Using a Simple Button#
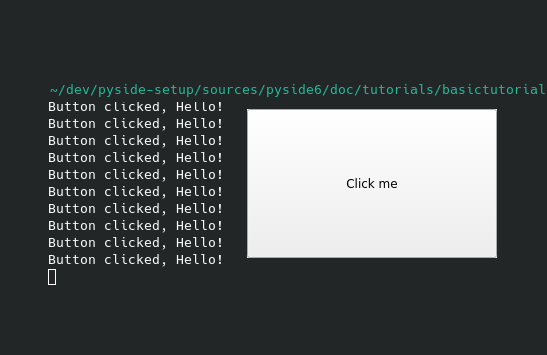
In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to handle signals and slots using Qt for Python. Signals and slots is a Qt feature that lets your graphical widgets communicate with other graphical widgets or your python code. Our application creates a button that logs the Button clicked, Hello! message to the python console each time you click it.
Let’s start by importing the necessary PySide6 classes and python sys module:
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QPushButton
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot
Let’s also create a python function that logs the message to the console:
# Greetings
@Slot()
def say_hello():
print("Button clicked, Hello!")
Note
The @Slot() is a decorator that identifies a function as a slot. It is not important to understand why for now, but use it always to avoid unexpected behavior.
Now, as mentioned in previous examples you must create the QApplication to run your PySide6 code:
# Create the Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
Let’s create the clickable button, which is a QPushButton instance. To label the button, we pass a python string to the constructor:
# Create a button
button = QPushButton("Click me")
Before we show the button, we must connect it to the say_hello() function that we defined earlier. There are two ways of doing this; using the old style or the new style, which is more pythonic. Let’s use the new style in this case. You can find more information about both these styles in the Signals and Slots in PySide6 wiki page.
The QPushButton has a predefined signal called clicked, which is triggered every time the button is clicked. We’ll connect this signal to the say_hello() function:
# Connect the button to the function
button.clicked.connect(say_hello)
Finally, we show the button and start the Qt main loop:
# Show the button
button.show()
# Run the main Qt loop
app.exec()
Here is the complete code for this example:
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QPushButton
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot
@Slot()
def say_hello():
print("Button clicked, Hello!")
# Create the Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# Create a button, connect it and show it
button = QPushButton("Click me")
button.clicked.connect(say_hello)
button.show()
# Run the main Qt loop
app.exec()
After a few clicks, you will get something like this on your terminal: