QAbstractSpinBox¶
The QAbstractSpinBox class provides a spinbox and a line edit to display values. More…
Inherited by: QSpinBox, QDoubleSpinBox, QDateTimeEdit, QTimeEdit, QDateEdit
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
def
alignment()def
buttonSymbols()def
correctionMode()def
hasAcceptableInput()def
hasFrame()def
interpretText()def
isAccelerated()def
isGroupSeparatorShown()def
isReadOnly()def
keyboardTracking()def
lineEdit()def
setAccelerated(on)def
setAlignment(flag)def
setButtonSymbols(bs)def
setCorrectionMode(cm)def
setFrame(arg__1)def
setGroupSeparatorShown(shown)def
setKeyboardTracking(kt)def
setLineEdit(edit)def
setReadOnly(r)def
setSpecialValueText(txt)def
setWrapping(w)def
specialValueText()def
text()def
wrapping()
Virtual functions¶
def
clear()def
fixup(input)def
initStyleOption(option)def
stepBy(steps)def
stepEnabled()def
validate(input, pos)
Slots¶
Signals¶
def
editingFinished()
Detailed Description¶
The class is designed as a common super class for widgets like QSpinBox , QDoubleSpinBox and QDateTimeEdit
Here are the main properties of the class:
text: The text that is displayed in theQAbstractSpinBox.alignment : The alignment of the text in the
QAbstractSpinBox.
wrapping: Whether theQAbstractSpinBoxwraps from the minimum value to the maximum value and vice versa.
QAbstractSpinBox provides a virtual stepBy() function that is called whenever the user triggers a step. This function takes an integer value to signify how many steps were taken. E.g. Pressing Key_Down will trigger a call to stepBy (-1).
When the user triggers a step whilst holding the ControlModifier , QAbstractSpinBox steps by 10 instead of making a single step. This step modifier affects wheel events, key events and interaction with the spinbox buttons. Note that on macOS, Control corresponds to the Command key.
Since Qt 5.12, SH_SpinBox_StepModifier can be used to select which KeyboardModifier increases the step rate. NoModifier disables this feature.
QAbstractSpinBox also provide a virtual function stepEnabled() to determine whether stepping up/down is allowed at any point. This function returns a bitset of StepEnabled .
- class PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox([parent=None])¶
- Parameters
parent –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Constructs an abstract spinbox with the given parent with default wrapping , and alignment properties.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.StepEnabledFlag¶
Constant
Description
QAbstractSpinBox.StepNone
QAbstractSpinBox.StepUpEnabled
QAbstractSpinBox.StepDownEnabled
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.ButtonSymbols¶
This enum type describes the symbols that can be displayed on the buttons in a spin box.
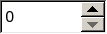
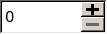
Constant
Description
QAbstractSpinBox.UpDownArrows
Little arrows in the classic style.
QAbstractSpinBox.PlusMinus
+ and - symbols.
QAbstractSpinBox.NoButtons
Don’t display buttons.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.CorrectionMode¶
This enum type describes the mode the spinbox will use to correct an Intermediate value if editing finishes.
Constant
Description
QAbstractSpinBox.CorrectToPreviousValue
The spinbox will revert to the last valid value.
QAbstractSpinBox.CorrectToNearestValue
The spinbox will revert to the nearest valid value.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.StepType¶
Constant
Description
QAbstractSpinBox.DefaultStepType
QAbstractSpinBox.AdaptiveDecimalStepType
New in version 5.12.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.alignment()¶
- Return type
Alignment
This property holds the alignment of the spin box.
Possible Values are AlignLeft , AlignRight , and AlignHCenter .
By default, the alignment is AlignLeft
Attempting to set the alignment to an illegal flag combination does nothing.
See also
Alignment
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.buttonSymbols()¶
- Return type
This property holds the current button symbol mode.
The possible values can be either UpDownArrows or PlusMinus. The default is UpDownArrows.
Note that some styles might render PlusMinus and UpDownArrows identically.
See also
ButtonSymbols
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.clear()¶
Clears the lineedit of all text but prefix and suffix.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.correctionMode()¶
- Return type
This property holds the mode to correct an Intermediate value if editing finishes.
The default mode is CorrectToPreviousValue .
See also
acceptableInputvalidate()fixup()
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.editingFinished()¶
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.fixup(input)¶
- Parameters
input – str
This virtual function is called by the QAbstractSpinBox if the input is not validated to Acceptable when Return is pressed or interpretText() is called. It will try to change the text so it is valid. Reimplemented in the various subclasses.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.hasAcceptableInput()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether the input satisfies the current validation.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.hasFrame()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether the spin box draws itself with a frame.
