Neptune 3 UI - System UI
The System UI in Neptune 3 UI is a QML application that consists of one or more top-level QWindows: a Center Console window, an optional Instrument Cluster window, and an optional HUD window. The System UI is a special QML application as it uses the QtApplicationManager that turns it into a fully-fledged compositing manager.
Regular applications, known as Neptune 3 apps, then show up on the System UI as plain QML Items which the System UI positions on its QML scene accordingly.
On target hardware, each of the System UI windows drive an entire display or screen, typically fullscreen, controlling all that is rendered on them. This rendering is usually done with the eglfs backend. However, on a desktop development environment, each System UI window is seen as a plain desktop window.
The System UI lets you take screenshots of Neptune 3 UI's current state and export it. At the same time, it also exports the Qt diagnostic tool's output. The exported files are stored in the /tmp folder. To take a screenshot in the Center Console, press and hold the clock at the top right corner; or press CTRL + P.
Settings and UI Persistence
The System UI stores the state of applications that the user has chosen to display as widgets. This behavior, implemented using the Settings QML Type, is stored on the user's local machine as a settings file. When the UI stops, and restarts later, Neptune 3 UI reloads applications that were shown as a widget before. However, if no widgets were selected before Neptune 3 UI stopped, then when Neptune 3 UI restarts, it loads the default set of applications, such as the Calendar app, Music app, and Phone app.
Wayland Compositor
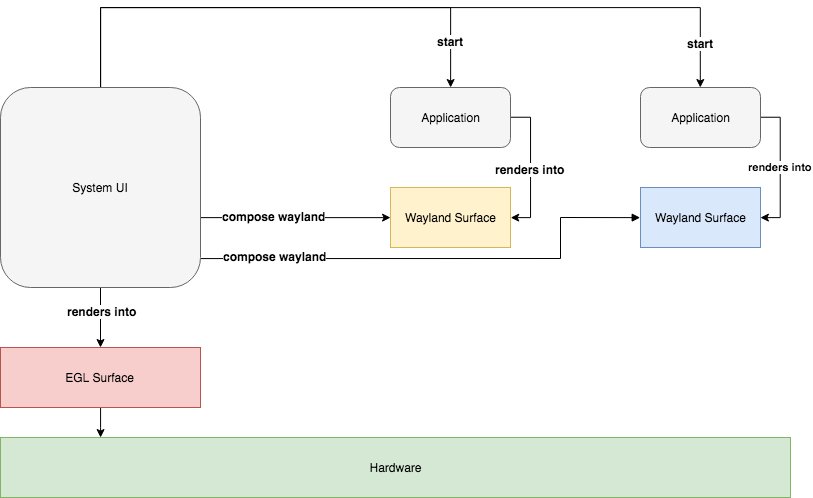
The diagram above shows the flow of how applications are composited by a system UI that uses Qt Wayland. For more information, see Qt Wayland and Wayland and Qt.
