Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Window Flags Example#
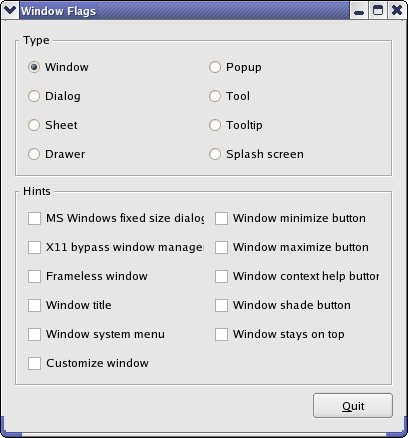
The Window Flags example shows how to use the window flags available in Qt.
A window flag is either a type or a hint. A type is used to specify various window-system properties for the widget. A widget can only have one type, and the default is Qt::Widget. However, a widget can have zero or more hints. The hints are used to customize the appearance of top-level windows.
A widget’s flags are stored in a Qt::WindowFlags type which stores an OR combination of the flags.
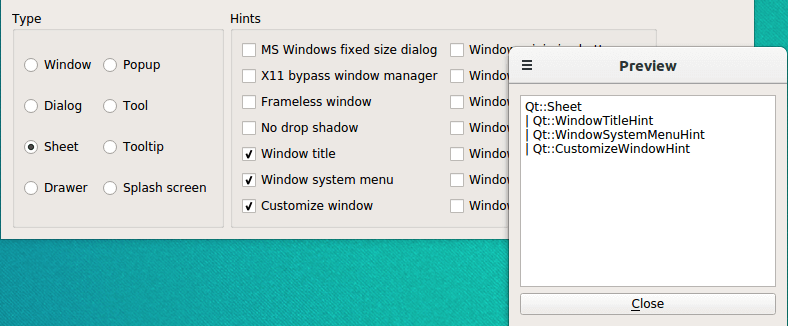
Screenshot of the Window Flags example
The example consists of two classes:
ControllerWindowis the main application widget that allows the user to choose among the available window flags, and displays the effect on a separate preview window.
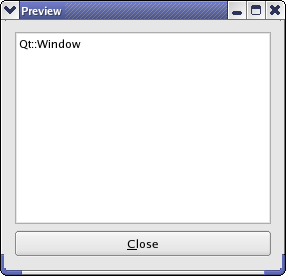
PreviewWindowis a custom widget displaying the name of its currently set window flags in a read-only text editor.
We will start by reviewing the ControllerWindow class, then we will take a look at the PreviewWindow class.
ControllerWindow Class Definition#
class ControllerWindow(QWidget): Q_OBJECT # public ControllerWindow(QWidget parent = None) # private slots def updatePreview(): # private def createTypeGroupBox(): def createHintsGroupBox(): createCheckBox = QCheckBox(QString text) createRadioButton = QRadioButton(QString text) previewWindow = PreviewWindow() typeGroupBox = QGroupBox() hintsGroupBox = QGroupBox() quitButton = QPushButton() windowRadioButton = QRadioButton() dialogRadioButton = QRadioButton() sheetRadioButton = QRadioButton() drawerRadioButton = QRadioButton() popupRadioButton = QRadioButton() toolRadioButton = QRadioButton() toolTipRadioButton = QRadioButton() splashScreenRadioButton = QRadioButton() msWindowsFixedSizeDialogCheckBox = QCheckBox() x11BypassWindowManagerCheckBox = QCheckBox() framelessWindowCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowNoShadowCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowTitleCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowSystemMenuCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowMinimizeButtonCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowMaximizeButtonCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowCloseButtonCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowContextHelpButtonCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowShadeButtonCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowStaysOnTopCheckBox = QCheckBox() windowStaysOnBottomCheckBox = QCheckBox() customizeWindowHintCheckBox = QCheckBox()
The ControllerWindow class inherits QWidget . The widget allows the user to choose among the available window flags, and displays the effect on a separate preview window.
We declare a private updatePreview() slot to refresh the preview window whenever the user changes the window flags.
We also declare several private functions to simplify the constructor: We call the createTypeGroupBox() function to create a radio button for each available window type, using the private createButton() function, and gather them within a group box. In a similar way we use the createHintsGroupBox() function to create a check box for each available hint, using the private createCheckBox() function.
In addition to the various radio buttons and checkboxes, we need an associated PreviewWindow to show the effect of the currently chosen window flags.
ControllerWindow Class Implementation#
def __init__(self, parent): super().__init__(parent) previewWindow = PreviewWindow(self) createTypeGroupBox() createHintsGroupBox() quitButton = QPushButton(tr("Quit")) quitButton.clicked.connect( qApp.quit) bottomLayout = QHBoxLayout() bottomLayout.addStretch() bottomLayout.addWidget(quitButton) mainLayout = QHBoxLayout() mainLayout.addWidget(typeGroupBox) mainLayout.addWidget(hintsGroupBox) mainLayout.addLayout(bottomLayout) setLayout(mainLayout) setWindowTitle(tr("Window Flags")) updatePreview()
In the constructor we first create the preview window. Then we create the group boxes containing the available window flags using the private createTypeGroupBox() and createHintsGroupBox() functions. In addition we create a Quit button. We put the button and a stretchable space in a separate layout to make the button appear in the WindowFlag widget’s right bottom corner.
