HTTPクライアント
単純な HTTP クライアントをデモします。
この例では、単純な HTTP クライアントがリモート・ホストからファイルを取得する方法を示します。
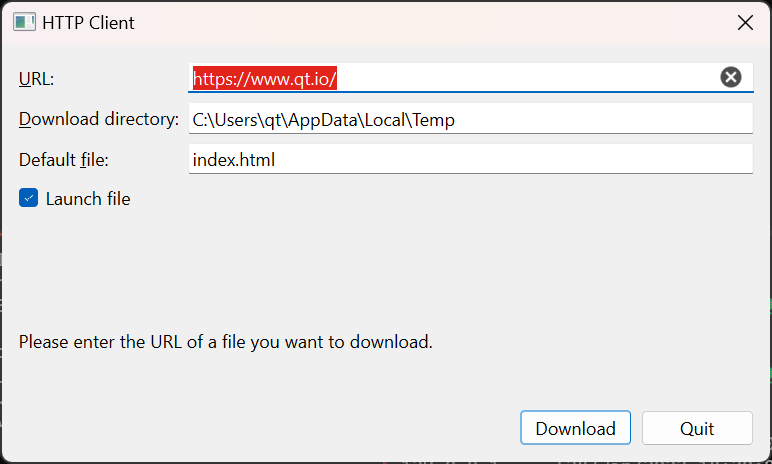
この例の主な作業はHttpWindowクラスで行われます。そのため、この例ではHttpWindowクラスに焦点を当てます。
reply.reset(qnam.get(QNetworkRequest(url)));
QNetworkAccessManager を使って、url が指すリソースのダウンロードを開始します。QNetworkAccessManager::get() という関数についてよく知らない場合や、もっと詳しく知りたい場合は、QNetworkReply とQNetworkRequest のドキュメントを参照してください。
connect(reply.get(), &QNetworkReply::finished, this, &HttpWindow::httpFinished); connect(reply.get(), &QIODevice::readyRead, this, &HttpWindow::httpReadyRead); #if QT_CONFIG(ssl) connect(reply.get(), &QNetworkReply::sslErrors, this, &HttpWindow::sslErrors); #endif
上記では、リプライのシグナルのいくつかをクラスのスロットに接続しています。これらのスロットは、データの受信とダウンロードの最終処理/エラーの処理の両方を行います。
connect(reply.get(), &QIODevice::readyRead, this, &HttpWindow::httpReadyRead);
受信データの処理に関しては、どのような潜在的な入力の最大ダウンロード・サイズもわからないし、サンプル・プログラムを実行する可能性のあるコンピューターのメモリーを使い果たしたくないので、QNetworkReply::finished ()ではなく、QNetworkReply::readyRead ()で受信データを処理する。
void HttpWindow::httpReadyRead() { // This slot gets called every time the QNetworkReply has new data. // We read all of its new data and write it into the file. // That way we use less RAM than when reading it at the finished() // signal of the QNetworkReply if (file) file->write(reply->readAll()); }
そして、到着したデータをファイルに書き込む。不便ですが、アプリケーションのピーク時のメモリー消費は少なくなります!
connect(reply.get(), &QNetworkReply::sslErrors, this, &HttpWindow::sslErrors);
QNetworkReply::sslErrors() シグナルを使えば、安全なウェブサイト(HTTPSなど)に接続する際にTLSハンドシェイク中に発生する可能性のあるエラーも処理できる。
void HttpWindow::sslErrors(const QList<QSslError> &errors) { QString errorString; for (const QSslError &error : errors) { if (!errorString.isEmpty()) errorString += '\n'; errorString += error.errorString(); } if (QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("TLS Errors"), tr("One or more TLS errors has occurred:\n%1").arg(errorString), QMessageBox::Ignore | QMessageBox::Abort) == QMessageBox::Ignore) { reply->ignoreSslErrors(); } }
この例では、ユーザーにダイアログを表示して、エラーを無視するかどうかを選択できるようにしています。
QNetworkReply::NetworkError error = reply->error(); const QString &errorString = reply->errorString(); if (error != QNetworkReply::NoError) { QFile::remove(fi.absoluteFilePath()); // For "request aborted" we handle the label and button in cancelDownload() if (!httpRequestAborted) { statusLabel->setText(tr("Download failed:\n%1.").arg(errorString)); downloadButton->setEnabled(true); } return; }
エラーが発生すると、QNetworkReply がQNetworkReply::errorOccurred() シグナルを発し、続いてQNetworkReply::finished() シグナルを発する。この例では、後者にのみ接続する。それぞれのスロットで潜在的なエラーが発生した場合は、書き込み先のファイルを削除して処理し、ステータス・ラベルでエラーを表示します。
connect(&qnam, &QNetworkAccessManager::authenticationRequired, this, &HttpWindow::slotAuthenticationRequired);
HTTP認証を使用するWebサイトに接続する場合、事前に使用すべき認証情報を与えなかったと仮定すると、Webサイトが認証情報を要求したときに、足りない認証情報を処理することができる。QNetworkAccessManager では、シグナルQNetworkAccessManager::authenticationRequired() に接続されたスロットでこれを行う。この接続はコンストラクタで一度だけ行います。
void HttpWindow::slotAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkReply *, QAuthenticator *authenticator) { QDialog authenticationDialog; Ui::Dialog ui; ui.setupUi(&authenticationDialog); authenticationDialog.adjustSize(); ui.siteDescription->setText(tr("%1 at %2").arg(authenticator->realm(), url.host())); // Did the URL have information? Fill the UI. // This is only relevant if the URL-supplied credentials were wrong ui.userEdit->setText(url.userName()); ui.passwordEdit->setText(url.password()); if (authenticationDialog.exec() == QDialog::Accepted) { authenticator->setUser(ui.userEdit->text()); authenticator->setPassword(ui.passwordEdit->text()); } }
この例では、ユーザがユーザ名とパスワードを入力するか、キャンセルするかのダイアログを表示します。キャンセルすると、リクエストは失敗する。
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

