Qml オシロスコープ
この例では、Qt Charts QML API を使用して、厳密な性能が要求されるアプリケーションを実装する方法を示します。
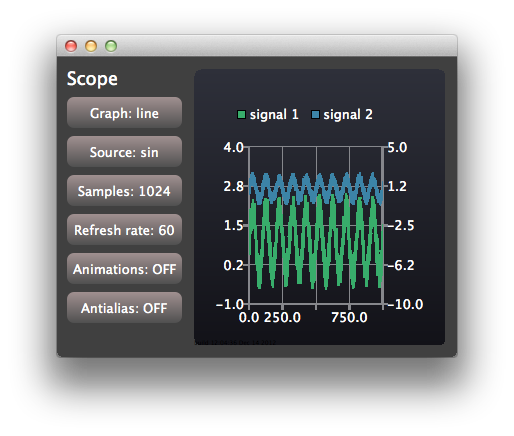
このオシロスコープ・アプリケーションは、Qt Charts QML API を使用して、厳しい性能要件を満たすアプリケーションを実装する方法を示しています。このアプリケーションは、シンプルなオシロスコープのユーザーインターフェースを模倣するために、設定可能な特性を持つ生成データを使用します。
アプリケーションの出力コンソールに表示される実際のレンダリング速度に関する情報を得るには、QSG_RENDER_TIMING = 1を実行環境設定に設定します。これを行うには、Qt Creator の Projects - Run - Run environment を開き、Add を選択します。その後、サンプルアプリケーションの様々な設定可能なオプションを試して、あなたの環境で最高のパフォーマンスが得られる設定を見つけることができます。
サンプルを実行する
からサンプルを実行するには Qt Creatorからサンプルを実行するには、Welcome モードを開き、Examples からサンプルを選択します。詳細については、Qt Creator:Tutorialを参照してください:ビルドと実行を参照してください。
ビューの作成
アプリケーションウィンドウは、コントロールビューとスコープビューによって共有されます:
Item { id: main width: 600 height: 400 ControlPanel { id: controlPanel anchors.top: parent.top anchors.topMargin: 10 anchors.bottom: parent.bottom anchors.left: parent.left anchors.leftMargin: 10 ... ScopeView { id: scopeView anchors.top: parent.top anchors.bottom: parent.bottom anchors.right: parent.right anchors.left: controlPanel.right height: main.height }
ControlViewは、コンフィギュレーションに使用するボタンを実装しています。ScopeViewはChartView 、2つの折れ線グラフを表示します:
ChartView { id: chartView property bool openGL: openGLSupported animationOptions: ChartView.NoAnimation theme: ChartView.ChartThemeDark onOpenGLChanged: { if (openGLSupported) { var series1 = series("signal 1") if (series1) series1.useOpenGL = openGL; var series2 = series("signal 2") if (series2) series2.useOpenGL = openGL; } } ValueAxis { id: axisY1 min: -1 max: 4 } ValueAxis { id: axisY2 min: -10 max: 5 } ValueAxis { id: axisX min: 0 max: 1024 } LineSeries { id: lineSeries1 name: "signal 1" axisX: axisX axisY: axisY1 useOpenGL: chartView.openGL } LineSeries { id: lineSeries2 name: "signal 2" axisX: axisX axisYRight: axisY2 useOpenGL: chartView.openGL } ...
折れ線グラフのデータは QML タイマーで更新されます。実際のアプリケーションでは、Qt C++ コードからの信号で更新をトリガーすることができます。
Timer { id: refreshTimer interval: 1 / 60 * 1000 // 60 Hz running: true repeat: true onTriggered: { dataSource.update(chartView.series(0)); dataSource.update(chartView.series(1)); } }
オシロスコープでは、信号源の可視化に使用する系列の種類を切り替えることもできます。これは、シリーズの動的な破棄と作成によって実装されています:
function changeSeriesType(type) { chartView.removeAllSeries(); // Create two new series of the correct type. Axis x is the same for both of the series, // but the series have their own y-axes to make it possible to control the y-offset // of the "signal sources". var series1 var series2 if (type === "line") { series1 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeLine, "signal 1", axisX, axisY1); series1.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL series2 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeLine, "signal 2", axisX, axisY2); series2.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL } else { series1 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeScatter, "signal 1", axisX, axisY1); series1.markerSize = 2; series1.borderColor = "transparent"; series1.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL series2 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeScatter, "signal 2", axisX, axisY2); series2.markerSize = 2; series2.borderColor = "transparent"; series2.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL } } function createAxis(min, max) { // The following creates a ValueAxis object that can be then set as a x or y axis for a series return Qt.createQmlObject("import QtQuick 2.0; import QtCharts 2.0; ValueAxis { min: " + min + "; max: " + max + " }", chartView); }
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

