Qt Quick 3D 物理 - 大炮示例
演示如何生成物理对象。
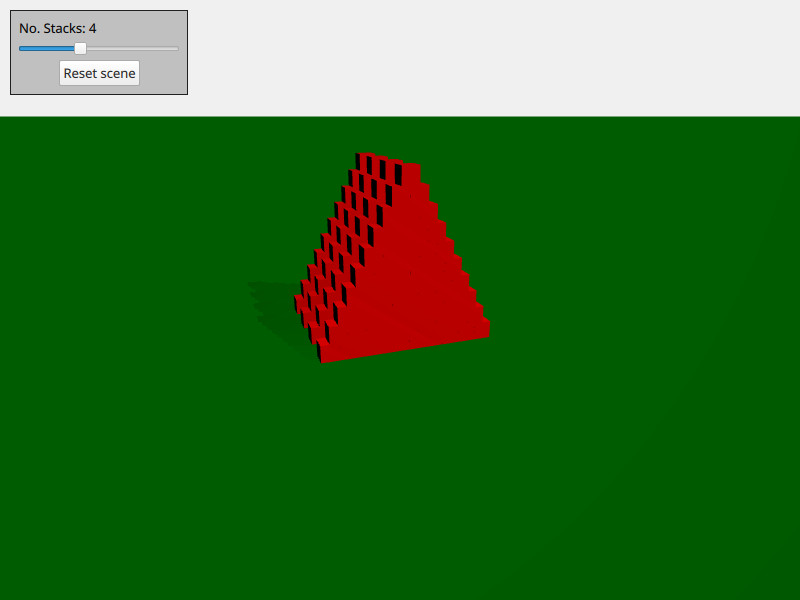
本示例演示如何按需创建和删除物理对象。场景由若干堆叠的盒子组成。您可以使用WASD 和鼠标进行移动,按space 可以发射小球。
场景的设置包括视图、摄像机和灯光等常用Qt Quick 3D 对象:
PerspectiveCamera { id: camera position: Qt.vector3d(-4000, 5000, 10000) eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-20, -20, 0) clipFar: 200000 clipNear: 100 } DirectionalLight { eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-45, 45, 0) castsShadow: true brightness: 1 shadowMapQuality: Light.ShadowMapQualityVeryHigh shadowMapFar: camera.clipFar shadowFactor: 50 csmNumSplits: 2 csmSplit1: 0.1 csmSplit2: 0.3 softShadowQuality: Light.PCF4 }
我们还添加了一个静态地板:
StaticRigidBody { eulerRotation: Qt.vector3d(-90, 0, 0) collisionShapes: PlaneShape {} Model { source: "#Rectangle" scale: Qt.vector3d(2000, 2000, 1) materials: PrincipledMaterial { baseColor: "green" } castsShadows: false receivesShadows: true } }
我们创建了一个节点(Node),用作对象的产卵器,并将其置于视图中:
Node { id: shapeSpawner property var instancesBoxes: [] property var instancesSpheres: [] property int stackCount: 0 property var boxComponent: Qt.createComponent("Box.qml") property var sphereComponent: Qt.createComponent("Sphere.qml") function createStack(stackZ, numStacks) { let size = 10 let extents = 400 for (var i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (var j = 0; j < size - i; j++) { let x = j * 2 - size + i let y = i * 2 + 1 let z = 5 * (stackZ - numStacks) let center = Qt.vector3d(x, y, z).times(0.5 * extents) let box = boxComponent.incubateObject(shapeSpawner, { "position": center, "xyzExtents": extents }) instancesBoxes.push(box) } } } function createBall(position, forward) { var diameter = 600 var speed = 20000 let settings = { "position": position, "sphereDiameter": diameter } let sphere = sphereComponent.createObject(shapeSpawner, settings) sphere.setLinearVelocity(forward.times(speed)) instancesSpheres.push(sphere) if (sphere === null) { console.log("Error creating object") } } function reset() { // Only run method if previous stack has been created fully for (var i = 0; i < instancesBoxes.length; i++) if (!instancesBoxes[i].object) return instancesSpheres.forEach(sphere => { sphere.collisionShapes = [] sphere.destroy() }) instancesBoxes.forEach(box => { box.object.collisionShapes = [] box.object.destroy() }) instancesSpheres = [] instancesBoxes = [] for (var stackI = 0; stackI < stackSlider.value; stackI++) { shapeSpawner.createStack(stackI, stackSlider.value) } } }
我们有三个方法:createStack 用于创建堆栈,createBall 用于创建带速度的球,reset 用于重置场景。实际生成的盒子和球体存储在各自的 qml 文件中(box.qml 和sphere.qml )。
文件:
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

