Neptune 3 UI - 3D Integration
In Neptune 3 UI, there are two apps built with 3D elements:
- "com.theqtcompany.cluster" - the Instrument Cluster app, that manages gauges and telltales; This app can display plain or 3D gauges. The 3D gauges entity is created with Qt 3D Studio, that provides a compositing tool for scene creation. The Qt 3D Studio runtime provides QML APIs to integrate scenes into Qt applications.
- "com.luxoft.vehicle" - a built-in app, that contains two different 3D sub-parts. Both parts implement a similar 3D entity: the vehicle. The first part contains a 3D scene rendered by Qt 3D. Qt 3D provides functionality for near-realtime simulation systems, with support for 2D and 3D rendering in both Qt C++ and Qt Quick applications. The second part is based on Qt 3D Studio.
These apps support a popular use case: to use 3D visualization to improve the users' experience when they interact with features related to physical objects. Each app uses 3D in Qt, in a different way:
- One is to use Qt 3D directly, which requires additional code to construct the entire rendering pipeline correctly.
- The other is to use Qt 3D Studio's runtime that simplifies the app's code significantly, but also limits the 3D features to only those that Qt 3D Studio supports.
The sections below highlight some topics related to integrating 3D support in Qt, for the apps above.
3D Modeling
Generally, a 3D framework provides ways to draw 3D shapes, move them around, and move the camera. This is a baseline; additional features typically include:
- Mesh: a collection of vertices and edges which are probably triangulated; describes the shape of an object in 3D space.
- Material: a set of coefficients that define how the lighting should be applied to the model, and how it interacts with the surface.
- Shader: a programmable shading that is used to apply various levels of darkness, to produce appropriate levels of color within an image, to produce special effects, or to post-process videos.
- Texture: typically used for images to decorate 3D models, but it can also be used to store many different kinds of data.
- Camera: shows the current scene as seen from the view point of the camera that is currently active. To project the screen of a scene, we need to convert 3D coordinates into 2D coordinates. Then, to specify the projection, the points in the 3D scene are used on a virtual screen space. However, the parameters of a projection aren't entered directly; a virtual camera is configured and placed instead.
- Animation: illustrate movement of objects by altering their position.
Qt 3D
The Qt 3D provides some functionalities for modern 3D rendering backed by the performance of OpenGL across the platforms that Qt supports. Qt 3D allows developers to not only visualize 3D contents but to also freely customize and control the appearance of each object by using built-in materials or by providing custom OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) shaders. These controls are also accessible through QML, to extend the ability to create a 3D user interface. Additionally, QML's Scene3D component enables integration of 2D and 3D contents.
Qt 3D is an Entity Component System (ECS), an architectural pattern used mostly in game development. Applications based on the ECS pattern comprise of:
- Entity: a container for any component that can be added, usually hierarchical. An entity represents an object of components, but by itself is devoid of any specific behavior or characteristics. An entity can also have sub-entities.
- Component: a set of objects through which behaviors and data can be added to an entity. Each component is a vertical slice of bvehavior of an object type.
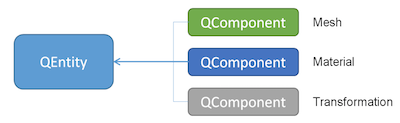
An Entity with a Component attached tells the system that it needs to be rendered and how to do it. The components of each entity can consist of a material, mesh, or transformation. These components should be defined as part of a particular entity, with a given identity for each component. A material component could have an effect that contains the rendering technique. In turn, within the rendering technique, the shader programs can be specified. These shader programs can be external shader files or written directly in QML. The 3D model might have textures - the connection between the 3D model and the textures can be binded with the shader and include the material component which has this material effect to the same entity as the mesh component. For more information on ECS, see Qt 3D Overview.
3D Gauges Integration with Qt 3D Studio
Previously, gauges in the Instrument Cluster app were implemented with 2D graphical assets. Starting from version 5.13, the Instrument Cluster app can use Qt 3D Studio runtime to show 3D gauges and it also includes new gauges created with Qt 3D Studio. The old implementation is still supported and can be enabled from the Companion App at runtime. The diagram below illustrates the Instrument Cluster's structure; colored elements demonstrate the main points of integration:
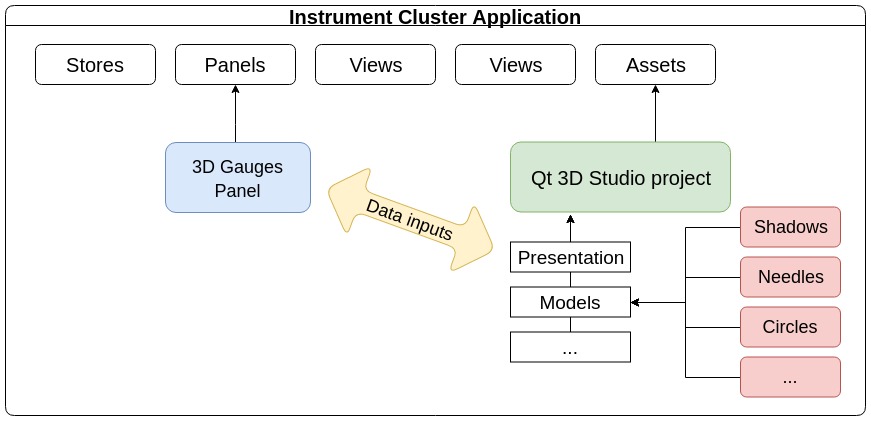
All 3D entities, shown in red, were provided by designers or created with any 3D editor, like Blender; some of these entities are reused from Qt 3D Studio's examples. The Qt 3D Studio project, shown in green, is maintained with the Qt 3D Studio tool. This project is stored as an asset, like the images. The whole 3D scene is imported into a .qml file via a presentation .uip file; the presentation is part of the Qt 3D Studio project and describes the composition of layers on the scene. All of the transformations, such as rotation, movement, and scaling are made via data inputs. For more details, see Qt 3D Studio.
Note: You must have Qt 3D Studio installed and your Qt installation must support OpenGL ES. For more details, see Use the Qt 3D Studio Runtime.
Vehicle 3D Model Integration with Qt 3D
The diagram below shows the current structure of the Vehicle app sub-part built with Qt 3D:
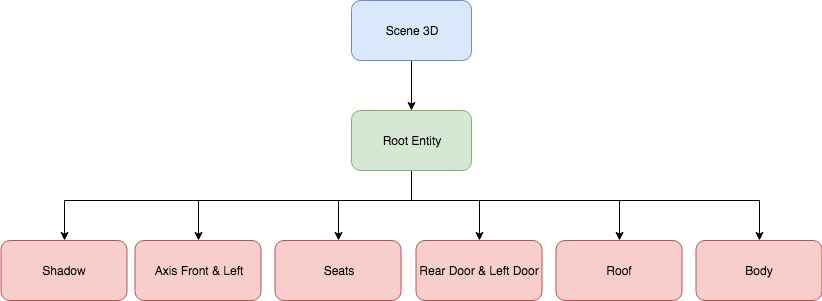
Each part of the Vehicle has its own entity that contains all the necessary parts, such as Mesh, Transformation, and Material. These entities are tailored to the root entity of the whole Scene 3D.
Neptune 3 UI has its own custom physical based material with Cook Torrance GGX distribution, since Qt 3D does not provide any material for OpenGL ES 2.0. This material is required because the app has microfacet theory-based lighting, which adds more realistic lighting to the car. The car model is mostly painted with a single color, to simplify lighting calculations. Additionally, most models today are modeled with Physically Based Rendering (PBR) materials in mind, which makes it easier to import models.
Animations in the Vehicle app comprise of matrices transformations, mostly. For example, a door animation is done with: transform the door to another origin, rotate it, then transform it back. As a result, the door doesn't rotate around its own axis.
Vehicle 3D Model Integration with Qt 3D Studio
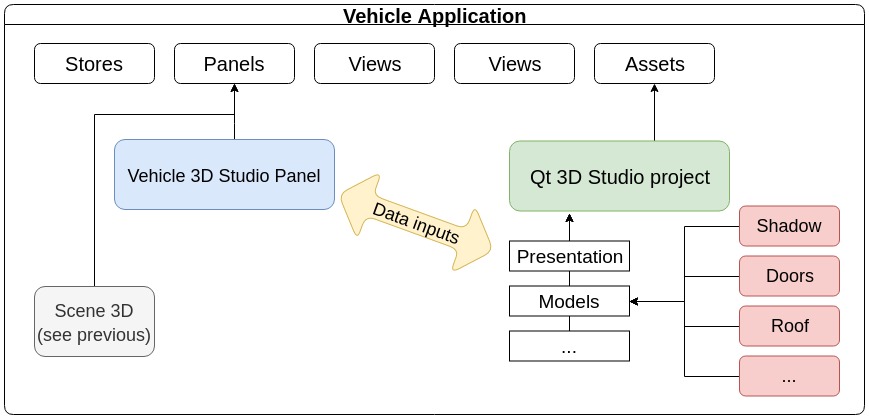
The integration scheme for the other sub-part, built with Qt 3D Studio, is similar to 3D Gauges Integration with Qt 3D Studio. The diagram below further illustrates this:
Modify the Settings to Use 3D in the Vehicle App
The Vehicle app has a settings section where you can change the complexity of the model used and switch between the implementation based on Qt 3D and Qt 3D Studio.
Use the Qt 3D Studio Runtime
The implementation based on the Qt 3D Studio runtime requires that it is installed on the desktop or on the embedded target. If it is installed, but your 3D content is not shown by Neptune 3 UI, this means that Qt was built without -opengl es2 option for Linux and macOS. In this case, Neptune 3 UI only shows the 3D Content on these platforms in single-process mode, provided that you set OpenGL ES 3.0 requirements in the .yaml config file. For more details, see Qt Application Manager.
If you installed Qt Automotive Suite via the Online Installer, it's likely that your installation doesn't contain Qt 3D Studio. In this case, to make sure everything works, build and install the required components from the source.
To build a custom Neptune 3 UI which uses the Qt 3D Studio runtime, do the following:
- Configure Qt with
-opengl es2, build and install it. Use this Qt instance to build all the components mentioned below. - Clone the Qt 3D Studio runtime git repository from https://code.qt.io/cgit/qt3dstudio/qt3d-runtime.git/
- Next, build and install the Qt 3D Studio runtime from the branch 2.1.
- Finally, build and install Qt Application Manager, Qt IVI and then Neptune 3 UI as explained in the Installation sections of those components.
Note: Due to an issue with configuring Qt 5.13.0 with -opengl es2", currently it's not possible to use Neptune 3 UI with Qt 3D Studio Runtime for macOs Mojave.
© 2019 Luxoft Sweden AB.
Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of
their respective owners.
The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation.
Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property
of their respective owners.
