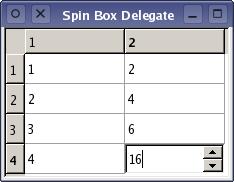
Spin Box Delegate Example¶
The Spin Box Delegate example shows how to create an editor for a custom delegate in the model/view framework by reusing a standard Qt editor widget.
The model/view framework provides a standard delegate that is used by default with the standard view classes. For most purposes, the selection of editor widgets available through this delegate is sufficient for editing text, boolean values, and other simple data types. However, for specific data types, it is sometimes necessary to use a custom delegate to either display the data in a specific way, or allow the user to edit it with a custom control.
This concepts behind this example are covered in the Delegate Classes chapter of the Model/View Programming overview.
SpinBoxDelegate Class Definition¶
The definition of the delegate is as follows:
class SpinBoxDelegate(QStyledItemDelegate): Q_OBJECT # public SpinBoxDelegate(QObject parent = None) createEditor(QWidget = QWidget() index) = QModelIndex() def setEditorData(editor, index): def setModelData(editor, model,): index) = QModelIndex() def updateEditorGeometry(editor, option,): index) = QModelIndex()
The delegate class declares only those functions that are needed to create an editor widget, display it at the correct location in a view, and communicate with a model. Custom delegates can also provide their own painting code by reimplementing the paintEvent() function. Furthermore it is also possible to reuse (and avoid deleting) the editor widget by reimplementing the destroyEditor() function. A reused widget could be a mutable member created in the constructor and deleted in the destructor.
SpinBoxDelegate Class Implementation¶
Delegates are often stateless. The constructor only needs to call the base class’s constructor with the parent QObject as its argument:
def __init__(self, parent): QStyledItemDelegate.__init__(self, parent)
Since the delegate is a subclass of QStyledItemDelegate , the data it retrieves from the model is displayed in a default style, and we do not need to provide a custom paintEvent().
The createEditor() function returns an editor widget, in this case a spin box that restricts values from the model to integers from 0 to 100 inclusive.
SpinBoxDelegate::createEditor(QWidget = QWidget() /* = QStyleOptionViewItem() /* = QModelIndex() editor = QSpinBox(parent) editor.setFrame(False) editor.setMinimum(0) editor.setMaximum(100) return editor
We install an event filter on the spin box to ensure that it behaves in a way that is consistent with other delegates. The implementation for the event filter is provided by the base class.
The setEditorData() function reads data from the model, converts it to an integer value, and writes it to the editor widget.
def setEditorData(self, editor,): index) = QModelIndex() value = index.model().data(index, Qt.EditRole).toInt() spinBox = QSpinBox(editor) spinBox.setValue(value)
Since the view treats delegates as ordinary QWidget instances, we have to use a static cast before we can set the value in the spin box.
The setModelData() function reads the contents of the spin box, and writes it to the model.
def setModelData(self, editor, model,): index) = QModelIndex() spinBox = QSpinBox(editor) spinBox.interpretText() value = spinBox.value() model.setData(index, value, Qt.EditRole)
We call interpretText() to make sure that we obtain the most up-to-date value in the spin box.
The updateEditorGeometry() function updates the editor widget’s geometry using the information supplied in the style option. This is the minimum that the delegate must do in this case.
def updateEditorGeometry(self, editor,): option, = QStyleOptionViewItem() /* = QModelIndex() editor.setGeometry(option.rect)
More complex editor widgets may divide the rectangle available in option.rect between different child widgets if required.
The Main Function¶
This example is written in a slightly different way to many of the other examples supplied with Qt. To demonstrate the use of a custom editor widget in a standard view, it is necessary to set up a model containing some arbitrary data and a view to display it.
We set up the application in the normal way, construct a standard item model to hold some data, set up a table view to use the data in the model, and construct a custom delegate to use for editing:
if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication([]) model = QStandardItemModel(4, 2) tableView = QTableView() tableView.setModel(model) delegate = SpinBoxDelegate() tableView.setItemDelegate(delegate)
The table view is informed about the delegate, and will use it to display each of the items. Since the delegate is a subclass of QStyledItemDelegate , each cell in the table will be rendered using standard painting operations.
We insert some arbitrary data into the model for demonstration purposes:
for row in range(0, 4): for column in range(0, 2): index = model.index(row, column, QModelIndex()) model.setData(index, QVariant((row + 1) * (column + 1)))
Finally, the table view is displayed with a window title, and we start the application’s event loop:
tableView.setWindowTitle(QObject.tr("Spin Box Delegate")) tableView.show() sys.exit(app.exec())
Each of the cells in the table can now be edited in the usual way, but the spin box ensures that the data returned to the model is always constrained by the values allowed by the spin box delegate.
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.