C
Qt App Lister
Demonstrates usage of the Qt Android Apps Utils API.
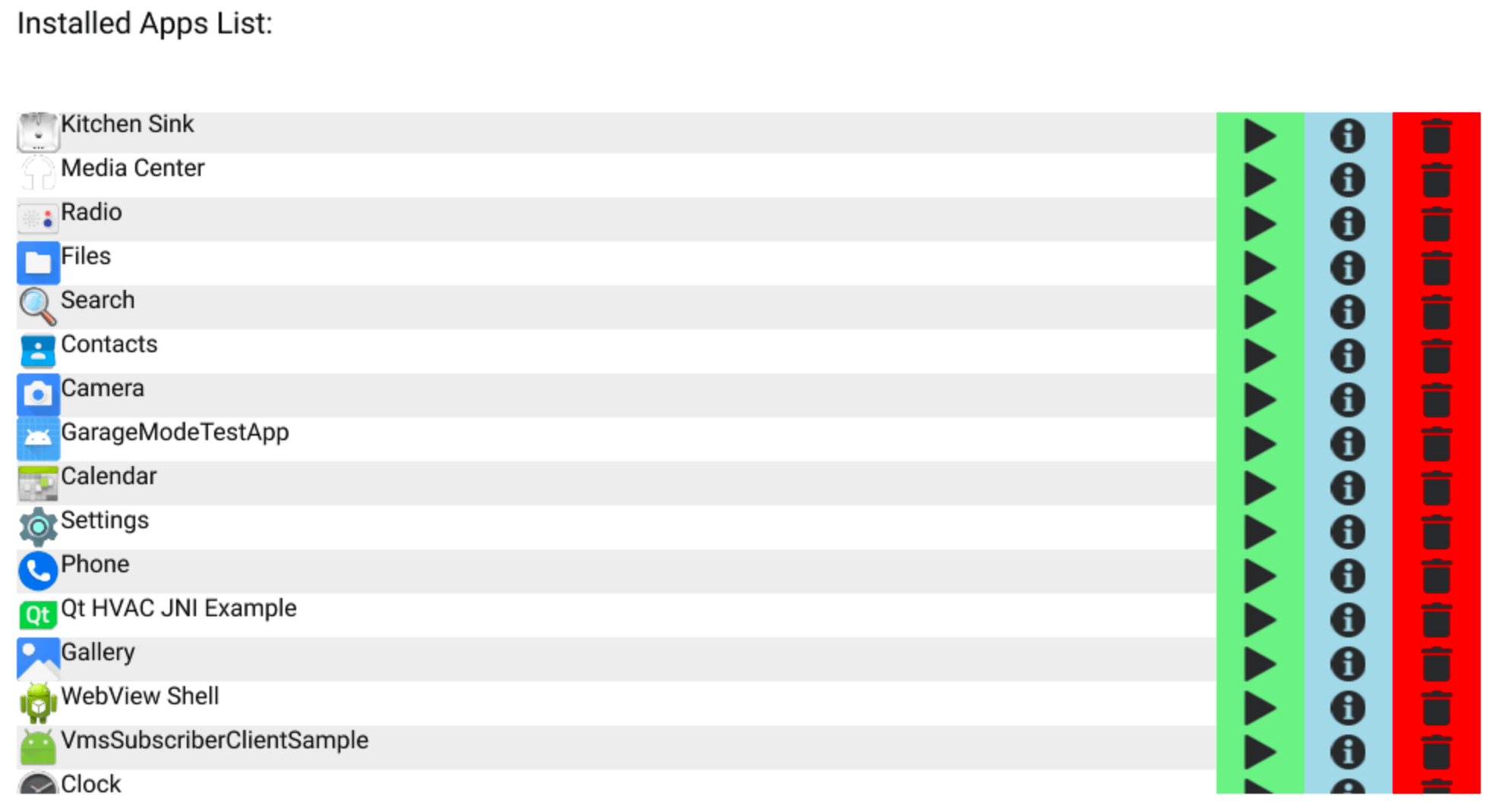
This example demonstrates how to use Qt Android Apps Utils to show a list of installed apps in an Android or Android Automotive device and how to handle relevant events. The application UI is created by using Qt Quick.
When starting the app, a list of all installed apps, excluding system apps, is shown as ListView. Each app has a Button to start the app, show the app info page, or uninstall the app. App Lister also keeps track of installed or uninstalled apps and adds them to the list, as well as showing a text notification on those events.
Running the Example
To run the example from Qt Creator, open the Welcome mode and select the example from Examples. For more information, visit Building and Running an Example.
Using the Model
The installed apps model is based on a QAbstractListModel from C++ and it is extended to QML. The model can be used with ListView or GridView as needed.
In this example, a cListView is used. The model is attached to the list as follows:
ListView { id: listView width: parent.width clip: true flickableDirection: Flickable.VerticalFlick anchors.bottomMargin: window.marginSize anchors.right: parent.right anchors.rightMargin: window.marginSize anchors.left: parent.left anchors.leftMargin: window.marginSize anchors.top: updatesText.bottom anchors.topMargin: window.marginSize anchors.bottom: parent.bottom model: AndroidAppsUtils.installedAppsModel
Then, we set the list's delegate to use a Row that contains the app's icon, name and few controls buttons.
delegate: Rectangle { id: delegate height: window.height * 0.05 width: ListView.view.width color: index % 2 == 0 ? "#EDEDED" : "#FFFFFF" Row { id: row Image { id: appIcon height: delegate.height width: delegate.height source: model.AppIconString } Text { id: appName text: model.appName width: delegate.width - delegate.height - 3 * listView.buttonWidth } Button { id: startrightBtn width: listView.buttonWidth onClicked: AndroidAppsUtils.startApp(model.packageName) background: Rectangle { color: "light green" } icon.source: "qrc:/icons/play.png" icon.height: listView.iconSize icon.width: listView.iconSize anchors.verticalCenter: row.verticalCenter } Button { id: infoBtn width: listView.buttonWidth onClicked: AndroidAppsUtils.showAppInfo(model.packageName) background: Rectangle { color: "light blue" } icon.source: "qrc:/icons/info.png" icon.height: listView.iconSize icon.width: listView.iconSize anchors.verticalCenter: row.verticalCenter } Button { id: removeBtn width: listView.buttonWidth onClicked: AndroidAppsUtils.uninstallApp(model.packageName) background: Rectangle { color: "red" } icon.source: "qrc:/icons/delete.png" icon.height: listView.iconSize icon.width: listView.iconSize anchors.verticalCenter: row.verticalCenter } } } }
Using the API Calls
Inside the ListView delegate, we can trigger some calls to the Java API to execute the common operations like starting, uninstalling, and showing the app's info. To start an app for example:
onClicked: AndroidAppsUtils.startApp(model.packageName)
The Qt Android Apps Utils component ensures to report any event of app installation or un-installation. To receive those signals and execute an operation in response to that, we need to implement a Connections, as follows:
Connections { target: AndroidAppsUtils function onAppUninstalled(message) { updatesText.text = qsTr("Uninstalled: %1").arg(message) } function onAppInstalled(app) { updatesText.text = qsTr("Installed: %1").arg(app.packageName) } }
See also Qt for Android and Qt Android Extras.
Available under certain Qt licenses.
Find out more.


