Qt Quick 3D - 屏幕空间反射示例
演示Qt Quick 3D 中的反射。
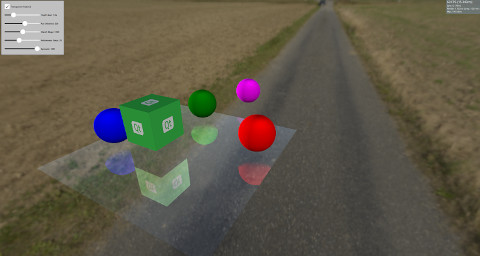
本例演示如何使用屏幕空间反射(SSR) 在模型上创建反射效果。屏幕空间反射是一种后处理效果,可以通过添加反射来增强场景效果。SSR 的原理是在渲染物体后在屏幕空间中计算反射。对于每个片段,从摄像机向该片段发射一条射线,然后在片段的法线周围进行反射。之后,我们会跟踪反射的光线,判断它是否会击中某个物体。如果有物体被击中,那么片段就会反射这个物体。在某些情况下,SSR 会失效。例如,当反射光线击中摄像机后面的物体时。由于反射是在渲染物体后在屏幕空间中计算的,因此无法获得摄像机后面物体的颜色信息。虽然 SSR 有一些缺点,但它能增加场景的真实感。
本示例使用Custom Materials 实现 SSR,可用于Model ,使其反射周围环境。
Model { source: "#Rectangle" scale: Qt.vector3d(5, 5, 5) eulerRotation.x: -90 eulerRotation.z: 180 position: Qt.vector3d(0.0, -50.0, 0.0) materials: ScreenSpaceReflections { depthBias: depthBiasSlider.value rayMaxDistance: distanceSlider.value marchSteps: marchSlider.value refinementSteps: refinementStepsSlider.value specular: specularSlider.value materialColor: materialColorCheckBox.checked ? "transparent" : "dimgray" } }
场景的其余部分有一些物体,它们要么静止不动,要么在表面上方旋转,以显示反射效果。
Node { Model { source: "#Cube" eulerRotation.y: 0 scale: Qt.vector3d(1, 1, 1) position: Qt.vector3d(50.0, 40.0, 50.0) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColorMap: Texture { source: "qt_logo_rect.png" } } } Node{ Model { source: "#Sphere" position: Qt.vector3d(-400.0, screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelHeight, 0.0) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "magenta" } } } Node{ eulerRotation.y: screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelRotation position.y: screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelHeight Model { source: "#Sphere" pivot: Qt.vector3d(0, 0.0, 0.0) position: Qt.vector3d(200.0, 0.0, 0.0) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } } } Node{ eulerRotation.y: screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelRotation position.y: screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelHeight Model { source: "#Sphere" eulerRotation.y: 45 position: Qt.vector3d(0.0, 0.0, -200.0) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "blue" } } } Node{ eulerRotation.y: screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelRotation position.y: screenSpaceReflectionsView.modelHeight Model { source: "#Sphere" position: Qt.vector3d(0.0, 0.0, 200.0) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "red" } } }
着色器代码
在深入学习着色器代码之前,让我们先检查一下可用于控制反射的一些参数。
depthBias | 该参数用于检查光线与物体之间的深度差是否在某个阈值范围内。 |
rayMaxDistance | 控制光线终点在视图空间中的距离。 |
marchSteps | 控制计算的步数。增加步数可以减少每次迭代中射线移动的碎片数量,提高质量。 |
refinementSteps | 在找到反射光线击中物体的位置后,会进行细化处理,尝试找到击中的准确位置。该参数可以控制应该使用多少步。当marchSteps 较小的时候,它可以得到更好的结果。 |
specular | 一个介于 0 和 1 之间的值,用于控制模型的反射率。 |
materialColor | 为模型赋予颜色。该颜色与反射颜色相混合。 |
着色器首先会获取从摄像机到片段的方向,然后围绕片段的法线进行反射。射线的起点和终点在视图空间中计算,然后将这些点转换到屏幕空间。在屏幕空间中行进反射光线的好处是可以获得更好的质量。此外,光线在视图空间中可以覆盖很长的距离,但在屏幕空间中只能覆盖几个片段。
计算从起始片段指向终止片段的矢量并除以marchSteps 。
之后调用rayMarch 函数。它将射线在屏幕空间中移动每一步,然后将其转换回视图空间。它还会使用场景的DEPTH_TEXTURE 获取该片段中的物体。计算光线和物体深度之间的差值,并与depthBias 进行比较。如果发现命中,则调用refinementStep 函数。
void rayMarch(vec2 rayStepVector, vec2 size)
{
for(int i = 0; i < marchSteps; i++)
{
rayData.rayFragCurr += rayStepVector;
rayData.rayCoveredPart = length(rayData.rayFragCurr - rayData.rayFragStart) / length(rayData.rayFragEnd - rayData.rayFragStart);
rayData.rayCoveredPart = clamp(rayData.rayCoveredPart, 0.0, 1.0);
float rayDepth = rayViewDepthFromScreen(size);