Wireframe
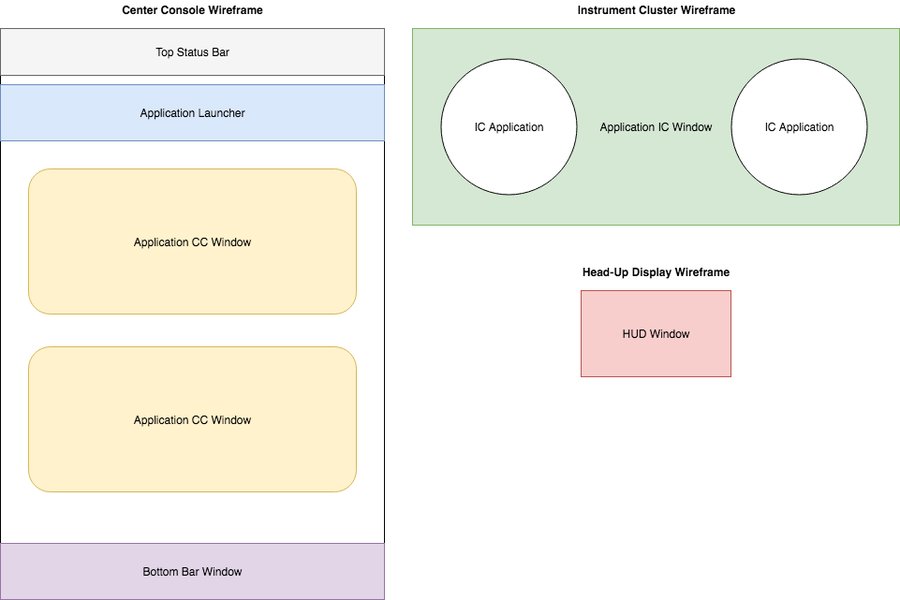
Neptune 3 UI defines five types of application windows; the System UI handles each of them differently. These five windows are:
- application center console window
- application instrument cluster window
- HUD window
- bottom bar window
- application pop-up window
The System UI differentiates between multiple types of windows using the windowType property. Application code doesn't have to worry about this implementation detail, as it's taken care of by the specialized ApplicationCCWindow, ApplicationICWindow, and PopupWindow QML components.
System UI Window Item vs. Application Window
The System UI Window Item is on the compositor-side and is used to position surfaces from the applications. In contrast, the Application Window is used on the client-side to show its content which is on the compositor-side, within the System UI Window Item.
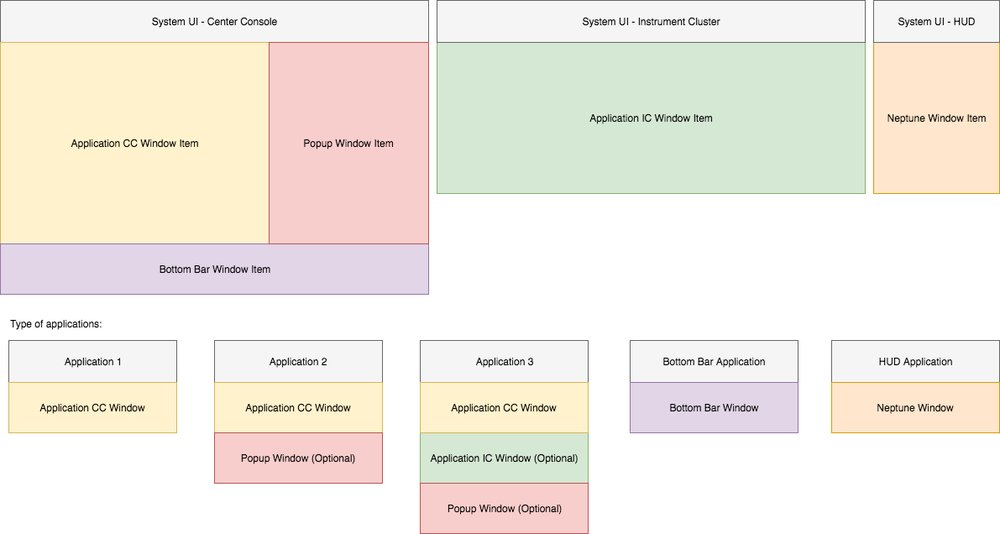
System UI Window Item
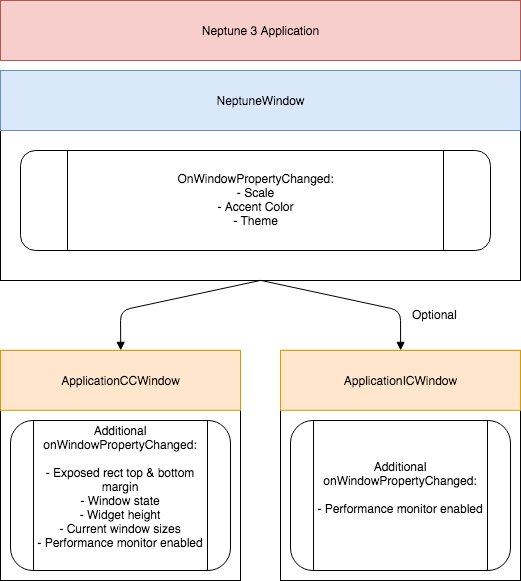
The System UI contains several window items, such as application center console window item, application instrument cluster window item, popup window item, bottom bar window item and top bar window item. They inherit NeptuneWindowItem that carries basic properties to be used by the applications, such as scale factor, accent color, and current theme. Each window item component has its own specific window properties for different purposes.
Application Center Console Window Item
The System UI uses the ApplicationCCWindowItem component to display application windows of type ApplicationCCWindow, where "CC" stands for "Center Console". The ApplicationCCWindowItem carries some properties the application needs, such as the states of application widget (widget 1 row, widget 2 rows, and widget 3 rows) and one state for the maximized view. The application needs to receive the current state of the application widget being used by this application to apply some animations; as each state has its own appearance. Hence, the System UI needs to set the window property of the widget state for the application. Additionally, an exposed rectangle property provides x, y, width, and height of the visible rectangular window area in the application widget. The application can use these properties to correctly adapt to the window that's clipped by the System UI when the widget area is composited.
Application Instrument Cluster Window Item
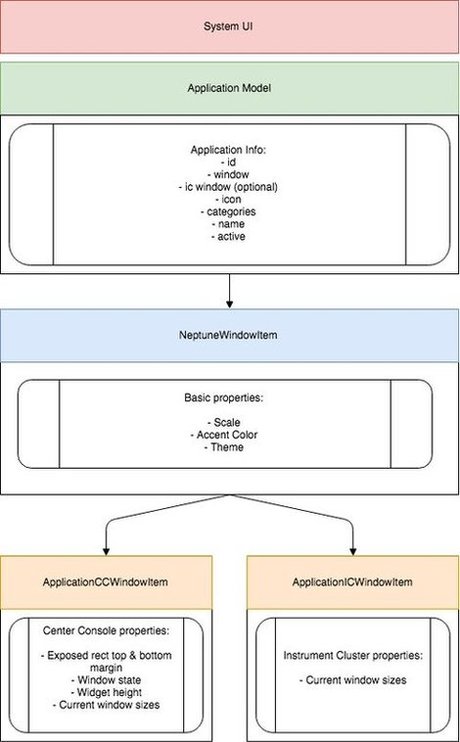
The System UI uses the ApplicationICWindowItem component to display application windows of type ApplicationICWindow, where "IC" stands for "Instrument Cluster". The System UI orchestrates and assigns the window to the responsible window item. In this case, it's shown behind the Instrument Cluster's gauges.
Application Window
Neptune 3 UI provides two main types of application windows for apps to use: ApplicationCCWindow and ApplicationICWindow.
Application Center Console Window
The ApplicationCCWindow is the one to use for an application that needs to be shown in the Center Console. It inherits from NeptuneWindow and some additional properties that receive the windowPropertyChanged signal that the System UI emits. Additionally, for debugging purposes, the MonitorOverlay can be used to show the performance consumption of a particular application. This can be enabled through the System UI's performanceOverlayVisible property.
Application Instrument Cluster Window
Similar to the ApplicationCCWindow, the ApplicationICWindow also inherits from NeptuneWindow and adds some additional window size properties. The ApplicationICWindow is an optional feature that a Neptune 3 UI application can use to show content behind the Instrument Cluster's gauges.
Additional Windows
There are several additional windows for some specific use cases, such as Popup Window, Bottom Bar Window, and Top Bar Window. The System UI takes care of showing these windows on their dedicated window item.
Popup Window
Any application that needs to show a popup in Neptune 3 UI can use the Popup Window. The System UI composes the popup window for applications and shows it on request.
Bottom Bar Window
The Bottom Bar Window is the window to use if you need to show a special application at the bottom of the Center Console. Currently, in Neptune 3 UI, this is where the Climate app is shown.
© 2019 Luxoft Sweden AB.
Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of
their respective owners.
The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation.
Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property
of their respective owners.