If enabled (the default) the spin box draws itself inside a frame, otherwise the spin box draws itself without any frame.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.initStyleOption(option)¶
- Parameters
Initialize option with the values from this QSpinBox . This method is useful for subclasses when they need a QStyleOptionSpinBox , but don’t want to fill in all the information themselves.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.interpretText()¶
This function interprets the text of the spin box. If the value has changed since last interpretation it will emit signals.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.isAccelerated()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether the spin box will accelerate the frequency of the steps when pressing the step Up/Down buttons..
If enabled the spin box will increase/decrease the value faster the longer you hold the button down.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.isGroupSeparatorShown()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether a thousands separator is enabled. By default this property is false..
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.isReadOnly()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether the spin box is read only..
In read-only mode, the user can still copy the text to the clipboard, or drag and drop the text; but cannot edit it.
The QLineEdit in the QAbstractSpinBox does not show a cursor in read-only mode.
See also
readOnly
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.keyboardTracking()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether keyboard tracking is enabled for the spinbox..
If keyboard tracking is enabled (the default), the spinbox emits the valueChanged() and textChanged() signals while the new value is being entered from the keyboard.
E.g. when the user enters the value 600 by typing 6, 0, and 0, the spinbox emits 3 signals with the values 6, 60, and 600 respectively.
If keyboard tracking is disabled, the spinbox doesn’t emit the valueChanged() and textChanged() signals while typing. It emits the signals later, when the return key is pressed, when keyboard focus is lost, or when other spinbox functionality is used, e.g. pressing an arrow key.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.lineEdit()¶
- Return type
This function returns a pointer to the line edit of the spin box.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.selectAll()¶
Selects all the text in the spinbox except the prefix and suffix.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setAccelerated(on)¶
- Parameters
on – bool
This property holds whether the spin box will accelerate the frequency of the steps when pressing the step Up/Down buttons..
If enabled the spin box will increase/decrease the value faster the longer you hold the button down.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setAlignment(flag)¶
- Parameters
flag –
Alignment
This property holds the alignment of the spin box.
Possible Values are AlignLeft , AlignRight , and AlignHCenter .
By default, the alignment is AlignLeft
Attempting to set the alignment to an illegal flag combination does nothing.
See also
Alignment
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setButtonSymbols(bs)¶
- Parameters
bs –
ButtonSymbols
This property holds the current button symbol mode.
The possible values can be either UpDownArrows or PlusMinus. The default is UpDownArrows.
Note that some styles might render PlusMinus and UpDownArrows identically.
See also
ButtonSymbols
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setCorrectionMode(cm)¶
- Parameters
cm –
CorrectionMode
This property holds the mode to correct an Intermediate value if editing finishes.
The default mode is CorrectToPreviousValue .
See also
acceptableInputvalidate()fixup()
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setFrame(arg__1)¶
- Parameters
arg__1 – bool
This property holds whether the spin box draws itself with a frame.
If enabled (the default) the spin box draws itself inside a frame, otherwise the spin box draws itself without any frame.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setGroupSeparatorShown(shown)¶
- Parameters
shown – bool
This property holds whether a thousands separator is enabled. By default this property is false..
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setKeyboardTracking(kt)¶
- Parameters
kt – bool
This property holds whether keyboard tracking is enabled for the spinbox..
If keyboard tracking is enabled (the default), the spinbox emits the valueChanged() and textChanged() signals while the new value is being entered from the keyboard.
E.g. when the user enters the value 600 by typing 6, 0, and 0, the spinbox emits 3 signals with the values 6, 60, and 600 respectively.
If keyboard tracking is disabled, the spinbox doesn’t emit the valueChanged() and textChanged() signals while typing. It emits the signals later, when the return key is pressed, when keyboard focus is lost, or when other spinbox functionality is used, e.g. pressing an arrow key.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setLineEdit(edit)¶
- Parameters
edit –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLineEdit
Sets the line edit of the spinbox to be lineEdit instead of the current line edit widget. lineEdit cannot be None.
QAbstractSpinBox takes ownership of the new lineEdit
If validator() for the lineEdit returns None, the internal validator of the spinbox will be set on the line edit.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setReadOnly(r)¶
- Parameters
r – bool
This property holds whether the spin box is read only..
In read-only mode, the user can still copy the text to the clipboard, or drag and drop the text; but cannot edit it.
The QLineEdit in the QAbstractSpinBox does not show a cursor in read-only mode.
See also
readOnly
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setSpecialValueText(txt)¶
- Parameters
txt – str
This property holds the special-value text.
If set, the spin box will display this text instead of a numeric value whenever the current value is equal to minimum(). Typical use is to indicate that this choice has a special (default) meaning.
For example, if your spin box allows the user to choose a scale factor (or zoom level) for displaying an image, and your application is able to automatically choose one that will enable the image to fit completely within the display window, you can set up the spin box like this:
zoomSpinBox = QSpinBox() zoomSpinBox.setRange(0, 1000) zoomSpinBox.setSingleStep(10) zoomSpinBox.setSuffix("%") zoomSpinBox.setSpecialValueText(tr("Automatic")) zoomSpinBox.setValue(100)
The user will then be able to choose a scale from 1% to 1000% or select “Auto” to leave it up to the application to choose. Your code must then interpret the spin box value of 0 as a request from the user to scale the image to fit inside the window.
All values are displayed with the prefix and suffix (if set), except for the special value, which only shows the special value text. This special text is passed in the textChanged() signal that passes a QString .
To turn off the special-value text display, call this function with an empty string. The default is no special-value text, i.e. the numeric value is shown as usual.
If no special-value text is set, returns an empty string.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.setWrapping(w)¶
- Parameters
w – bool
This property holds whether the spin box is circular..
If wrapping is true stepping up from maximum() value will take you to the minimum() value and vice versa. Wrapping only make sense if you have minimum() and maximum() values set.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.specialValueText()¶
- Return type
str
This property holds the special-value text.
If set, the spin box will display this text instead of a numeric value whenever the current value is equal to minimum(). Typical use is to indicate that this choice has a special (default) meaning.
For example, if your spin box allows the user to choose a scale factor (or zoom level) for displaying an image, and your application is able to automatically choose one that will enable the image to fit completely within the display window, you can set up the spin box like this:
zoomSpinBox = QSpinBox() zoomSpinBox.setRange(0, 1000) zoomSpinBox.setSingleStep(10) zoomSpinBox.setSuffix("%") zoomSpinBox.setSpecialValueText(tr("Automatic")) zoomSpinBox.setValue(100)
The user will then be able to choose a scale from 1% to 1000% or select “Auto” to leave it up to the application to choose. Your code must then interpret the spin box value of 0 as a request from the user to scale the image to fit inside the window.
All values are displayed with the prefix and suffix (if set), except for the special value, which only shows the special value text. This special text is passed in the textChanged() signal that passes a QString .
To turn off the special-value text display, call this function with an empty string. The default is no special-value text, i.e. the numeric value is shown as usual.
If no special-value text is set, returns an empty string.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.stepBy(steps)¶
- Parameters
steps – int
Virtual function that is called whenever the user triggers a step. The steps parameter indicates how many steps were taken. For example, pressing Qt::Key_Down will trigger a call to stepBy(-1), whereas pressing Qt::Key_PageUp will trigger a call to stepBy(10).
If you subclass QAbstractSpinBox you must reimplement this function. Note that this function is called even if the resulting value will be outside the bounds of minimum and maximum. It’s this function’s job to handle these situations.
See also
stepUp()stepDown()keyPressEvent()
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.stepDown()¶
Steps down by one linestep Calling this slot is analogous to calling stepBy (-1);
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.stepEnabled()¶
- Return type
StepEnabled
Virtual function that determines whether stepping up and down is legal at any given time.
The up arrow will be painted as disabled unless ( & StepUpEnabled ) != 0.
The default implementation will return ( StepUpEnabled | StepDownEnabled ) if wrapping is turned on. Else it will return StepDownEnabled if value is > minimum() or’ed with StepUpEnabled if value < maximum().
If you subclass QAbstractSpinBox you will need to reimplement this function.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.stepUp()¶
Steps up by one linestep Calling this slot is analogous to calling stepBy (1);
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.text()¶
- Return type
str
This property holds the spin box’s text, including any prefix and suffix.
There is no default text.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.validate(input, pos)¶
- Parameters
input – str
pos – int
- Return type
PyObject
This virtual function is called by the QAbstractSpinBox to determine whether input is valid. The pos parameter indicates the position in the string. Reimplemented in the various subclasses.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QAbstractSpinBox.wrapping()¶
- Return type
bool
This property holds whether the spin box is circular..
If wrapping is true stepping up from maximum() value will take you to the minimum() value and vice versa. Wrapping only make sense if you have minimum() and maximum() values set.
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