rayData.objHitViewPos = viewPosFromScreen(rayData.rayFragCurr, size);
float deltaDepth = rayDepth - rayData.objHitViewPos.z;
if(deltaDepth > 0 && deltaDepth < depthBias)
{
rayData.hit = 1;
refinementStep(rayStepVector, size);
return;
}
}
}细化步骤与rayMarch 相同,只是它试图找到撞击发生的准确位置,因此每迭代一次都会将射线前进一半的距离。
void refinementStep(vec2 rayStepVector, vec2 size)
{
for(int i = 0; i < refinementSteps; i++)
{
rayData.rayCoveredPart = length(rayData.rayFragCurr - rayData.rayFragStart) / length(rayData.rayFragEnd - rayData.rayFragStart);
rayData.rayCoveredPart = clamp(rayData.rayCoveredPart, 0.0, 1.0);
float rayDepth = rayViewDepthFromScreen(size);
rayData.objHitViewPos = viewPosFromScreen(rayData.rayFragCurr, size);
float deltaDepth = rayDepth - rayData.objHitViewPos.z;
rayStepVector *= 0.5;
if(deltaDepth > 0 && deltaDepth < depthBias)
rayData.rayFragCurr -= rayStepVector;
else
rayData.rayFragCurr += rayStepVector;
}
}反射的可见度被设置为命中值,之后会进行一些可见度检查。如前所述,如果反射光线击中了摄像机后面的东西,SSR 就会失败,因此会根据反射光线朝向摄像机的方向逐渐减弱可见度。能见度也会根据被击中物体距离射线起点的远近而减弱。
float visibility = rayData.hit; /* Check if the ray hit an object behind the camera. This means information about the object can not be obtained from SCREEN_TEXTURE. Start fading the visibility according to how much the reflected ray is moving toward the opposite direction of the camera */ visibility *= (1 - max(dot(-normalize(fragViewPos), reflected), 0)); /* Fade out visibility according how far is the hit object from the fragment */ visibility *= (1 - clamp(length(rayData.objHitViewPos - rayData.rayViewStart) / rayMaxDistance, 0, 1)); visibility = clamp(visibility, 0, 1);
最后,根据SCREEN_TEXTURE 计算出反射颜色,并与材质颜色混合。
vec2 uv = rayData.rayFragCurr / size; uv = correctTextureCoordinates(uv); vec3 reflectionColor = texture(SCREEN_TEXTURE, uv).rgb; reflectionColor *= specular; vec3 mixedColor = mix(materialColor.rgb, reflectionColor, visibility); BASE_COLOR = vec4(mixedColor, materialColor.a);
辅助函数
着色器代码中使用了一些辅助函数。correctTextureCoordinates 函数根据所使用的图形 API 固定纹理坐标。在使用 D3D11 或 Metal 时必须这样做。更多信息,请参阅CustomMaterial 文档。
vec2 correctTextureCoordinates(vec2 uv)
{
if(FRAMEBUFFER_Y_UP < 0 && NDC_Y_UP == 1)
uv.y = 1 - uv.y;
return uv;
}rayFragOutOfBound 函数检查光线在行进后是否超出屏幕。在这种情况下,不会使用反射颜色,因为没有屏幕外的任何信息。
bool rayFragOutOfBound(vec2 rayFrag, vec2 size)
{
if(rayFrag.x > size.x || rayFrag.y > size.y)
return true;
if(rayFrag.x < 0 || rayFrag.y < 0)
return true;
return false;
}viewPosFromScreen 函数通过使用DEPTH_TEXTURE 获取对象在视图空间中的位置。
vec3 viewPosFromScreen(vec2 fragPos, vec2 size)
{
vec2 uv = fragPos / size;
vec2 texuv = correctTextureCoordinates(uv);
float depth = textureLod(DEPTH_TEXTURE, texuv, 0).r;
if(NEAR_CLIP_VALUE < 0.0)
depth = 2 * depth - 1.0;
vec3 ndc = vec3(2 * uv - 1, depth);
vec4 viewPos = INVERSE_PROJECTION_MATRIX * vec4(ndc, 1.0);
viewPos /= viewPos.w;
return viewPos.xyz;
}rayViewDepthFromScreen 函数获取射线在视图空间中的当前位置。这次的深度值是通过对射线起点深度和终点深度之间的值进行线性插值得到的。
float rayViewDepthFromScreen(vec2 size)
{
vec2 uv = rayData.rayFragCurr / size;
float depth = mix(rayData.rayFragStartDepth, rayData.rayFragEndDepth, rayData.rayCoveredPart);
vec3 ndc = vec3(2 * uv - 1, depth);
vec4 viewPos = INVERSE_PROJECTION_MATRIX * vec4(ndc, 1.0);
viewPos /= viewPos.w;
return viewPos.z;
}© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