Finally, we add the button’s layout and the two goup boxes to a QVBoxLayout , set the window title and refresh the preview window using the updatePreview() slot.
def updatePreview(self): Qt.WindowFlags flags if windowRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.Window elif dialogRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.Dialog elif sheetRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.Sheet elif drawerRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.Drawer elif popupRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.Popup elif toolRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.Tool elif toolTipRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.ToolTip elif splashScreenRadioButton.isChecked(): flags = Qt.SplashScreen <Code snippet "widgets/windowflags/controllerwindow.cpp:2" not found>
The updatePreview() slot is called whenever the user changes any of the window flags. First we create an empty Qt::WindowFlags flags, then we determine which one of the types that is checked and add it to flags.
if msWindowsFixedSizeDialogCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.MSWindowsFixedSizeDialogHint if x11BypassWindowManagerCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.X11BypassWindowManagerHint if framelessWindowCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.FramelessWindowHint if windowNoShadowCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.NoDropShadowWindowHint if windowTitleCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowTitleHint if windowSystemMenuCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowSystemMenuHint if windowMinimizeButtonCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowMinimizeButtonHint if windowMaximizeButtonCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowMaximizeButtonHint if windowCloseButtonCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowCloseButtonHint if windowContextHelpButtonCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowContextHelpButtonHint if windowShadeButtonCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowShadeButtonHint if windowStaysOnTopCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint if windowStaysOnBottomCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.WindowStaysOnBottomHint if customizeWindowHintCheckBox.isChecked(): flags |= Qt.CustomizeWindowHint previewWindow.setWindowFlags(flags)
We also determine which of the hints that are checked, and add them to flags using an OR operator. We use flags to set the window flags for the preview window.
pos = previewWindow.pos() if pos.x() < 0: pos.setX(0) if pos.y() < 0: pos.setY(0) previewWindow.move(pos) previewWindow.show()
We adjust the position of the preview window. The reason we do that, is that playing around with the window’s frame may on some platforms cause the window’s position to be changed behind our back. If a window is located in the upper left corner of the screen, parts of the window may not be visible. So we adjust the widget’s position to make sure that, if this happens, the window is moved within the screen’s boundaries. Finally, we call show() to make sure the preview window is visible.
def createTypeGroupBox(self): typeGroupBox = QGroupBox(tr("Type")) windowRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Window")) dialogRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Dialog")) sheetRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Sheet")) drawerRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Drawer")) popupRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Popup")) toolRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Tool")) toolTipRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Tooltip")) splashScreenRadioButton = createRadioButton(tr("Splash screen")) windowRadioButton.setChecked(True) layout = QGridLayout() layout.addWidget(windowRadioButton, 0, 0) layout.addWidget(dialogRadioButton, 1, 0) layout.addWidget(sheetRadioButton, 2, 0) layout.addWidget(drawerRadioButton, 3, 0) layout.addWidget(popupRadioButton, 0, 1) layout.addWidget(toolRadioButton, 1, 1) layout.addWidget(toolTipRadioButton, 2, 1) layout.addWidget(splashScreenRadioButton, 3, 1) typeGroupBox.setLayout(layout)
The private createTypeGroupBox() function is called from the constructor.
First we create a group box, and then we create a radio button (using the private createRadioButton() function) for each of the available types among the window flags. We make Qt::Window the initially applied type. We put the radio buttons into a QGridLayout and install the layout on the group box.
We do not include the default Qt::Widget type. The reason is that it behaves somewhat different than the other types. If the type is not specified for a widget, and it has no parent, the widget is a window. However, if it has a parent, it is a standard child widget. The other types are all top-level windows, and since the hints only affect top-level windows, we abandon the Qt::Widget type.
def createHintsGroupBox(self): hintsGroupBox = QGroupBox(tr("Hints")) msWindowsFixedSizeDialogCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("MS Windows fixed size dialog")) x11BypassWindowManagerCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("X11 bypass window manager")) framelessWindowCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Frameless window")) windowNoShadowCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("No drop shadow")) windowTitleCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window title")) windowSystemMenuCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window system menu")) windowMinimizeButtonCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window minimize button")) windowMaximizeButtonCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window maximize button")) windowCloseButtonCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window close button")) windowContextHelpButtonCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window context help button")) windowShadeButtonCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window shade button")) windowStaysOnTopCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window stays on top")) windowStaysOnBottomCheckBox = createCheckBox(tr("Window stays on bottom")) customizeWindowHintCheckBox= createCheckBox(tr("Customize window")) layout = QGridLayout() layout.addWidget(msWindowsFixedSizeDialogCheckBox, 0, 0) layout.addWidget(x11BypassWindowManagerCheckBox, 1, 0) layout.addWidget(framelessWindowCheckBox, 2, 0) layout.addWidget(windowNoShadowCheckBox, 3, 0) layout.addWidget(windowTitleCheckBox, 4, 0) layout.addWidget(windowSystemMenuCheckBox, 5, 0) layout.addWidget(customizeWindowHintCheckBox, 6, 0) layout.addWidget(windowMinimizeButtonCheckBox, 0, 1) layout.addWidget(windowMaximizeButtonCheckBox, 1, 1) layout.addWidget(windowCloseButtonCheckBox, 2, 1) layout.addWidget(windowContextHelpButtonCheckBox, 3, 1) layout.addWidget(windowShadeButtonCheckBox, 4, 1) layout.addWidget(windowStaysOnTopCheckBox, 5, 1) layout.addWidget(windowStaysOnBottomCheckBox, 6, 1) hintsGroupBox.setLayout(layout)
The private createHintsGroupBox() function is also called from the constructor.
Again, the first thing we do is to create a group box. Then we create a checkbox, using the private createCheckBox() function, for each of the available hints among the window flags. We put the checkboxes into a QGridLayout and install the layout on the group box.
QCheckBox ControllerWindow.createCheckBox(QString text) checkBox = QCheckBox(text) checkBox.clicked.connect( self.updatePreview) return checkBox
The private createCheckBox() function is called from createHintsGroupBox().
We simply create a QCheckBox with the provided text, connect it to the private updatePreview() slot, and return a pointer to the checkbox.
QRadioButton ControllerWindow.createRadioButton(QString text) button = QRadioButton(text) button.clicked.connect( self.updatePreview) return button
In the private createRadioButton() function it is a QRadioButton we create with the provided text, and connect to the private updatePreview() slot. The function is called from createTypeGroupBox(), and returns a pointer to the button.
PreviewWindow Class Definition#
class PreviewWindow(QWidget): Q_OBJECT # public PreviewWindow(QWidget parent = None) def setWindowFlags(flags): # private textEdit = QTextEdit() closeButton = QPushButton()
The PreviewWindow class inherits QWidget . It is a custom widget that displays the names of its currently set window flags in a read-only text editor. It is also provided with a QPushbutton that closes the window.
We reimplement the constructor to create the Close button and the text editor, and the setWindowFlags() function to display the names of the window flags.
PreviewWindow Class Implementation#
def __init__(self, parent): super().__init__(parent) textEdit = QTextEdit() textEdit.setReadOnly(True) textEdit.setLineWrapMode(QTextEdit.NoWrap) closeButton = QPushButton(tr("Close")) closeButton.clicked.connect( self.close) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(textEdit) layout.addWidget(closeButton) setLayout(layout) setWindowTitle(tr("Preview"))
In the constructor, we first create a QTextEdit and make sure that it is read-only.
We also prohibit any line wrapping in the text editor using the setLineWrapMode() function. The result is that a horizontal scrollbar appears when a window flag’s name exceeds the width of the editor. This is a reasonable solution since we construct the displayed text with built-in line breaks. If no line breaks were guaranteed, using another LineWrapMode would perhaps make more sense.
Then we create the Close button, and put both the widgets into a QVBoxLayout before we set the window title.
def setWindowFlags(self, flags): QWidget.setWindowFlags(flags) text = QString() Qt.WindowFlags type = (flags Qt.WindowType_Mask) if type == Qt.Window: text = "Qt.Window" elif type == Qt.Dialog: text = "Qt.Dialog" elif type == Qt.Sheet: text = "Qt.Sheet" elif type == Qt.Drawer: text = "Qt.Drawer" elif type == Qt.Popup: text = "Qt.Popup" elif type == Qt.Tool: text = "Qt.Tool" elif type == Qt.ToolTip: text = "Qt.ToolTip" elif type == Qt.SplashScreen: text = "Qt.SplashScreen" if flags Qt.MSWindowsFixedSizeDialogHint: text += "\n| Qt.MSWindowsFixedSizeDialogHint" if flags Qt.X11BypassWindowManagerHint: text += "\n| Qt.X11BypassWindowManagerHint" if flags Qt.FramelessWindowHint: text += "\n| Qt.FramelessWindowHint" if flags Qt.NoDropShadowWindowHint: text += "\n| Qt.NoDropShadowWindowHint" if flags Qt.WindowTitleHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowTitleHint" if flags Qt.WindowSystemMenuHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowSystemMenuHint" if flags Qt.WindowMinimizeButtonHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowMinimizeButtonHint" if flags Qt.WindowMaximizeButtonHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowMaximizeButtonHint" if flags Qt.WindowCloseButtonHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowCloseButtonHint" if flags Qt.WindowContextHelpButtonHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowContextHelpButtonHint" if flags Qt.WindowShadeButtonHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowShadeButtonHint" if flags Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint" if flags Qt.WindowStaysOnBottomHint: text += "\n| Qt.WindowStaysOnBottomHint" if flags Qt.CustomizeWindowHint: text += "\n| Qt.CustomizeWindowHint" textEdit.setPlainText(text)
In our reimplementation of the setWindowFlags() function, we first set the widgets flags using the setWindowFlags() function. Then we run through the available window flags, creating a text that contains the names of the flags that matches the flags parameter. Finally, we display the text in the widgets text editor.