Displaying Data Using a Tree Widget#
If you want to display data arranged in a tree, use a QTreeWidget to do so.
Notice that using a QTreeWidget is not the only path to display
information in trees. You can also create a data model and display it using a
QTreeView, but that is not in the scope of this tutorial.
Note
This Widget is a ready-to-use version of something you can customize further on. To know more about the Model/View architecture in Qt, refer to its official documentation.
Import
QTreeWidgetandQTreeWidgetItemfor this application:import sys from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QTreeWidget, QTreeWidgetItem
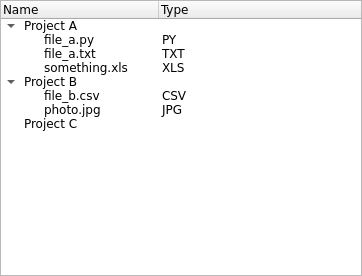
Define a dictionary with project structures to display the information as a tree, with files belonging to each project:
data = {"Project A": ["file_a.py", "file_a.txt", "something.xls"], "Project B": ["file_b.csv", "photo.jpg"], "Project C": []}
Initialize the
QApplicationsingleton:app = QApplication()
Configure the
QTreeWidgetto have two columns, one for the item name, and the other for item type information of the files in the project directories. You can set the column name with thesetHeaderLabelsas described below:tree = QTreeWidget() tree.setColumnCount(2) tree.setHeaderLabels(["Name", "Type"])
Iterate the data structure, create the
QTreeWidgetItemelements, and add the corresponding children to each parent. We also extract the extension name for only the files and add them into the second column. In the constructor, you can see that each element (QTreeWidgetItem) is added to different columns of the tree (QTreeWidget).items = [] for key, values in data.items(): item = QTreeWidgetItem([key]) for value in values: ext = value.split(".")[-1].upper() child = QTreeWidgetItem([value, ext]) item.addChild(child) items.append(item) tree.insertTopLevelItems(0, items)
Show the tree and execute the
QApplication.tree.show() sys.exit(app.exec())
The final application will look like this: