantiated.Qt.AA_NativeWindows
Ensures that widgets have native windows.
Qt.AA_DontCreateNativeWidgetSiblings
Ensures that siblings of native widgets stay non-native unless specifically set by the
WA_NativeWindowattribute.Qt.AA_PluginApplication
Indicates that Qt is used to author a plugin. Depending on the operating system, it suppresses specific initializations that do not necessarily make sense in the plugin case. For example on macOS, this includes avoiding loading our nib for the main menu and not taking possession of the native menu bar. Setting this attribute to true will also set the AA_DontUseNativeMenuBar attribute to true. It also disables native event filters. This attribute must be set before QGuiApplication constructed. This value was added in Qt 5.7.
Qt.AA_DontUseNativeMenuBar
All menubars created while this attribute is set to true won’t be used as a native menubar (e.g, the menubar at the top of the main screen on macOS).
Qt.AA_MacDontSwapCtrlAndMeta
Keyboard shortcuts on Apple platforms are typically based on the Command (or Cmd) keyboard modifier, represented by the ⌘ symbol. For example, the ‘Copy’ action is Command+C (⌘+C). To ease cross platform development Qt will by default remap Command to the
ControlModifier, to align with other platforms. This allows creating keyboard shortcuts such as “Ctrl+J”, which on macOS will then map to Command+J, as expected by macOS users. The actual Control (or Ctrl) modifier on Apple platforms, represented by ⌃, is mapped toMetaModifier.
When this attribute is true Qt will not do the remapping, and pressing the Command modifier will result in MetaModifier , while pressing the Control modifier will result in ControlModifier .
Note that the QKeySequence::StandardKey sequences will always be based on the same modifier (i.e., QKeySequence::Copy will be Command+C regardless of the value set), but what is output for QKeySequence::toString() will be different.
Constant
Description
Qt.AA_Use96Dpi
Assume the screen has a resolution of 96 DPI rather than using the OS-provided resolution. This will cause font rendering to be consistent in pixels-per-point across devices rather than defining 1 point as 1/72 inch.
Qt.AA_SynthesizeTouchForUnhandledMouseEvents
All mouse events that are not accepted by the application will be translated to touch events instead.
Qt.AA_SynthesizeMouseForUnhandledTouchEvents
All touch events that are not accepted by the application will be translated to left button mouse events instead. This attribute is enabled by default.
Qt.AA_ForceRasterWidgets
Make top-level widgets use pure raster surfaces, and do not support non-native GL-based child widgets.
Qt.AA_UseDesktopOpenGL
Forces the usage of desktop OpenGL (for example, opengl32.dll or libGL.so) on platforms that use dynamic loading of the OpenGL implementation. This attribute must be set before QGuiApplication is constructed. This value was added in Qt 5.3.
Qt.AA_UseOpenGLES
Forces the usage of OpenGL ES 2.0 or higher on platforms that use dynamic loading of the OpenGL implementation. This attribute must be set before QGuiApplication is constructed. This value was added in Qt 5.3.
Qt.AA_UseSoftwareOpenGL
Forces the usage of a software based OpenGL implementation on platforms that use dynamic loading of the OpenGL implementation. This will typically be a patched build of Mesa llvmpipe , providing OpenGL 2.1. The value may have no effect if no such OpenGL implementation is available. The default name of this library is
opengl32sw.dlland can be overridden by setting the environment variable QT_OPENGL_DLL. See the platform-specific pages, for instance Qt for Windows, for more information. This attribute must be set before QGuiApplication is constructed. This value was added in Qt 5.4.Qt.AA_ShareOpenGLContexts
Enables resource sharing between the OpenGL contexts used by classes like QOpenGLWidget and QQuickWidget. This allows sharing OpenGL resources, like textures, between QOpenGLWidget instances that belong to different top-level windows. This attribute must be set before QGuiApplication is constructed. This value was added in Qt 5.4.
Qt.AA_SetPalette
Indicates whether a palette was explicitly set on the QGuiApplication. This value was added in Qt 5.5.
Qt.AA_UseStyleSheetPropagationInWidgetStyles
By default, Qt Style Sheets disable regular QWidget palette and font propagation. When this flag is enabled, font and palette changes propagate as though the user had manually called the corresponding QWidget methods. See The Style Sheet Syntax - Inheritance for more details. This value was added in Qt 5.7.
Qt.AA_DontUseNativeDialogs
All dialogs created while this attribute is set to true won’t use the native dialogs provided by the platform. This value was added in Qt 5.7.
Qt.AA_SynthesizeMouseForUnhandledTabletEvents
All tablet events that are not accepted by the application will be translated to mouse events instead. This attribute is enabled by default. This value was added in Qt 5.7.
Qt.AA_CompressHighFrequencyEvents
Enables compression of certain frequent events. On the X11 windowing system, the default value is true, which means that
MouseMove,TouchUpdate, and changes in window size and position will be combined whenever they occur more frequently than the application handles them, so that they don’t accumulate and overwhelm the application later. On Windows 8 and above the default value is also true, but it only applies to touch events. Mouse and window events remain unaffected by this flag. On other platforms, the default is false. (In the future, the compression feature may be implemented across platforms.) You can test the attribute to see whether compression is enabled. If your application needs to handle all events with no compression, you can unset this attribute. Notice that input events from tablet devices will not be compressed. See AA_CompressTabletEvents if you want these to be compressed as well. This value was added in Qt 5.7.Qt.AA_CompressTabletEvents
Enables compression of input events from tablet devices. Notice that AA_CompressHighFrequencyEvents must be true for events compression to be enabled, and that this flag extends the former to tablet events. Currently supported on the X11 windowing system, Windows 8 and above. The default value is false. This value was added in Qt 5.10.
Qt.AA_DontCheckOpenGLContextThreadAffinity
When making a context current using QOpenGLContext, do not check that the
QObject thread affinityof the QOpenGLContext object is the same thread calling makeCurrent(). This value was added in Qt 5.8.Qt.AA_DisableShaderDiskCache
Disables caching of shader program binaries on disk. By default Qt Quick, QPainter’s OpenGL backend, and any application using QOpenGLShaderProgram with one of its addCacheableShaderFromSource overloads will employ a disk-based program binary cache in either the shared or per-process cache storage location, on systems that support glProgramBinary(). In the unlikely event of this being problematic, set this attribute to disable all disk-based caching of shaders.
Qt.AA_DisableSessionManager
Disables the QSessionManager. By default Qt will connect to a running session manager for a GUI application on supported platforms, use of a session manager may be redundant for system services. This attribute must be set before QGuiApplication is constructed. This value was added in 5.14
Qt.AA_DisableNativeVirtualKeyboard
When this attribute is set, the native on-screen virtual keyboard will not be shown automatically when a text input widget gains focus on a system without a physical keyboard. Currently supported on the Windows platform only. This value was added in 5.15
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ImageConversionFlag#
(inherits enum.Flag) The options marked “(default)” are set if no other values from the list are included (since the defaults are zero):
Color/Mono preference (ignored for QBitmap):
Constant
Description
Qt.AutoColor
(default) - If the image has depth 1 and contains only black and white pixels, the pixmap becomes monochrome.
Qt.ColorOnly
The pixmap is dithered/converted to the native display depth.
Qt.MonoOnly
The pixmap becomes monochrome. If necessary, it is dithered using the chosen dithering algorithm.
Dithering mode preference:
Constant
Description
Qt.DiffuseDither
(default) - A high-quality dither using error diffusion.
Qt.OrderedDither
A faster, ordered dither.
Qt.ThresholdDither
No dithering; closest color is used.
Dithering mode preference for 1-bit alpha masks:
Constant
Description
Qt.ThresholdAlphaDither
(default) - No dithering.
Qt.OrderedAlphaDither
A faster, ordered dither.
Qt.DiffuseAlphaDither
A high-quality dither using error diffusion.
Color matching versus dithering preference:
Constant
Description
Qt.PreferDither
Always dither images when converting to smaller color-spaces.
Qt.AvoidDither
Only dither to indexed formats if the source image uses more different colors than the size of the color table of the destination format.
Qt.AutoDither
(default) - Only dither when down-converting to 1 or 8-bit indexed formats.
Qt.NoOpaqueDetection
Do not check whether the image contains non-opaque pixels. Use this if you know that the image is semi-transparent and you want to avoid the overhead of checking the pixels in the image until a non-opaque pixel is found, or if you want the pixmap to retain an alpha channel for some other reason. If the image has no alpha channel this flag has no effect.
Qt.NoFormatConversion
Don’t do any format conversions on the image. Can be useful when converting a QImage to a QPixmap for a one-time rendering operation for example. Note that a QPixmap not in the preferred format will be much slower as a paint device.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.BGMode#
Background mode:
Constant
Description
Qt.TransparentMode
Qt.OpaqueMode
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.Key#
(inherits enum.IntEnum) The key names used by Qt.
Constant
Description
Qt.Key_Escape
Qt.Key_Tab
Qt.Key_Backtab
Qt.Key_Backspace
Qt.Key_Return
Qt.Key_Enter
Typically located on the keypad.
Qt.Key_Insert
Qt.Key_Delete
Qt.Key_Pause
The Pause/Break key (Note: Not related to pausing media)
Qt.Key_Print
Qt.Key_SysReq
Qt.Key_Clear
Corresponds to the Clear key on selected Apple keyboard models. On other systems it is commonly mapped to the numeric keypad key 5, when Num Lock is
off.Qt.Key_Home
Qt.Key_End
Qt.Key_Left
Qt.Key_Up
Qt.Key_Right
Qt.Key_Down
Qt.Key_PageUp
Qt.Key_PageDown
Qt.Key_Shift
Qt.Key_Control
On macOS, this corresponds to the Command keys.
Qt.Key_Meta
On macOS, this corresponds to the Control keys. On Windows keyboards, this key is mapped to the Windows key.
Qt.Key_Alt
Qt.Key_AltGr
On Windows, when the KeyDown event for this key is sent, the Ctrl+Alt modifiers are also set.
Qt.Key_CapsLock
Qt.Key_NumLock
Qt.Key_ScrollLock
Qt.Key_F1
Qt.Key_F2
Qt.Key_F3
Qt.Key_F4
Qt.Key_F5
Qt.Key_F6
Qt.Key_F7
Qt.Key_F8
Qt.Key_F9
Qt.Key_F10
Qt.Key_F11
Qt.Key_F12
Qt.Key_F13
Qt.Key_F14
Qt.Key_F15
Qt.Key_F16
Qt.Key_F17
Qt.Key_F18
Qt.Key_F19
Qt.Key_F20
Qt.Key_F21
Qt.Key_F22
Qt.Key_F23
Qt.Key_F24
Qt.Key_F25
Qt.Key_F26
Qt.Key_F27
Qt.Key_F28
Qt.Key_F29
Qt.Key_F30
Qt.Key_F31
Qt.Key_F32
Qt.Key_F33
Qt.Key_F34
Qt.Key_F35
Qt.Key_Super_L
Qt.Key_Super_R
Qt.Key_Menu
Qt.Key_Hyper_L
Qt.Key_Hyper_R
Qt.Key_Help
Qt.Key_Direction_L
Qt.Key_Direction_R
Qt.Key_Space
Qt.Key_Any
Qt.Key_Exclam
Qt.Key_QuoteDbl
Qt.Key_NumberSign
Qt.Key_Dollar
Qt.Key_Percent
Qt.Key_Ampersand
Qt.Key_Apostrophe
Qt.Key_ParenLeft
Qt.Key_ParenRight
Qt.Key_Asterisk
Qt.Key_Plus
Qt.Key_Comma
Qt.Key_Minus
Qt.Key_Period
Qt.Key_Slash
Qt.Key_0
Qt.Key_1
Qt.Key_2
Qt.Key_3
Qt.Key_4
Qt.Key_5
Qt.Key_6
Qt.Key_7
Qt.Key_8
Qt.Key_9
Qt.Key_Colon
Qt.Key_Semicolon
Qt.Key_Less
Qt.Key_Equal
Qt.Key_Greater
Qt.Key_Question
Qt.Key_At
Qt.Key_A
Qt.Key_B
Qt.Key_C
Qt.Key_D
Qt.Key_E
Qt.Key_F
Qt.Key_G
Qt.Key_H
Qt.Key_I
Qt.Key_J
Qt.Key_K
Qt.Key_L
Qt.Key_M
Qt.Key_N
Qt.Key_O
Qt.Key_P
Qt.Key_Q
Qt.Key_R
Qt.Key_S
Qt.Key_T
Qt.Key_U
Qt.Key_V
Qt.Key_W
Qt.Key_X
Qt.Key_Y
Qt.Key_Z
Qt.Key_BracketLeft
Qt.Key_Backslash
Qt.Key_BracketRight
Qt.Key_AsciiCircum
Qt.Key_Underscore
Qt.Key_QuoteLeft
Qt.Key_BraceLeft
Qt.Key_Bar
Qt.Key_BraceRight
Qt.Key_AsciiTilde
Qt.Key_nobreakspace
Qt.Key_exclamdown
Qt.Key_cent
Qt.Key_sterling
Qt.Key_currency
Qt.Key_yen
Qt.Key_brokenbar
Qt.Key_section
Qt.Key_diaeresis
Qt.Key_copyright
Qt.Key_ordfeminine
Qt.Key_guillemotleft
Qt.Key_notsign
Qt.Key_hyphen
Qt.Key_registered
Qt.Key_macron
Qt.Key_degree
Qt.Key_plusminus
Qt.Key_twosuperior
Qt.Key_threesuperior
Qt.Key_acute
Qt.Key_mu
Qt.Key_paragraph
Qt.Key_periodcentered
Qt.Key_cedilla
Qt.Key_onesuperior
Qt.Key_masculine
Qt.Key_guillemotright
Qt.Key_onequarter
Qt.Key_onehalf
Qt.Key_threequarters
Qt.Key_questiondown
Qt.Key_Agrave
Qt.Key_Aacute
Qt.Key_Acircumflex
Qt.Key_Atilde
Qt.Key_Adiaeresis
Qt.Key_Aring
Qt.Key_AE
Qt.Key_Ccedilla
Qt.Key_Egrave
Qt.Key_Eacute
Qt.Key_Ecircumflex
Qt.Key_Ediaeresis
Qt.Key_Igrave
Qt.Key_Iacute
Qt.Key_Icircumflex
Qt.Key_Idiaeresis
Qt.Key_ETH
Qt.Key_Ntilde
Qt.Key_Ograve
Qt.Key_Oacute
Qt.Key_Ocircumflex
Qt.Key_Otilde
Qt.Key_Odiaeresis
Qt.Key_multiply
Qt.Key_Ooblique
Qt.Key_Ugrave
Qt.Key_Uacute
Qt.Key_Ucircumflex
Qt.Key_Udiaeresis
Qt.Key_Yacute
Qt.Key_THORN
Qt.Key_ssharp
Qt.Key_division
Qt.Key_ydiaeresis
Qt.Key_Multi_key
Qt.Key_Codeinput
Qt.Key_SingleCandidate
Qt.Key_MultipleCandidate
Qt.Key_PreviousCandidate
Qt.Key_Mode_switch
Qt.Key_Kanji
Qt.Key_Muhenkan
Qt.Key_Henkan
Qt.Key_Romaji
Qt.Key_Hiragana
Qt.Key_Katakana
Qt.Key_Hiragana_Katakana
Qt.Key_Zenkaku
Qt.Key_Hankaku
Qt.Key_Zenkaku_Hankaku
Qt.Key_Touroku
Qt.Key_Massyo
Qt.Key_Kana_Lock
Qt.Key_Kana_Shift
Qt.Key_Eisu_Shift
Qt.Key_Eisu_toggle
Qt.Key_Hangul
Qt.Key_Hangul_Start
Qt.Key_Hangul_End
Qt.Key_Hangul_Hanja
Qt.Key_Hangul_Jamo
Qt.Key_Hangul_Romaja
Qt.Key_Hangul_Jeonja
Qt.Key_Hangul_Banja
Qt.Key_Hangul_PreHanja
Qt.Key_Hangul_PostHanja
Qt.Key_Hangul_Special
Qt.Key_Dead_Grave
Qt.Key_Dead_Acute
Qt.Key_Dead_Circumflex
Qt.Key_Dead_Tilde
Qt.Key_Dead_Macron
Qt.Key_Dead_Breve
Qt.Key_Dead_Abovedot
Qt.Key_Dead_Diaeresis
Qt.Key_Dead_Abovering
Qt.Key_Dead_Doubleacute
Qt.Key_Dead_Caron
Qt.Key_Dead_Cedilla
Qt.Key_Dead_Ogonek
Qt.Key_Dead_Iota
Qt.Key_Dead_Voiced_Sound
Qt.Key_Dead_Semivoiced_Sound
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowdot
Qt.Key_Dead_Hook
Qt.Key_Dead_Horn
Qt.Key_Dead_Stroke
Qt.Key_Dead_Abovecomma
Qt.Key_Dead_Abovereversedcomma
Qt.Key_Dead_Doublegrave
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowring
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowmacron
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowcircumflex
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowtilde
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowbreve
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowdiaeresis
Qt.Key_Dead_Invertedbreve
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowcomma
Qt.Key_Dead_Currency
Qt.Key_Dead_a
Qt.Key_Dead_A
Qt.Key_Dead_e
Qt.Key_Dead_E
Qt.Key_Dead_i
Qt.Key_Dead_I
Qt.Key_Dead_o
Qt.Key_Dead_O
Qt.Key_Dead_u
Qt.Key_Dead_U
Qt.Key_Dead_Small_Schwa
Qt.Key_Dead_Capital_Schwa
Qt.Key_Dead_Greek
Qt.Key_Dead_Lowline
Qt.Key_Dead_Aboveverticalline
Qt.Key_Dead_Belowverticalline
Qt.Key_Dead_Longsolidusoverlay
Qt.Key_Back
Qt.Key_Forward
Qt.Key_Stop
Qt.Key_Refresh
Qt.Key_VolumeDown
Qt.Key_VolumeMute
Qt.Key_VolumeUp
Qt.Key_BassBoost
Qt.Key_BassUp
Qt.Key_BassDown
Qt.Key_TrebleUp
Qt.Key_TrebleDown
Qt.Key_MediaPlay
A key setting the state of the media player to play
Qt.Key_MediaStop
A key setting the state of the media player to stop
Qt.Key_MediaPrevious
Qt.Key_MediaNext
Qt.Key_MediaRecord
Qt.Key_MediaPause
A key setting the state of the media player to pause (Note: not the pause/break key)
Qt.Key_MediaTogglePlayPause
A key to toggle the play/pause state in the media player (rather than setting an absolute state)
Qt.Key_HomePage
Qt.Key_Favorites
Qt.Key_Search
Qt.Key_Standby
Qt.Key_OpenUrl
Qt.Key_LaunchMail
Qt.Key_LaunchMedia
Qt.Key_Launch0
Qt.Key_Launch1
Qt.Key_Launch2
Qt.Key_Launch3
Qt.Key_Launch4
Qt.Key_Launch5
Qt.Key_Launch6
Qt.Key_Launch7
Qt.Key_Launch8
Qt.Key_Launch9
Qt.Key_LaunchA
Qt.Key_LaunchB
Qt.Key_LaunchC
Qt.Key_LaunchD
Qt.Key_LaunchE
Qt.Key_LaunchF
Qt.Key_LaunchG
Qt.Key_LaunchH
Qt.Key_MonBrightnessUp
Qt.Key_MonBrightnessDown
Qt.Key_KeyboardLightOnOff
Qt.Key_KeyboardBrightnessUp
Qt.Key_KeyboardBrightnessDown
Qt.Key_PowerOff
Qt.Key_WakeUp
Qt.Key_Eject
Qt.Key_ScreenSaver
Qt.Key_WWW
Qt.Key_Memo
Qt.Key_LightBulb
Qt.Key_Shop
Qt.Key_History
Qt.Key_AddFavorite
Qt.Key_HotLinks
Qt.Key_BrightnessAdjust
Qt.Key_Finance
Qt.Key_Community
Qt.Key_AudioRewind
Qt.Key_BackForward
Qt.Key_ApplicationLeft
Qt.Key_ApplicationRight
Qt.Key_Book
Qt.Key_CD
Qt.Key_Calculator
Qt.Key_ToDoList
Qt.Key_ClearGrab
Qt.Key_Close
Qt.Key_Copy
Qt.Key_Cut
Qt.Key_Display
Qt.Key_DOS
Qt.Key_Documents
Qt.Key_Excel
Qt.Key_Explorer
Qt.Key_Game
Qt.Key_Go
Qt.Key_iTouch
Qt.Key_LogOff
Qt.Key_Market
Qt.Key_Meeting
Qt.Key_MenuKB
Qt.Key_MenuPB
Qt.Key_MySites
Qt.Key_News
Qt.Key_OfficeHome
Qt.Key_Option
Qt.Key_Paste
Qt.Key_Phone
Qt.Key_Calendar
Qt.Key_Reply
Qt.Key_Reload
Qt.Key_RotateWindows
Qt.Key_RotationPB
Qt.Key_RotationKB
Qt.Key_Save
Qt.Key_Send
Qt.Key_Spell
Qt.Key_SplitScreen
Qt.Key_Support
Qt.Key_TaskPane
Qt.Key_Terminal
Qt.Key_Tools
Qt.Key_Travel
Qt.Key_Video
Qt.Key_Word
Qt.Key_Xfer
Qt.Key_ZoomIn
Qt.Key_ZoomOut
Qt.Key_Away
Qt.Key_Messenger
Qt.Key_WebCam
Qt.Key_MailForward
Qt.Key_Pictures
Qt.Key_Music
Qt.Key_Battery
Qt.Key_Bluetooth
Qt.Key_WLAN
Qt.Key_UWB
Qt.Key_AudioForward
Qt.Key_AudioRepeat
Qt.Key_AudioRandomPlay
Qt.Key_Subtitle
Qt.Key_AudioCycleTrack
Qt.Key_Time
Qt.Key_Hibernate
Qt.Key_View
Qt.Key_TopMenu
Qt.Key_PowerDown
Qt.Key_Suspend
Qt.Key_ContrastAdjust
Qt.Key_TouchpadToggle
Qt.Key_TouchpadOn
Qt.Key_TouchpadOff
Qt.Key_MicMute
Qt.Key_Red
Qt.Key_Green
Qt.Key_Yellow
Qt.Key_Blue
Qt.Key_ChannelUp
Qt.Key_ChannelDown
Qt.Key_Guide
Qt.Key_Info
Qt.Key_Settings
Qt.Key_MicVolumeUp
Qt.Key_MicVolumeDown
Qt.Key_New
Qt.Key_Open
Qt.Key_Find
Qt.Key_Undo
Qt.Key_Redo
Qt.Key_MediaLast
Qt.Key_unknown
Qt.Key_Call
A key to answer or initiate a call (see Qt::Key_ToggleCallHangup for a key to toggle current call state)
Qt.Key_Camera
A key to activate the camera shutter. On Windows Runtime, the environment variable QT_QPA_ENABLE_CAMERA_KEYS must be set to receive the event.
Qt.Key_CameraFocus
A key to focus the camera. On Windows Runtime, the environment variable QT_QPA_ENABLE_CAMERA_KEYS must be set to receive the event.
Qt.Key_Context1
Qt.Key_Context2
Qt.Key_Context3
Qt.Key_Context4
Qt.Key_Flip
Qt.Key_Hangup
A key to end an ongoing call (see Qt::Key_ToggleCallHangup for a key to toggle current call state)
Qt.Key_No
Qt.Key_Select
Qt.Key_Yes
Qt.Key_ToggleCallHangup
A key to toggle the current call state (ie. either answer, or hangup) depending on current call state
Qt.Key_VoiceDial
Qt.Key_LastNumberRedial
Qt.Key_Execute
Qt.Key_Printer
Qt.Key_Play
Qt.Key_Sleep
Qt.Key_Zoom
Qt.Key_Exit
Qt.Key_Cancel
See also
key()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.KeyboardModifier#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum describes the modifier keys.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoModifier
No modifier key is pressed.
Qt.ShiftModifier
A Shift key on the keyboard is pressed.
Qt.ControlModifier
A Ctrl key on the keyboard is pressed.
Qt.AltModifier
An Alt key on the keyboard is pressed.
Qt.MetaModifier
A Meta key on the keyboard is pressed.
Qt.KeypadModifier
A keypad button is pressed.
Qt.GroupSwitchModifier
X11 only (unless activated on Windows by a command line argument). A Mode_switch key on the keyboard is pressed.
Note
On macOS, the ControlModifier value corresponds to the Command keys on the keyboard, and the MetaModifier value corresponds to the Control keys. The KeypadModifier value will also be set when an arrow key is pressed as the arrow keys are considered part of the keypad.
Note
On Windows Keyboards, Qt::MetaModifier and Key_Meta are mapped to the Windows key.
See also
MouseButton Modifier
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.Modifier#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum provides shorter names for the keyboard modifier keys supported by Qt.
Note
On macOS, the CTRL value corresponds to the Command keys on the keyboard, and the META value corresponds to the Control keys.
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
Qt.SHIFT |
The Shift keys provided on all standard keyboards. |
Qt.META |
The Meta keys. |
Qt.CTRL |
The Ctrl keys. |
Qt.ALT |
The normal Alt keys, but not keys like AltGr. |
See also
KeyboardModifier MouseButton
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ArrowType#
Constant
Description
Qt.NoArrow
Qt.UpArrow
Qt.DownArrow
Qt.LeftArrow
Qt.RightArrow
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.PenStyle#
This enum type defines the pen styles that can be drawn using QPainter. The styles are:
Qt::SolidLine
Qt::DashLine
Qt::DotLine
Qt::DashDotLine
Qt::DashDotDotLine
Qt::CustomDashLine
Constant
Description
Qt.NoPen
no line at all. For example, QPainter::drawRect() fills but does not draw any boundary line.
Qt.SolidLine
A plain line.
Qt.DashLine
Dashes separated by a few pixels.
Qt.DotLine
Dots separated by a few pixels.
Qt.DashDotLine
Alternate dots and dashes.
Qt.DashDotDotLine
One dash, two dots, one dash, two dots.
Qt.CustomDashLine
A custom pattern defined using QPainterPathStroker::setDashPattern().
See also
QPen
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.PenCapStyle#
This enum type defines the pen cap styles supported by Qt, i.e. the line end caps that can be drawn using QPainter.
Qt::SquareCap
Qt::FlatCap
Qt::RoundCap
Constant
Description
Qt.FlatCap
a square line end that does not cover the end point of the line.
Qt.SquareCap
a square line end that covers the end point and extends beyond it by half the line width.
Qt.RoundCap
a rounded line end.
See also
QPen
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.PenJoinStyle#
This enum type defines the pen join styles supported by Qt, i.e. which joins between two connected lines can be drawn using QPainter.
Qt::BevelJoin
Qt::MiterJoin
Qt::RoundJoin
Constant
Description
Qt.MiterJoin
The outer edges of the lines are extended to meet at an angle, and this area is filled.
Qt.BevelJoin
The triangular notch between the two lines is filled.
Qt.RoundJoin
A circular arc between the two lines is filled.
Qt.SvgMiterJoin
A miter join corresponding to the definition of a miter join in the SVG 1.2 Tiny specification.
See also
QPen
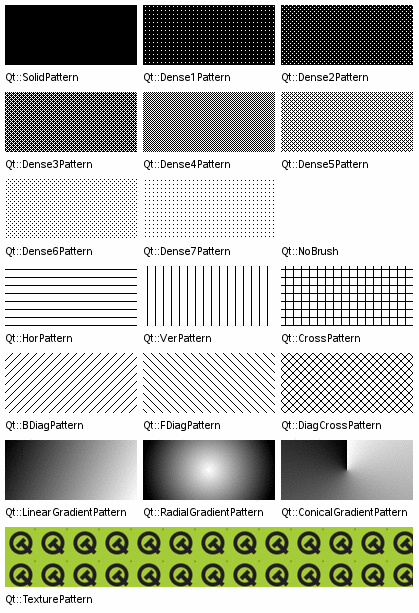
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.BrushStyle#
This enum type defines the brush styles supported by Qt, i.e. the fill pattern of shapes drawn using QPainter.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoBrush
No brush pattern.
Qt.SolidPattern
Uniform color.
Qt.Dense1Pattern
Extremely dense brush pattern.
Qt.Dense2Pattern
Very dense brush pattern.
Qt.Dense3Pattern
Somewhat dense brush pattern.
Qt.Dense4Pattern
Half dense brush pattern.
Qt.Dense5Pattern
Somewhat sparse brush pattern.
Qt.Dense6Pattern
Very sparse brush pattern.
Qt.Dense7Pattern
Extremely sparse brush pattern.
Qt.HorPattern
Horizontal lines.
Qt.VerPattern
Vertical lines.
Qt.CrossPattern
Crossing horizontal and vertical lines.
