PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry¶
- class QQuick3DGeometry¶
Base class for defining custom geometry.
Details
The
QQuick3DGeometrycan be used to specify custom geometry for a Model in the Qt Quick 3D scene.While not strictly required, the typical usage is to inherit from this class. The subclass is then exposed to QML by registering it to the type system. The geometry property of a Model can then be set to reference an instance of the registered type.
The high-level structure of such a class is typically similar to the following:
class CustomGeometry : public QQuick3DGeometry { public: CustomGeometry() { rebuildGeometry(); } void setSomething() { // Change relevant internal data. // ... // Then rebuild the vertex and index data and pass it to QQuick3DGeometry. rebuildGeometry(); // Finally, trigger an update. This is relevant in case nothing else // is changing in the scene; this way we make sure a new frame will // be rendered. update(); } private: void rebuildGeometry() { QByteArray vertices; QByteArray indices; ... setPrimitiveType(Lines); setVertexBuffer(vertices); setIndexBuffer(indices); setStride(3 * sizeof(float)); // e.g. when having 3 components per vertex setBounds(...); // minimum and maximum extents, for picking addAttribute(PositionSemantic, 0, F32Type); ... } };
This class can then be registered as a QML type and used with Model .
In Qt 5 type registration happened with qmlRegisterType:
qmlRegisterType<CustomGeometry>("Example", 1, 0, "CustomGeometry");
In Qt 6 the default approach is to use automatic registration with the help of the build system. Instead of calling qmlRegisterType, the
.profile can now contain:CONFIG += qmltypes QML_IMPORT_NAME = Example QML_IMPORT_MAJOR_VERSION = 1
With CMake, automatic registration is the default behavior, so no special settings are needed beyond basic QML module setup:
qt_add_qml_module(application URI Example VERSION 1.0 )
The class implementation should add QML_NAMED_ELEMENT:
class CustomGeometry : public QQuick3DGeometry { Q_OBJECT QML_NAMED_ELEMENT(CustomGeometry) ... };
The QML code can then use the custom type:
import Example 1.0 Model { id: customModel geometry: CustomGeometry { } }
At minimum, a custom geometry should have the following specified:
vertex data,
vertex stride,
primitive type,
an attribute with PositionSemantic.
These are sufficient to render the mesh. For indexed drawing, the index buffer data and an attribute with IndexSemantic needs to be specified as well. In order to support picking (input), the class must specify the bounding volume using
setBounds(). For proper lighting, an attribute with NormalSemantic is needed. When the material uses texturing, at least one set of UV coordinates must be provided and described in an TexCoord0Semantic or TexCoord1Semantic attribute. Some materials may require tangents and binormals as well.As a concrete, minimal example, the following class would provide geometry for a single triangle:
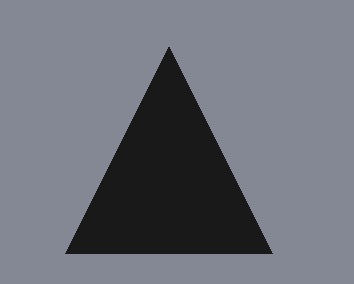
class ExampleGeometry : public QQuick3DGeometry { Q_OBJECT QML_NAMED_ELEMENT(ExampleGeometry) public: ExampleGeometry(); private: void updateData(); }; ExampleGeometry::ExampleGeometry() { updateData(); } void ExampleGeometry::updateData() { QByteArray v; v.resize(3 * 3 * sizeof(float)); float *p = reinterpret_cast<float *>(v.data()); // a triangle, front face = counter-clockwise *p++ = -1.0f; *p++ = -1.0f; *p++ = 0.0f; *p++ = 1.0f; *p++ = -1.0f; *p++ = 0.0f; *p++ = 0.0f; *p++ = 1.0f; *p++ = 0.0f; setVertexData(v); setStride(3 * sizeof(float)); setPrimitiveType(QQuick3DGeometry::PrimitiveType::Triangles); addAttribute(QQuick3DGeometry::Attribute::PositionSemantic, 0, QQuick3DGeometry::Attribute::F32Type); }
Depending on the lighting in the scene, the result of referencing this geometry from a Model:
Synopsis¶
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
addAttribute()def
addSubset()def
attribute()def
attributeCount()def
boundsMax()def
boundsMin()def
clear()def
indexData()def
primitiveType()def
setBounds()def
setIndexData()def
setStride()def
setTargetData()def
setVertexData()def
stride()def
subsetCount()def
subsetName()def
subsetOffset()def
targetData()def
vertexData()
Signals¶
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
- class PrimitiveType¶
- __init__([parent=None])¶
- Parameters:
parent –
QQuick3DObject
Adds vertex attribute description. Each attribute has a semantic, which specifies the usage of the attribute and the number of components it has, an offset from the beginning to the vertex to the attribute location inside a vertex and a componentType specifying the datatype and size of the attribute.
