Qml 示波器
该示例展示了如何使用Qt Charts QML API 实现具有严格性能要求的应用程序。
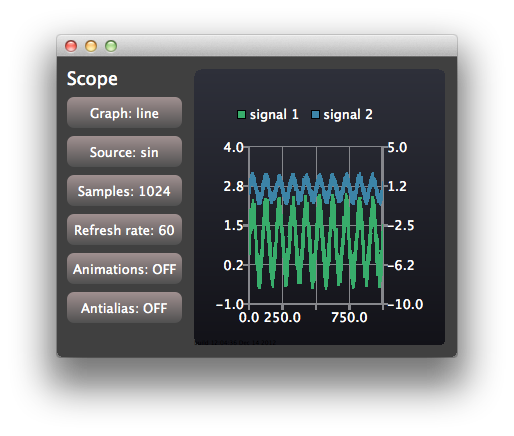
示波器应用程序演示了如何使用Qt Charts QML API 实现具有严格性能要求的应用程序。该应用程序使用具有可配置特性的生成数据来模拟简单的示波器用户界面。
要获取应用程序输出控制台中显示的实际渲染速度信息,可以在运行环境设置中设置 QSG_RENDER_TIMING = 1。为此,请进入Qt Creator 的项目 - 运行 - 运行环境并选择添加。然后,您可以尝试使用示例应用程序的不同可配置选项,以找到能在您的环境中实现最佳性能的配置。
运行示例
要从 Qt Creator,打开Welcome 模式并从Examples 中选择示例。更多信息,请参阅Qt Creator: 教程:构建并运行。
创建视图
应用程序窗口由控制视图和作用域视图共享:
Item { id: main width: 600 height: 400 ControlPanel { id: controlPanel anchors.top: parent.top anchors.topMargin: 10 anchors.bottom: parent.bottom anchors.left: parent.left anchors.leftMargin: 10 ... ScopeView { id: scopeView anchors.top: parent.top anchors.bottom: parent.bottom anchors.right: parent.right anchors.left: controlPanel.right height: main.height }
ControlView 实现了用于配置的按钮。ScopeView 使用ChartView 显示带有两个线性序列的图表:
ChartView { id: chartView property bool openGL: openGLSupported animationOptions: ChartView.NoAnimation theme: ChartView.ChartThemeDark onOpenGLChanged: { if (openGLSupported) { var series1 = series("signal 1") if (series1) series1.useOpenGL = openGL; var series2 = series("signal 2") if (series2) series2.useOpenGL = openGL; } } ValueAxis { id: axisY1 min: -1 max: 4 } ValueAxis { id: axisY2 min: -10 max: 5 } ValueAxis { id: axisX min: 0 max: 1024 } LineSeries { id: lineSeries1 name: "signal 1" axisX: axisX axisY: axisY1 useOpenGL: chartView.openGL } LineSeries { id: lineSeries2 name: "signal 2" axisX: axisX axisYRight: axisY2 useOpenGL: chartView.openGL } ...
线性序列的数据通过 QML 定时器更新。在实际应用中,可通过 Qt C++ 代码的信号触发更新。
Timer { id: refreshTimer interval: 1 / 60 * 1000 // 60 Hz running: true repeat: true onTriggered: { dataSource.update(chartView.series(0)); dataSource.update(chartView.series(1)); } }
示波器还允许切换用于可视化信号源的系列类型。这是通过动态销毁和创建序列来实现的:
function changeSeriesType(type) { chartView.removeAllSeries(); // Create two new series of the correct type. Axis x is the same for both of the series, // but the series have their own y-axes to make it possible to control the y-offset // of the "signal sources". var series1 var series2 if (type === "line") { series1 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeLine, "signal 1", axisX, axisY1); series1.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL series2 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeLine, "signal 2", axisX, axisY2); series2.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL } else { series1 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeScatter, "signal 1", axisX, axisY1); series1.markerSize = 2; series1.borderColor = "transparent"; series1.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL series2 = chartView.createSeries(ChartView.SeriesTypeScatter, "signal 2", axisX, axisY2); series2.markerSize = 2; series2.borderColor = "transparent"; series2.useOpenGL = chartView.openGL } } function createAxis(min, max) { // The following creates a ValueAxis object that can be then set as a x or y axis for a series return Qt.createQmlObject("import QtQuick 2.0; import QtCharts 2.0; ValueAxis { min: " + min + "; max: " + max + " }", chartView); }
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