Qt.BDiagPattern
Backward diagonal lines.
Qt.FDiagPattern
Forward diagonal lines.
Qt.DiagCrossPattern
Crossing diagonal lines.
Qt.LinearGradientPattern
Linear gradient (set using a dedicated QBrush constructor).
Qt.ConicalGradientPattern
Conical gradient (set using a dedicated QBrush constructor).
Qt.RadialGradientPattern
Radial gradient (set using a dedicated QBrush constructor).
Qt.TexturePattern
Custom pattern (see QBrush::setTexture()).
See also
QBrush
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.SizeMode#
This enum is used by QPainter::drawRoundedRect() and QPainterPath::addRoundedRect() functions to specify the radii of rectangle corners with respect to the dimensions of the bounding rectangles specified.
Constant
Description
Qt.AbsoluteSize
Specifies the size using absolute measurements.
Qt.RelativeSize
Specifies the size relative to the bounding rectangle, typically using percentage measurements.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.UIEffect#
This enum describes the available UI effects.
By default, Qt will try to use the platform specific desktop settings for each effect. Use the QApplication::setDesktopSettingsAware() function (passing false as argument) to prevent this, and the QApplication::setEffectEnabled() to enable or disable a particular effect.
Note that all effects are disabled on screens running at less than 16-bit color depth.
Constant
Description
Qt.UI_AnimateMenu
Show animated menus.
Qt.UI_FadeMenu
Show faded menus.
Qt.UI_AnimateCombo
Show animated comboboxes.
Qt.UI_AnimateTooltip
Show tooltip animations.
Qt.UI_FadeTooltip
Show tooltip fading effects.
Qt.UI_AnimateToolBox
Reserved
See also
setDesktopSettingsAware()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.CursorShape#
This enum type defines the various cursors that can be used.
The standard arrow cursor is the default for widgets in a normal state.
Constant
Description
Qt.ArrowCursor
The standard arrow cursor.
Qt.UpArrowCursor
An arrow pointing upwards toward the top of the screen.
Qt.CrossCursor
A crosshair cursor, typically used to help the user accurately select a point on the screen.
Qt.WaitCursor
An hourglass or watch cursor, usually shown during operations that prevent the user from interacting with the application.
Qt.IBeamCursor
A caret or ibeam cursor, indicating that a widget can accept and display text input.
Qt.SizeVerCursor
A cursor used for elements that are used to vertically resize top-level windows.
Qt.SizeHorCursor
A cursor used for elements that are used to horizontally resize top-level windows.
Qt.SizeBDiagCursor
A cursor used for elements that are used to diagonally resize top-level windows at their top-right and bottom-left corners.
Qt.SizeFDiagCursor
A cursor used for elements that are used to diagonally resize top-level windows at their top-left and bottom-right corners.
Qt.SizeAllCursor
A cursor used for elements that are used to resize top-level windows in any direction.
Qt.BlankCursor
A blank/invisible cursor, typically used when the cursor shape needs to be hidden.
Qt.SplitVCursor
A cursor used for vertical splitters, indicating that a handle can be dragged horizontally to adjust the use of available space.
Qt.SplitHCursor
A cursor used for horizontal splitters, indicating that a handle can be dragged vertically to adjust the use of available space.
Qt.PointingHandCursor
A pointing hand cursor that is typically used for clickable elements such as hyperlinks.
Qt.ForbiddenCursor
A slashed circle cursor, typically used during drag and drop operations to indicate that dragged content cannot be dropped on particular widgets or inside certain regions.
Qt.OpenHandCursor
A cursor representing an open hand, typically used to indicate that the area under the cursor is the visible part of a canvas that the user can click and drag in order to scroll around.
Qt.ClosedHandCursor
A cursor representing a closed hand, typically used to indicate that a dragging operation is in progress that involves scrolling.
Qt.WhatsThisCursor
An arrow with a question mark, typically used to indicate the presence of What’s This? help for a widget.
Qt.BusyCursor
An hourglass or watch cursor, usually shown during operations that allow the user to interact with the application while they are performed in the background.
Qt.DragMoveCursor
A cursor that is usually used when dragging an item.
Qt.DragCopyCursor
A cursor that is usually used when dragging an item to copy it.
Qt.DragLinkCursor
A cursor that is usually used when dragging an item to make a link to it.
Qt.BitmapCursor
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TextFormat#
This enum is used in widgets that can display both plain text and rich text, for example QLabel. It is used for deciding whether a text string should be interpreted as one or the other. This is normally done by passing one of the enum values to a QTextEdit::setTextFormat() function.
Constant
Description
Qt.PlainText
The text string is interpreted as a plain text string.
Qt.RichText
The text string is interpreted as a rich text string. See Supported HTML Subset for the definition of rich text.
Qt.AutoText
The text string is interpreted as for Qt::RichText if Qt::mightBeRichText() returns
true, otherwise as Qt::PlainText.Qt.MarkdownText
The text string is interpreted as Markdown-formatted text. This enum value was added in Qt 5.14.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.AspectRatioMode#
This enum type defines what happens to the aspect ratio when scaling an rectangle.

Constant
Description
Qt.IgnoreAspectRatio
The size is scaled freely. The aspect ratio is not preserved.
Qt.KeepAspectRatio
The size is scaled to a rectangle as large as possible inside a given rectangle, preserving the aspect ratio.
Qt.KeepAspectRatioByExpanding
The size is scaled to a rectangle as small as possible outside a given rectangle, preserving the aspect ratio.
See also
scale()scaled()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetArea#
(inherits enum.Flag) Represents the areas a QDockWidget can be plugged to.
Note
A floating dock widget with tabs can be docked anywhere.
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
Qt.LeftDockWidgetArea |
The left dock area of a QMainWindow. |
Qt.RightDockWidgetArea |
The right dock area of a QMainWindow. |
Qt.TopDockWidgetArea |
The top dock area of a QMainWindow. |
Qt.BottomDockWidgetArea |
The bottom dock area of a QMainWindow. |
Qt.AllDockWidgetAreas |
All dock widget areas (default). |
Qt.NoDockWidgetArea |
No dock widget areas. |
See also
isAreaAllowed
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.DockWidgetAreaSizes#
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ToolBarArea#
Constant
Description
Qt.LeftToolBarArea
Qt.RightToolBarArea
Qt.TopToolBarArea
Qt.BottomToolBarArea
Qt.AllToolBarAreas
Qt.NoToolBarArea
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ToolBarAreaSizes#
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.DateFormat#
Constant
Description
Qt.TextDate
The default Qt format, which includes the day and month name, the day number in the month, and the year in full. The day and month names will be short names in English (C locale). This effectively uses, for a date, format
ddd MMM d yyyy, for a timeHH:mm:ssand combines these asddd MMM d HH:mm:ss yyyyfor a date-time, with an optional zone-offset suffix, where relevant. When reading from a string, a fractional part is also recognized on the seconds of a time part, asHH:mm:ss.zzz, and some minor variants on the format may be recognized, for compatibility with earlier versions of Qt and with changes to the format planned for the future. In particular, the zone-offset suffix presently usesGMT[±tzoff]with atzoffinHH[[:]mm]format (two-digit hour and optional two-digit minutes, with optional colon separator); this shall change to useUTCin place ofGMTin a future release of Qt, so the plannedUTCformat is recognized.Qt.ISODateWithMs
ISO 8601 extended format: uses
yyyy-MM-ddfor dates,HH:mm:ss.zzzfor times oryyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.zzz(e.g. 2017-07-24T15:46:29.739) for combined dates and times, optionally with a time-zone suffix (Z for UTC otherwise an offset as ±HH:mm) where appropriate. When parsed, a single space,' ', may be used in place of the'T'separator between date and time; no other spacing characters are permitted. This format also acceptsHH:mmand plainHHformats for the time part, either of which may include a fractional part,HH:mm.zzzorHH.zzz, applied to the last field present (hour or minute).Qt.ISODate
ISO 8601 extended format, as for
ISODateWithMs, but omitting the milliseconds (.zzz) part when converting to a string. There is no difference when reading from a string: if a fractional part is present on the last time field, either format will accept it.Qt.RFC2822Date
RFC 2822, RFC 850 and RFC 1036 format: when converting dates to string form, format
dd MMM yyyyis used, for times the format isHH:mm:ss. For combined date and time, these are combined asdd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss ±tzoff(omitting the optional leading day of the week from the first format recognized). When reading from a string either[ddd,] dd MMM yyyy [HH:mm[:ss]][ ±tzoff]orddd MMM dd[ HH:mm:ss] yyyy[ ±tzoff]will be recognized for combined dates and times, wheretzoffis a timezone offset inHHmmformat. Arbitrary spacing may appear before or after the text and any non-empty spacing may replace the spaces in this format. For dates and times separately, the same formats are matched and the unwanted parts are ignored. In particular, note that a time is not recognized without an accompanying date.
Note
For ISODate formats, each y, M and d represents a single digit of the year, month, and day used to specify the date. Each H, m, and s represents a single digit of the hour (up to 24), minute and second used to specify the time. An hour of 24, with zero for all other time fields, is understood as the start of the next day. A .zzz stands for a fractional part suffix on the preceding field, which may be separated from that field either by a comma ',' or the dot '.' shown. Precision beyond milliseconds is accepted but discarded, rounding to the nearest representable millisecond. The presence of a literal T character is used to separate the date and time when both are specified. For the TextDate and RFC2822Date formats, ddd stands for the first three letters of the name of the day of the week and MMM stands for the first three letters of the month name. The names of days and months are always in English (C locale) regardless of user preferences or system settings. The other format characters have the same meaning as for the ISODate format, except that 24 is not accepted as an hour. Parts of a format enclosed in square brackets [...] are optional; the square brackets do not form part of the format. The plus-or-minus character '±' here stands for either sign character, '-' for minus or '+' for plus.
Note
Zone offsets are measured positive to the east of Greenwich, negative to the west, as is usual for UTC-based offset notations (conflicting with some GMT-based zones-names, such as Etc/GMT+3, which use the opposite convention).
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TimeSpec#
Constant
Description
Qt.LocalTime
Local time, controlled by a system time-zone setting.
Qt.UTC
Coordinated Universal Time.
Qt.OffsetFromUTC
An offset in seconds from Coordinated Universal Time.
Qt.TimeZone
A named time zone.
Both LocalTime and TimeZone will take care of transitions, such as the start and end of daylight-saving time. UTC is the standard time relative to which time-zones are usually specified: Greenwich Mean Time has zero offset from it. Neither UTC nor OffsetFromUTC has any transitions.
When specifying a datetime using OffsetFromUTC, the offset from UTC must also be supplied (it is measured in seconds). To specify a datetime using TimeZone, a QTimeZone must be supplied. From Qt 6.5, a QTimeZone can now package a timespec with, where needed, an offset as a lightweight time description, so that passing a QTimeZone now provides a uniform way to use datetime APIs, saving the need to call them differently for different timespecs.
Note
After a change to the system time-zone setting, the behavior of LocalTime-based QDateTime objects created before the change is undefined: QDateTime may have cached data that the change invalidates. (This is not triggered by transitions of the system time-zone.) In long-running processes, updates to the system’s time-zone data (e.g. when politicians change the rules for a zone) may likewise lead to conflicts between the updated time-zone information and data cached by QDateTime objects created before the update, using either LocalTime or TimeZone.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.DayOfWeek#
Constant
Description
Qt.Monday
Qt.Tuesday
Qt.Wednesday
Qt.Thursday
Qt.Friday
Qt.Saturday
Qt.Sunday
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ScrollBarPolicy#
This enum type describes the various modes of QAbstractScrollArea’s scroll bars.
Constant
Description
Qt.ScrollBarAsNeeded
QAbstractScrollArea shows a scroll bar when the content is too large to fit and not otherwise. This is the default.
Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOff
QAbstractScrollArea never shows a scroll bar.
Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOn
QAbstractScrollArea always shows a scroll bar. This property is ignored on systems with transient scroll bars (e.g., on Mac from version 10.7).
(The modes for the horizontal and vertical scroll bars are independent.)
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.CaseSensitivity#
Constant
Description
Qt.CaseInsensitive
Qt.CaseSensitive
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.Corner#
This enum type specifies a corner in a rectangle:
Constant
Description
Qt.TopLeftCorner
The top-left corner of the rectangle.
Qt.TopRightCorner
The top-right corner of the rectangle.
Qt.BottomLeftCorner
The bottom-left corner of the rectangle.
Qt.BottomRightCorner
The bottom-right corner of the rectangle.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.Edge#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum type specifies an edge in a rectangle:
Constant
Description
Qt.TopEdge
The top edge of the rectangle.
Qt.LeftEdge
The left edge of the rectangle.
Qt.RightEdge
The right edge of the rectangle.
Qt.BottomEdge
The bottom edge of the rectangle.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ConnectionType#
This enum describes the types of connection that can be used between signals and slots. In particular, it determines whether a particular signal is delivered to a slot immediately or queued for delivery at a later time.
Constant
Description
Qt.AutoConnection
(Default) If the receiver
lives inthe thread that emits the signal, Qt::DirectConnection is used. Otherwise, Qt::QueuedConnection is used. The connection type is determined when the signal is emitted.Qt.DirectConnection
The slot is invoked immediately when the signal is emitted. The slot is executed in the signalling thread.
Qt.QueuedConnection
The slot is invoked when control returns to the event loop of the receiver’s thread. The slot is executed in the receiver’s thread.
Qt.BlockingQueuedConnection
Same as Qt::QueuedConnection, except that the signalling thread blocks until the slot returns. This connection must not be used if the receiver lives in the signalling thread, or else the application will deadlock.
Qt.UniqueConnection
This is a flag that can be combined with any one of the above connection types, using a bitwise OR. When Qt::UniqueConnection is set,
connect()will fail if the connection already exists (i.e. if the same signal is already connected to the same slot for the same pair of objects).Qt.SingleShotConnection
This is a flag that can be combined with any one of the above connection types, using a bitwise OR. When Qt::SingleShotConnection is set, the slot is going to be called only once; the connection will be automatically broken when the signal is emitted. This flag was introduced in Qt 6.0.
With queued connections, the parameters must be of types that are known to Qt’s meta-object system, because Qt needs to copy the arguments to store them in an event behind the scenes. If you try to use a queued connection and get the error message:
QObject::connect: Cannot queue arguments of type 'MyType'
Call qRegisterMetaType() to register the data type before you establish the connection.
When using signals and slots with multiple threads, see Signals and Slots Across Threads.
See also
connect()qRegisterMetaType()Q_DECLARE_METATYPE()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ShortcutContext#
For a Shortcut event to occur, the shortcut’s key sequence must be entered by the user in a context where the shortcut is active. The possible contexts are these:
Constant
Description
Qt.WidgetShortcut
The shortcut is active when its parent widget has focus.
Qt.WidgetWithChildrenShortcut
The shortcut is active when its parent widget, or any of its children has focus. Children which are top-level widgets, except pop-ups, are not affected by this shortcut context.
Qt.WindowShortcut
The shortcut is active when its parent widget is a logical subwidget of the active top-level window.
Qt.ApplicationShortcut
The shortcut is active when one of the applications windows are active.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.FillRule#
Specifies which method should be used to fill the paths and polygons.
Constant
Description
Qt.OddEvenFill
Specifies that the region is filled using the odd even fill rule. With this rule, we determine whether a point is inside the shape by using the following method. Draw a horizontal line from the point to a location outside the shape, and count the number of intersections. If the number of intersections is an odd number, the point is inside the shape. This mode is the default.
Qt.WindingFill
Specifies that the region is filled using the non zero winding rule. With this rule, we determine whether a point is inside the shape by using the following method. Draw a horizontal line from the point to a location outside the shape. Determine whether the direction of the line at each intersection point is up or down. The winding number is determined by summing the direction of each intersection. If the number is non zero, the point is inside the shape. This fill mode can also in most cases be considered as the intersection of closed shapes.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.MaskMode#
This enum specifies the behavior of the QPixmap::createMaskFromColor() and QImage::createMaskFromColor() functions.
Constant
Description
Qt.MaskInColor
Creates a mask where all pixels matching the given color are opaque.
Qt.MaskOutColor
Creates a mask where all pixels matching the given color are transparent.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ClipOperation#
Constant
Description
Qt.NoClip
This operation turns clipping off.
Qt.ReplaceClip
Replaces the current clip path/rect/region with the one supplied in the function call.
Qt.IntersectClip
Intersects the current clip path/rect/region with the one supplied in the function call.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ItemSelectionMode#
This enum is used in QGraphicsItem, QGraphicsScene and QGraphicsView to specify how items are selected, or how to determine if shapes and items collide.
Constant
Description
Qt.ContainsItemShape
The output list contains only items whose shape is fully contained inside the selection area. Items that intersect with the area’s outline are not included.
Qt.IntersectsItemShape
The output list contains both items whose shape is fully contained inside the selection area, and items that intersect with the area’s outline. This is a common mode for rubber band selection.
Qt.ContainsItemBoundingRect
The output list contains only items whose bounding rectangle is fully contained inside the selection area. Items that intersect with the area’s outline are not included.
Qt.IntersectsItemBoundingRect
The output list contains both items whose bounding rectangle is fully contained inside the selection area, and items that intersect with the area’s outline. This method is commonly used for determining areas that need redrawing.
See also
collidesWithPath()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ItemSelectionOperation#
This enum is used in QGraphicsScene to specify what to do with currently selected items when setting a selection area.
Constant
Description
Qt.ReplaceSelection
The currently selected items are replaced by items in the selection area.
Qt.AddToSelection
The items in the selection area are added to the currently selected items.
See also
setSelectionArea()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TransformationMode#
This enum type defines whether image transformations (e.g., scaling) should be smooth or not.
Constant
Description
Qt.FastTransformation
The transformation is performed quickly, with no smoothing.
Qt.SmoothTransformation
The resulting image is transformed using bilinear filtering.
See also
scaled()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.Axis#
This enum type defines three values to represent the three axes in the cartesian coordinate system.
Constant
Description
Qt.XAxis
The X axis.
Qt.YAxis
The Y axis.
Qt.ZAxis
The Z axis.
See also
rotateRadians()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.FocusReason#
This enum specifies why the focus changed. It will be passed through QWidget::setFocus and can be retrieved in the QFocusEvent sent to the widget upon focus change.
Constant
Description
Qt.MouseFocusReason
A mouse action occurred.
Qt.TabFocusReason
The Tab key was pressed.
Qt.BacktabFocusReason
A Backtab occurred. The input for this may include the Shift or Control keys; e.g. Shift+Tab.
Qt.ActiveWindowFocusReason
The window system made this window either active or inactive.
Qt.PopupFocusReason
The application opened/closed a pop-up that grabbed/released the keyboard focus.
Qt.ShortcutFocusReason
The user typed a label’s buddy shortcut
Qt.MenuBarFocusReason
The menu bar took focus.
Qt.OtherFocusReason
Another reason, usually application-specific.
See also
Keyboard Focus in Widgets
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ContextMenuPolicy#
This enum type defines the various policies a widget can have with respect to showing a context menu.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoContextMenu
the widget does not feature a context menu, context menu handling is deferred to the widget’s parent.