- addAttribute(semantic, offset, componentType)
- Parameters:
semantic –
Semanticoffset – int
componentType –
ComponentType
Adds vertex attribute description. Each attribute has a
semantic, which specifies the usage of the attribute and the number of components it has, anoffsetfrom the beginning to the vertex to the attribute location inside a vertex and acomponentTypespecifying the datatype and size of the attribute.The semantic can be one of the following:
PositionSemantic
The attribute is a position. 3 components: x, y, and z
In addition,
semanticcan beIndexSemantic. In this case the attribute does not represent an entry in the vertex buffer, but rather describes the index data in the index buffer. Since there is always just one index per vertex,offsetmakes no sense for the index buffer, and should be left at zero.The component type can be one of the following:
U16Type
The index component type is unsigned 16-bit integer. Only supported for
IndexSemantic.
Note
The joint index data is typically
I32Type.F32Typeis also supported in order to enable functioning with APIs, such as OpenGL ES 2.0, that do not support integer vertex input attributes.Note
For index data (
IndexSemantic) only U16Type and U32Type are sensible and supported.Note
TargetXXXSemantics will be deprecated.
addTargetAttributecan be used for the morph targets. Now these semantics are just supported for backward compatibility. If they are mixed-used withaddTargetAttributeandsetTargetData, the result cannot be quaranteed.- addSubset(offset, count, boundsMin, boundsMax[, name={}])¶
Adds new subset to the geometry. Subsets allow rendering parts of the geometry with different materials. The materials are specified in the model .
If the geometry has index buffer, then the
offsetandcountare the primitive offset and count of indices in the subset. If the geometry has only vertex buffer, the offset is the vertex offset and count is the number of vertices in the subset.The bounds
boundsMinandboundsMaxshould enclose the subset just like geometry bounds. Also the subset can have aname.- addTargetAttribute(att)¶
- Parameters:
att –
TargetAttribute
Adds morph target attribute description. Each attribute has a targetId which the attribute belongs to, a semantic, which specifies the usage of the attribute and the number of components it has, an offset from the beginning to the vertex to the attribute location inside a vertex, and a stride which is a byte size between the elements.
- addTargetAttribute(targetId, semantic, offset[, stride=0])
- Parameters:
targetId – int
semantic –
Semanticoffset – int
stride – int
Adds morph target attribute description. Each attribute has a
targetIdwhich the attribute belongs to, asemantic, which specifies the usage of the attribute and the number of components it has, anoffsetfrom the beginning to the vertex to the attribute location inside a vertex, and astridewhich is a byte size between the elements.Note
The targetId should be increased from 0 without skipping any number and all the targets should have the same attributes.
Note
The semantic is the same as the vertex attribute but IndexSemantic, JointSementic and WeightSemantic are not allowed for target attributes.
Note
The componentTypes of all the target attributes must be F32Type.
Note
If the stride is not given or less than or equal to zero, the attribute is considered to be tightly packed.
See also
Returns attribute definition number
indexThe attribute definitions are numbered from 0 to
attributeCount() - 1- attributeCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of attributes defined for this geometry.
See also
Returns the maximum coordinate of the bounding volume.
See also
Returns the minimum coordinate of the bounding volume.
See also
- clear()¶
Resets the geometry to its initial state, clearing previously set vertex and index data as well as attributes.
- geometryChanged()¶
- geometryNodeDirty()¶
- indexData()¶
- Return type:
Returns the index buffer data.