Qt.PreventContextMenu
the widget does not feature a context menu, and in contrast to
NoContextMenu, the handling is not deferred to the widget’s parent. This means that all right mouse button events are guaranteed to be delivered to the widget itself through QWidget::mousePressEvent(), and QWidget::mouseReleaseEvent().Qt.DefaultContextMenu
the widget’s QWidget::contextMenuEvent() handler is called.
Qt.ActionsContextMenu
the widget displays its QWidget::actions() as context menu.
Qt.CustomContextMenu
the widget emits the QWidget::customContextMenuRequested() signal.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.InputMethodQuery#
Constant
Description
Qt.ImEnabled
(inherits
enum.Flag) The widget accepts input method input.Qt.ImCursorRectangle
The rectangle covering the area of the input cursor in widget coordinates.
Qt.ImFont
The currently used font for text input.
Qt.ImCursorPosition
The logical position of the cursor within the text surrounding the input area (see
ImSurroundingText). The position does not incorporate the offset of the cursor within the preedit area, as controlled by QInputMethodEvent::Cursor.Qt.ImSurroundingText
The plain text around the input area, for example the current paragraph.
Qt.ImCurrentSelection
The currently selected text.
Qt.ImMaximumTextLength
The maximum number of characters that the widget can hold. If there is no limit,
QVariant()is returned.Qt.ImAnchorPosition
The position of the selection anchor. This may be less or greater than
ImCursorPosition, depending on which side of selection the cursor is. If there is no selection, it returns the same asImCursorPosition.Qt.ImHints
The hints for input method on expected input. (See
InputMethodHints)Qt.ImPreferredLanguage
The preferred input language.
Qt.ImPlatformData
Platform specific data for input method.
Qt.ImAbsolutePosition
The logical position of the cursor within the entire document. The position does not incorporate the offset of the cursor within the preedit area, as controlled by QInputMethodEvent::Cursor.
Qt.ImTextBeforeCursor
The plain text before the cursor. The widget can decide how much text to return, but must not return an empty string unless the cursor is at the start of the document.
Qt.ImTextAfterCursor
The plain text after the cursor. The widget can decide how much text to return, but must not return an empty string unless the cursor is at the end of the document.
Qt.ImEnterKeyType
The Enter key type.
Qt.ImAnchorRectangle
The bounding rectangle of the selection anchor. This value was added in Qt 5.7.
Qt.ImInputItemClipRectangle
The actual exposed input item rectangle. Parts of the input item might be clipped. This value will take clipping into consideration and return the actual painted item rectangle. The rectangle is in widget coordinates.
Qt.ImReadOnly
The widget is read only. This value was added in Qt 6.2.
Masks:
Constant
Description
Qt.ImQueryInput
Commonly changed properties on input.
Qt.ImQueryAll
Query for all input method properties.
See also
QInputMethodQueryEvent
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.InputMethodHint#
Constant
Description
Qt.ImhNone
(inherits
enum.Flag) No hints.
Flags that alter the behavior:
Constant
Description
Qt.ImhHiddenText
The input method should not show the characters while typing. This is automatically set when setting QLineEdit::echoMode to
Password. Note that settingImhHiddenTextdoes not change the echo mode.Qt.ImhSensitiveData
Typed text should not be stored by the active input method in any persistent storage like predictive user dictionary.
Qt.ImhNoAutoUppercase
The input method should not try to automatically switch to upper case when a sentence ends.
Qt.ImhPreferNumbers
Numbers are preferred (but not required).
Qt.ImhPreferUppercase
Upper case letters are preferred (but not required).
Qt.ImhPreferLowercase
Lower case letters are preferred (but not required).
Qt.ImhNoPredictiveText
Do not use predictive text (i.e. dictionary lookup) while typing.
Qt.ImhDate
The text editor functions as a date field.
Qt.ImhTime
The text editor functions as a time field.
Qt.ImhPreferLatin
Latin characters are preferred (but not required).
Qt.ImhMultiLine
Multiple lines can be entered into the text field.
Qt.ImhNoEditMenu
Do not use built-in edit menu. This flag was introduced in Qt 5.11.
Qt.ImhNoTextHandles
Do not use built-in text cursor and selection handles. This flag was introduced in Qt 5.11.
Flags that restrict input (exclusive flags):
Constant
Description
Qt.ImhDigitsOnly
Only digits are allowed.
Qt.ImhFormattedNumbersOnly
Only number input is allowed. This includes decimal point and minus sign.
Qt.ImhUppercaseOnly
Only upper case letter input is allowed.
Qt.ImhLowercaseOnly
Only lower case letter input is allowed.
Qt.ImhDialableCharactersOnly
Only characters suitable for phone dialing are allowed.
Qt.ImhEmailCharactersOnly
Only characters suitable for email addresses are allowed.
Qt.ImhUrlCharactersOnly
Only characters suitable for URLs are allowed.
Qt.ImhLatinOnly
Only latin based input is allowed.
Masks:
Constant
Description
Qt.ImhExclusiveInputMask
This mask yields nonzero if any of the exclusive flags are used.
Note
If several exclusive flags are OR-ed together, the resulting character set will consist of the union of the specified sets. For instance specifying ImhNumbersOnly and ImhUppercaseOnly would yield a set consisting of numbers and uppercase letters.
See also
inputMethodHints()
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.EnterKeyType#
This can be used to alter the appearance of the Return key on an on-screen keyboard.
Note
Not all of these values are supported on all platforms. For unsupported values the default key will be used instead.
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
Qt.EnterKeyDefault |
The default Enter key. This can either be a button closing the keyboard, or a Return button causing a new line in case of a multi-line input field. |
Qt.EnterKeyReturn |
Show a Return button that inserts a new line. The keyboard will not close when this button is pressed. |
Qt.EnterKeyDone |
Show a “Done” button. The keyboard will close when this button is pressed. |
Qt.EnterKeyGo |
Show a “Go” button. Typically used in an address bar when entering a URL; the keyboard will close when this button is pressed. |
Qt.EnterKeySend |
Show a “Send” button. The keyboard will close when this button is pressed. |
Qt.EnterKeySearch |
Show a “Search” button. The keyboard will close when this button is pressed. |
Qt.EnterKeyNext |
Show a “Next” button. Typically used in a form to allow navigating to the next input field; the keyboard will not close when this button is pressed. |
Qt.EnterKeyPrevious |
Show a “Previous” button. The keyboard will not close when this button is pressed. |
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ToolButtonStyle#
The style of the tool button, describing how the button’s text and icon should be displayed.
Constant
Description
Qt.ToolButtonIconOnly
Only display the icon.
Qt.ToolButtonTextOnly
Only display the text.
Qt.ToolButtonTextBesideIcon
The text appears beside the icon.
Qt.ToolButtonTextUnderIcon
The text appears under the icon.
Qt.ToolButtonFollowStyle
Follow the style.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.LayoutDirection#
Specifies the direction of Qt’s layouts and text handling.
Constant
Description
Qt.LeftToRight
Left-to-right layout.
Qt.RightToLeft
Right-to-left layout.
Qt.LayoutDirectionAuto
Automatic layout.
Right-to-left layouts are necessary for certain languages, notably Arabic and Hebrew.
LayoutDirectionAuto serves two purposes. When used in conjunction with widgets and layouts, it will imply to use the layout direction set on the parent widget or QApplication. This has the same effect as QWidget::unsetLayoutDirection().
When LayoutDirectionAuto is used in conjunction with text layouting, it will imply that the text directionality is determined from the content of the string to be layouted.
See also
isRightToLeft()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.AnchorPoint#
Specifies a side of a layout item that can be anchored. This is used by QGraphicsAnchorLayout.
Constant
Description
Qt.AnchorLeft
The left side of a layout item.
Qt.AnchorHorizontalCenter
A “virtual” side that is centered between the left and the right side of a layout item.
Qt.AnchorRight
The right side of a layout item.
Qt.AnchorTop
The top side of a layout item.
Qt.AnchorVerticalCenter
A “virtual” side that is centered between the top and the bottom side of a layout item.
Qt.AnchorBottom
The bottom side of a layout item.
See also
QGraphicsAnchorLayout
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.FindChildOption#
Constant
Description
Qt.FindDirectChildrenOnly
(inherits
enum.Flag) Looks only at the direct children of the object.Qt.FindChildrenRecursively
Looks at all children of the object (recursive search).
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.DropAction#
Constant
Description
Qt.CopyAction
(inherits
enum.Flag) Copy the data to the target.Qt.MoveAction
Move the data from the source to the target.
Qt.LinkAction
Create a link from the source to the target.
Qt.ActionMask
Qt.IgnoreAction
Ignore the action (do nothing with the data).
Qt.TargetMoveAction
On Windows, this value is used when the ownership of the D&D data should be taken over by the target application, i.e., the source application should not delete the data. On X11 this value is used to do a move. TargetMoveAction is not used on the Mac.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.CheckState#
This enum describes the state of checkable items, controls, and widgets.
Constant
Description
Qt.Unchecked
The item is unchecked.
Qt.PartiallyChecked
The item is partially checked. Items in hierarchical models may be partially checked if some, but not all, of their children are checked.
Qt.Checked
The item is checked.
See also
ItemFlagsItemDataRole
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ItemDataRole#
(inherits enum.IntEnum) Each item in the model has a set of data elements associated with it, each with its own role. The roles are used by the view to indicate to the model which type of data it needs. Custom models should return data in these types.
The general purpose roles (and the associated types) are:
Constant
Description
Qt.DisplayRole
The key data to be rendered in the form of text. (
QString)Qt.DecorationRole
The data to be rendered as a decoration in the form of an icon. (QColor, QIcon or QPixmap)
Qt.EditRole
The data in a form suitable for editing in an editor. (
QString)Qt.ToolTipRole
The data displayed in the item’s tooltip. (
QString)Qt.StatusTipRole
The data displayed in the status bar. (
QString)Qt.WhatsThisRole
The data displayed for the item in “What’s This?” mode. (
QString)Qt.SizeHintRole
The size hint for the item that will be supplied to views. (
QSize)
Roles describing appearance and meta data (with associated types):
Constant
Description
Qt.FontRole
The font used for items rendered with the default delegate. (QFont)
Qt.TextAlignmentRole
The alignment of the text for items rendered with the default delegate. (
Alignment)Qt.BackgroundRole
The background brush used for items rendered with the default delegate. (QBrush)
Qt.ForegroundRole
The foreground brush (text color, typically) used for items rendered with the default delegate. (QBrush)
Qt.CheckStateRole
This role is used to obtain the checked state of an item. (
CheckState)Qt.InitialSortOrderRole
This role is used to obtain the initial sort order of a header view section. (
SortOrder).
Accessibility roles (with associated types):
Constant
Description
Qt.AccessibleTextRole
The text to be used by accessibility extensions and plugins, such as screen readers. (
QString)Qt.AccessibleDescriptionRole
A description of the item for accessibility purposes. (
QString)
User roles:
Constant
Description
Qt.UserRole
The first role that can be used for application-specific purposes.
For user roles, it is up to the developer to decide which types to use and ensure that components use the correct types when accessing and setting data.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ItemFlag#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum describes the properties of an item:
Constant
Description
Qt.NoItemFlags
It does not have any properties set.
Qt.ItemIsSelectable
It can be selected.
Qt.ItemIsEditable
It can be edited.
Qt.ItemIsDragEnabled
It can be dragged.
Qt.ItemIsDropEnabled
It can be used as a drop target.
Qt.ItemIsUserCheckable
It can be checked or unchecked by the user.
Qt.ItemIsEnabled
The user can interact with the item.
Qt.ItemIsAutoTristate
The item’s state depends on the state of its children. This enables automatic management of the state of parent items in QTreeWidget (checked if all children are checked, unchecked if all children are unchecked, or partially checked if only some children are checked).
Qt.ItemNeverHasChildren
The item never has child items. This is used for optimization purposes only.
Qt.ItemIsUserTristate
The user can cycle through three separate states. This value was added in Qt 5.5.
Note that checkable items need to be given both a suitable set of flags and an initial state, indicating whether the item is checked or not. This is handled automatically for model/view components, but needs to be explicitly set for instances of QListWidgetItem, QTableWidgetItem, and QTreeWidgetItem.
Note that it is undefined behavior to reimplement hasChildren to return true for an index if that index has the Qt::ItemNeverHasChildren flag set.
See also
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.MatchFlag#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum describes the type of matches that can be used when searching for items in a model.
Constant
Description
Qt.MatchExactly
Performs
QVariant-based matching.Qt.MatchFixedString
Performs string-based matching. String-based comparisons are case-insensitive unless the
MatchCaseSensitiveflag is also specified.Qt.MatchContains
The search term is contained in the item.
Qt.MatchStartsWith
The search term matches the start of the item.
Qt.MatchEndsWith
The search term matches the end of the item.
Qt.MatchCaseSensitive
The search is case sensitive.
Qt.MatchRegularExpression
Performs string-based matching using a regular expression as the search term. Uses
QRegularExpression. When using this flag, aQRegularExpressionobject can be passed as parameter and will directly be used to perform the search. The case sensitivity flag will be ignored as theQRegularExpressionobject is expected to be fully configured. This enum value was added in Qt 5.15.Qt.MatchWildcard
Performs string-based matching using a string with wildcards as the search term.
Qt.MatchWrap
Perform a search that wraps around, so that when the search reaches the last item in the model, it begins again at the first item and continues until all items have been examined.
Qt.MatchRecursive
Searches the entire hierarchy.
Note
Qt::MatchExactly, Qt::MatchContains, Qt::MatchStartsWith, Qt::MatchEndsWith, Qt::MatchRegularExpression, Qt::MatchWildcard, and Qt::MatchFixedString are mutually exclusive. The behavior achieved by setting several of them in a Qt::MatchFlags argument is undefined.
See also
compare() QRegularExpression
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.WindowModality#
This enum specifies the behavior of a modal window. A modal window is one that blocks input to other windows. Note that windows that are children of a modal window are not blocked.
The values are:
Constant
Description
Qt.NonModal
The window is not modal and does not block input to other windows.
Qt.WindowModal
The window is modal to a single window hierarchy and blocks input to its parent window, all grandparent windows, and all siblings of its parent and grandparent windows.
Qt.ApplicationModal
The window is modal to the application and blocks input to all windows.
See also
windowModalityQDialog
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TextInteractionFlag#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum specifies how a text displaying widget reacts to user input.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoTextInteraction
No interaction with the text is possible.
Qt.TextSelectableByMouse
Text can be selected with the mouse and copied to the clipboard using a context menu or standard keyboard shortcuts.
Qt.TextSelectableByKeyboard
Text can be selected with the cursor keys on the keyboard. A text cursor is shown.
Qt.LinksAccessibleByMouse
Links can be highlighted and activated with the mouse.
Qt.LinksAccessibleByKeyboard
Links can be focused using tab and activated with enter.
Qt.TextEditable
The text is fully editable.
Qt.TextEditorInteraction
The default for a text editor.
Qt.TextBrowserInteraction
The default for QTextBrowser.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.EventPriority#
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This enum can be used to specify event priorities.
Constant
Description
Qt.HighEventPriority
Events with this priority are sent before events with NormalEventPriority or LowEventPriority.
Qt.NormalEventPriority
Events with this priority are sent after events with HighEventPriority, but before events with LowEventPriority.
Qt.LowEventPriority
Events with this priority are sent after events with HighEventPriority or NormalEventPriority.
Note that these values are provided purely for convenience, since event priorities can be any value between INT_MAX and INT_MIN, inclusive. For example, you can define custom priorities as being relative to each other:
enum CustomEventPriority # An important event ImportantEventPriority = Qt.HighEventPriority, # A more important event MoreImportantEventPriority = ImportantEventPriority + 1, # A critical event CriticalEventPriority = 100 * MoreImportantEventPriority, # Not that important StatusEventPriority = Qt.LowEventPriority, # These are less important than Status events IdleProcessingDoneEventPriority = StatusEventPriority - 1See also
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.SizeHint#
This enum is used by QGraphicsLayoutItem::sizeHint()
Constant
Description
Qt.MinimumSize
is used to specify the minimum size of a graphics layout item.
Qt.PreferredSize
is used to specify the preferred size of a graphics layout item.
Qt.MaximumSize
is used to specify the maximum size of a graphics layout item.
Qt.MinimumDescent
is used to specify the minimum descent of a text string in a graphics layout item.
See also
sizeHint()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.WindowFrameSection#
This enum is used to describe parts of a window frame. It is returned by QGraphicsWidget::windowFrameSectionAt() to describe what section of the window frame is under the mouse.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoSection
Qt.LeftSection
Qt.TopLeftSection
Qt.TopSection
Qt.TopRightSection
Qt.RightSection
Qt.BottomRightSection
Qt.BottomSection
Qt.BottomLeftSection
Qt.TitleBarArea
See also
windowFrameSectionAt()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.CoordinateSystem#
This enum specifies the coordinate system.
Constant
Description
Qt.DeviceCoordinates
Coordinates are relative to the top-left corner of the object’s paint device.
Qt.LogicalCoordinates
Coordinates are relative to the top-left corner of the object.
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TouchPointState#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum represents the state of a touch point at the time a QTouchEvent occurred.
Constant
Description
Qt.TouchPointUnknownState
The state of the touch point is not known.
Qt.TouchPointPressed
The touch point is now pressed.
Qt.TouchPointMoved
The touch point moved.
Qt.TouchPointStationary
The touch point did not move.
Qt.TouchPointReleased
The touch point was released.
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.GestureState#
This enum type describes the state of a gesture.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoGesture
No gesture has been detected.
Qt.GestureStarted
A continuous gesture has started.
Qt.GestureUpdated
A gesture continues.
Qt.GestureFinished
A gesture has finished.
Qt.GestureCanceled
A gesture was canceled.
See also
QGesture
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.GestureType#
(inherits enum.IntEnum) This enum type describes the standard gestures.
Constant
Description
Qt.TapGesture
A Tap gesture.
Qt.TapAndHoldGesture
A Tap-And-Hold (Long-Tap) gesture.
Qt.PanGesture
A Pan gesture.
Qt.PinchGesture
A Pinch gesture.
Qt.SwipeGesture
A Swipe gesture.
Qt.CustomGesture
A flag that can be used to test if the gesture is a user-defined gesture ID.
User-defined gestures are registered with the QGestureRecognizer::registerRecognizer() function which generates a custom gesture ID with the Qt::CustomGesture flag set.
See also
grabGesture()
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.GestureFlag#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum type describes additional flags that can be used when subscribing to a gesture.
Constant
Description
Qt.DontStartGestureOnChildren
By default gestures can start on the widget or over any of its children. Use this flag to disable this and allow a gesture to start on the widget only.
Qt.ReceivePartialGestures
Allows any ignored gesture events to be propagated to parent widgets which have specified this hint. By default only gestures that are in the
GestureStartedstate are propagated and the widget always gets the full gesture sequence starting with a gesture in theGestureStartedstate and ending with a gesture in theGestureFinishedorGestureCanceledstates.Qt.IgnoredGesturesPropagateToParent
Allows fine-tuning of gesture event propagation. By setting the flag when grabbing a gesture all ignored partial gestures will propagate to their parent items.
See also
grabGesture()
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.NativeGestureType#
This enum returns the gesture type.
Constant
Description
Qt.BeginNativeGesture
Sent before gesture event stream.
Qt.EndNativeGesture
Sent after gesture event stream.
Qt.PanNativeGesture
Specifies the displacement delta in pixels.