See also
- primitiveType()¶
- Return type:
Returns the primitive type used when rendering. The default is
Triangles.See also
Sets the bounding volume of the geometry to the cube defined by the points
minandmax. This is used forpicking.- setIndexData(data)¶
- Parameters:
data –
QByteArray
Sets the index buffer to
data. To use indexed drawing, add an attribute withIndexSemanticSee also
- setIndexData(offset, data)
- Parameters:
offset – int
data –
QByteArray
Updates a subset of the index buffer.
offsetspecifies the offset in bytes,dataspecifies the size and the data.This function will not resize the buffer. If
offset + data.size()is greater than the current size of the buffer, the overshooting data will be ignored.Note
The partial update functions for vertex, index and morph target data do not offer any guarantee on how such changes are implemented internally. Depending on the underlying implementation, even partial changes may lead to updating the entire graphics resource.
- setPrimitiveType(type)¶
- Parameters:
type –
PrimitiveType
Sets the primitive type used for rendering to
type.Points
The primitives are points.
The initial value is
Triangles.Note
Be aware that triangle fans (TriangleFan) may not be supported at run time, depending on the underlying graphics API. For example, with Direct 3D this topology will not be functional at all.
Note
The point size for Points and the line width for Lines and LineStrip are controlled by the material . Be aware however that sizes other than 1 may not be supported at run time, depending on the underlying graphics API.
See also
- setStride(stride)¶
- Parameters:
stride – int
Sets the stride of the vertex buffer to
stride, measured in bytes. This is the distance between two consecutive vertices in the buffer.For example, a tightly packed, interleaved vertex buffer for a geometry using
PositionSemantic,IndexSemantic, andColorSemanticwill have a stride of28(Seven floats in total: Three for position, four for color, and none for indexes, which do not go in the vertex buffer.)Note
QQuick3DGeometryexpects, and works only with, vertex data with an interleaved attribute layout.See also
- setTargetData(data)¶
- Parameters:
data –
QByteArray
Sets the morph target buffer
data. The buffer should hold all the morph target data.See also
- setTargetData(offset, data)
- Parameters:
offset – int
data –
QByteArray
Updates a subset of the morph target buffer.
offsetspecifies the offset in bytes,dataspecifies the size and the data.This function will not resize the buffer. If
offset + data.size()is greater than the current size of the buffer, the overshooting data will be ignored.Note
The partial update functions for vertex, index and morph target data do not offer any guarantee on how such changes are implemented internally. Depending on the underlying implementation, even partial changes may lead to updating the entire graphics resource.
- setVertexData(data)¶
- Parameters:
data –
QByteArray
Sets the vertex buffer
data. The buffer should hold all the vertex data packed in the array, as described by the attribute definitions. Note that this does not include attributes withIndexSemantic, which belong in the index buffer.See also
- setVertexData(offset, data)
- Parameters:
offset – int
data –
QByteArray
Updates a subset of the vertex buffer.
offsetspecifies the offset in bytes,dataspecifies the size and the data.This function will not resize the buffer. If
offset + data.size()is greater than the current size of the buffer, the overshooting data will be ignored.Note
The partial update functions for vertex, index and morph target data do not offer any guarantee on how such changes are implemented internally. depending on the underlying implementation, even partial changes may lead to updating the entire graphics resource.
- stride()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the byte stride of the vertex buffer.
See also
Returns the number of maximum bounds of a
subset.See also
Returns the number of minimum bounds of a
subset.See also
- subsetCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of subsets.
- subsetCount(subset)
- Parameters:
subset – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the subset primitive count.
See also
- subsetName(subset)¶
- Parameters:
subset – int
- Return type:
str
Returns the
subsetname.- subsetOffset(subset)¶
- Parameters:
subset – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the
subsetoffset to the vertex or index buffer.See also
- targetAttribute(index)¶
- Parameters:
index – int
- Return type:
Returns morph target attribute definition number
indexThe attribute definitions are numbered from 0 to
attributeCount() - 1- targetAttributeCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of morph target attributes defined for this geometry.
See also
- targetData()¶
- Return type:
Returns the target buffer data set by
setTargetData.See also
- vertexData()¶
- Return type:
Returns the vertex buffer data set by
setVertexData.See also
- class Attribute¶
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
- class Semantic¶
- class ComponentType¶
- PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry.Attribute.semantic¶
- PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry.Attribute.offset¶
- PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry.Attribute.componentType¶
- class TargetAttribute¶
Added in version 6.6.
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
- PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry.TargetAttribute.targetId¶
- PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry.TargetAttribute.attr¶
- PySide6.QtQuick3D.QQuick3DGeometry.TargetAttribute.stride¶