Qt.ZoomNativeGesture
Specifies the magnification delta in percent.
Qt.SmartZoomNativeGesture
Boolean magnification state.
Qt.RotateNativeGesture
Specifies the rotation delta in degrees.
Qt.SwipeNativeGesture
Sent after a swipe movement.
This enum type describes the mode for moving focus.
Constant
Description
Qt.NavigationModeNone
Only the touch screen is used.
Qt.NavigationModeKeypadTabOrder
Key_UpandKey_Downare used to change focus.Qt.NavigationModeKeypadDirectional
Key_Up,Key_Down,Key_LeftandKey_Rightare used to change focus.Qt.NavigationModeCursorAuto
The mouse cursor is used to change focus, it is displayed only on non touchscreen devices. The keypad is used to implement a virtual cursor, unless the device has an analog mouse type of input device (e.g. touchpad). This is the recommended setting for an application such as a web browser that needs pointer control on both touch and non-touch devices.
Qt.NavigationModeCursorForceVisible
The mouse cursor is used to change focus, it is displayed regardless of device type. The keypad is used to implement a virtual cursor, unless the device has an analog mouse type of input device (e.g. touchpad)
Note
Cursor navigation is not currently implemented on any platform and behaves as NavigationModeNone.
See also
navigationMode()
New in version 4.6.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.CursorMoveStyle#
This enum describes the movement style available to text cursors. The options are:
Constant
Description
Qt.LogicalMoveStyle
Within a left-to-right text block, decrease cursor position when pressing left arrow key, increase cursor position when pressing the right arrow key. If the text block is right-to-left, the opposite behavior applies.
Qt.VisualMoveStyle
Pressing the left arrow key will always cause the cursor to move left, regardless of the text’s writing direction. Pressing the right arrow key will always cause the cursor to move right.
New in version 4.8.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.TimerType#
The timer type indicates how accurate a timer can be.
Constant
Description
Qt.PreciseTimer
Precise timers try to keep millisecond accuracy
Qt.CoarseTimer
Coarse timers try to keep accuracy within 5% of the desired interval
Qt.VeryCoarseTimer
Very coarse timers only keep full second accuracy
On UNIX (including Linux, macOS, and iOS), Qt will keep millisecond accuracy for Qt::PreciseTimer. For Qt::CoarseTimer, the interval will be adjusted up to 5% to align the timer with other timers that are expected to fire at or around the same time. The objective is to make most timers wake up at the same time, thereby reducing CPU wakeups and power consumption.
On Windows, Qt will use Windows’s Multimedia timer facility (if available) for Qt::PreciseTimer and normal Windows timers for Qt::CoarseTimer and Qt::VeryCoarseTimer.
On all platforms, the interval for Qt::VeryCoarseTimer is rounded to the nearest full second (e.g. an interval of 23500ms will be rounded to 24000ms, and 20300ms to 20000ms).
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ScrollPhase#
This enum describes the phase of scrolling.
Constant
Description
Qt.NoScrollPhase
The input device doesn’t support scroll phase. This value was introduced in Qt 5.7.
Qt.ScrollBegin
Scrolling is about to begin, but the scrolling distance did not yet change.
Qt.ScrollUpdate
The scrolling distance has changed (default).
Qt.ScrollEnd
Scrolling has ended, and the scrolling distance did not change anymore.
Qt.ScrollMomentum
The user no longer touches the input device, but scrolling continues due to scroll momentum. This value was introduced in Qt 5.12.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.MouseEventSource#
This enum describes the source of a mouse event and can be useful to determine if the event is an artificial mouse event originating from another device such as a touchscreen.
Constant
Description
Qt.MouseEventNotSynthesized
The most common value. On platforms where such information is available this value indicates that the event was generated in response to a genuine mouse event in the system.
Qt.MouseEventSynthesizedBySystem
Indicates that the mouse event was synthesized from a touch event by the platform.
Qt.MouseEventSynthesizedByQt
Indicates that the mouse event was synthesized from an unhandled touch event by Qt.
Qt.MouseEventSynthesizedByApplication
Indicates that the mouse event was synthesized by the application. This allows distinguishing application-generated mouse events from the ones that are coming from the system or are synthesized by Qt. This value was introduced in Qt 5.6
See also
AA_SynthesizeMouseForUnhandledTouchEvents
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.MouseEventFlag#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum provides additional information concerning a QMouseEvent.
Constant
Description
Qt.MouseEventCreatedDoubleClick
Indicates that Qt has created a
MouseButtonDblClickevent from this event. The flag is set in the causingMouseButtonPress, and not in the resultingMouseButtonDblClick.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ChecksumType#
This enum describes the possible standards used by qChecksum().
Constant
Description
Qt.ChecksumIso3309
Checksum calculation based on ISO 3309.
Qt.ChecksumItuV41
Checksum calculation based on ITU-V.41.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy#
This enum describes the possible High-DPI scale factor rounding policies, which decide how non-integer scale factors (such as Windows 150%) are handled.
The active policy is set by calling QGuiApplication::setHighDdpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy() before the application object is created.
Constant
Description
Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy.Round
Round up for .5 and above.
Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy.Ceil
Always round up.
Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy.Floor
Always round down.
Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy.RoundPreferFloor
Round up for .75 and above.
Qt.HighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy.PassThrough
Don’t round.
See also
setHighDpiScaleFactorRoundingPolicy()
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.PermissionStatus#
This enum describes the possible statuses of a permissions.
Constant
Description
Qt.PermissionStatus.Undetermined
The permission status is not yet known. Permission should be requested via
requestPermission()to determine the actual status. This status will never be the result of requesting a permission.Qt.PermissionStatus.Granted
The user has explicitly granted the application the permission, or the permission is known to not require user authorization on the given platform.
Qt.PermissionStatus.Denied
The user has explicitly denied the application the requested permission, or the permission is known to not be accessible or applicable to applications on the given platform.
Note
On Android, there is no Undetermined status by the platform’s APIs. Thus, if a permission is denied for an app, checkPermission() returns Undetermined by default until requestPermission() is called. After that checkPermission() reports a non Undetermined status.
See also
requestPermission() checkPermission() Application Permissions
New in version 6.5.
- PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ReturnByValueConstant#
This is a dummy type, designed to help users transition from certain deprecated APIs to their replacement APIs.
See also
pixmap()
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.beginPropertyUpdateGroup()#
Marks the beginning of a property update group. Inside this group, changing a property does neither immediately update any dependent properties nor does it trigger change notifications. Those are instead deferred until the group is ended by a call to endPropertyUpdateGroup .
Groups can be nested. In that case, the deferral ends only after the outermost group has been ended.
Note
Change notifications are only send after all property values affected by the group have been updated to their new values. This allows re-establishing a class invariant if multiple properties need to be updated, preventing any external observer from noticing an inconsistent state.
See also
endPropertyUpdateGroup QScopedPropertyUpdateGroup
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.bin(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setIntegerBase (2) on stream and returns stream.
See also
oct()dec()hex()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.bom(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Toggles insertion of the Byte Order Mark on stream when QTextStream is used with a UTF encoding.
See also
setGenerateByteOrderMark()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.center(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setFieldAlignment ( AlignCenter ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
left()right()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.dec(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setIntegerBase (10) on stream and returns stream.
See also
bin()oct()hex()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.endPropertyUpdateGroup()#
Ends a property update group. If the outermost group has been ended, and deferred binding evaluations and notifications happen now.
Warning
Calling endPropertyUpdateGroup without a preceding call to beginPropertyUpdateGroup results in undefined behavior.
See also
beginPropertyUpdateGroup QScopedPropertyUpdateGroup
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.endl(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Writes ‘\n’ to the stream and flushes the stream.
Equivalent to
stream << '\n' << Qt.flush
Note: On Windows, all ‘\n’ characters are written as ‘\r\n’ if QTextStream ‘s device or string is opened using the QIODevice::Text flag.
See also
flush()reset()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.fixed(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setRealNumberNotation ( FixedNotation ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
scientific()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.flush(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls flush() on stream and returns stream.
See also
endl()reset()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.forcepoint(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() | ForcePoint ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
noforcepoint()forcesign()showbase()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.forcesign(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() | ForceSign ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
noforcesign()forcepoint()showbase()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.hex(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setIntegerBase (16) on stream and returns stream.
Note
The hex modifier can only be used for writing to streams.
See also
bin() oct() dec() QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.left(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setFieldAlignment ( AlignLeft ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
right()center()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.lowercasebase(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() & ~ UppercaseBase ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
uppercasebase()lowercasedigits()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.lowercasedigits(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() & ~ UppercaseDigits ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
uppercasedigits()lowercasebase()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.noforcepoint(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() & ~ ForcePoint ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
forcepoint()noforcesign()noshowbase()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.noforcesign(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() & ~ ForceSign ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
forcesign()noforcepoint()noshowbase()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.noshowbase(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() & ~ ShowBase ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
showbase()noforcesign()noforcepoint()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.oct(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setIntegerBase (8) on stream and returns stream.
See also
bin()dec()hex()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.reset(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls reset() on stream and returns stream.
See also
flush()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.right(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setFieldAlignment ( AlignRight ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
left()center()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.scientific(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setRealNumberNotation ( ScientificNotation ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
fixed()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.showbase(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() | ShowBase ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
noshowbase()forcesign()forcepoint()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.uppercasebase(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() | UppercaseBase ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
lowercasebase()uppercasedigits()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.uppercasedigits(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls setNumberFlags ( numberFlags() | UppercaseDigits ) on stream and returns stream.
See also
lowercasedigits()uppercasebase()QTextStream manipulators
- static PySide6.QtCore.Qt.ws(s)#
- Parameters:
- Return type:
Calls skipWhiteSpace() on stream and returns stream.
See also
QTextStream manipulators