PySide6.QtGui.QRegion¶
- class QRegion¶
The
QRegionclass specifies a clip region for a painter. More…Synopsis¶
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
__getitem__()def
__len__()def
begin()def
boundingRect()def
cbegin()def
cend()def
contains()def
end()def
intersected()def
intersects()def
isEmpty()def
isNull()def
__ne__()def
__and__()def
__mul__()def
__add__()def
__iadd__()def
__sub__()def
__isub__()def
__eq__()def
__xor__()def
__ixor__()def
__or__()def
__ior__()def
rectCount()def
setRects()def
subtracted()def
swap()def
translate()def
translated()def
united()def
xored()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
QRegionis used withsetClipRegion()to limit the paint area to what needs to be painted. There is also a QWidget::repaint() function that takes aQRegionparameter.QRegionis the best tool for minimizing the amount of screen area to be updated by a repaint.This class is not suitable for constructing shapes for rendering, especially as outlines. Use
QPainterPathto create paths and shapes for use withQPainter.QRegionis an implicitly shared class.Creating and Using Regions¶
A region can be created from a rectangle, an ellipse, a polygon or a bitmap. Complex regions may be created by combining simple regions using
united(),intersected(),subtracted(), orxored()(exclusive or). You can move a region usingtranslate().You can test whether a region
isEmpty()or if itcontains()a QPoint or QRect. The bounding rectangle can be found withboundingRect().Iteration over the region (with
begin(),end(), or ranged-for loops) gives a decomposition of the region into rectangles.Example of using complex regions:
def paintEvent(self, arg__0): QRegion r1(QRect(100, 100, 200, 80), // r1: elliptic region QRegion.Ellipse) QRegion r2(QRect(100, 120, 90, 30)) # r2: rectangular region r3 = r1.intersected(r2) # r3: intersection painter = QPainter(self) painter.setClipRegion(r3) # ... // paint clipped graphics
See also
- class RegionType¶
Specifies the shape of the region to be created.
Constant
Description
QRegion.Rectangle
the region covers the entire rectangle.
QRegion.Ellipse
the region is an ellipse inside the rectangle.
- __init__()¶
Constructs an empty region.
See also
- __init__(bitmap)
- Parameters:
bitmap –
QBitmap
Constructs a region from the bitmap
bm.The resulting region consists of the pixels in bitmap
bmthat are Qt::color1, as if each pixel was a 1 by 1 rectangle.This constructor may create complex regions that will slow down painting when used. Note that drawing masked pixmaps can be done much faster using
setMask().- __init__(region)
- Parameters:
region –
QRegion
Constructs a new region which is equal to region
r.Constructs a polygon region from the point array
awith the fill rule specified byfillRule.If
fillRuleis Qt::WindingFill, the polygon region is defined using the winding algorithm; if it is Qt::OddEvenFill, the odd-even fill algorithm is used.Warning
This constructor can be used to create complex regions that will slow down painting when used.
- __init__(r[, t=QRegion.RegionType.Rectangle])
- Parameters:
r –
QRectt –
RegionType
This is an overloaded function.
Create a region based on the rectangle
rwith region typet.If the rectangle is invalid a null region will be created.
See also
- __init__(x, y, w, h[, t=QRegion.RegionType.Rectangle])
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
t –
RegionType
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.
If
tisRectangle, the region is the filled rectangle (x,y,w,h). IftisEllipse, the region is the filled ellipse with center at (x+w/ 2,y+h/ 2) and size (w,``h``).- __getitem__()¶
- __len__()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns a
const_iteratorpointing to the beginning of the range of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
Returns the bounding rectangle of this region. An empty region gives a rectangle that is QRect::isNull().
Same as
begin().Same as
end().Returns
trueif the region contains the pointp; otherwise returnsfalse.- contains(r)
- Parameters:
r –
QRect- Return type:
bool
This is an overloaded function.
Returns
trueif the region overlaps the rectangler; otherwise returnsfalse.Returns a
const_iteratorpointing to one past the end of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and the given
rect.See also
Returns a region which is the intersection of this region and
r.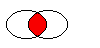
The figure shows the intersection of two elliptical regions.
See also
Returns
trueif this region intersects withrect, otherwise returnsfalse.- intersects(r)
- Parameters:
r –
QRegion- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif this region intersects withregion, otherwise returnsfalse.- isEmpty()¶
- Return type:
bool
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Returns
trueif the region is empty; otherwise returnsfalse. An empty region is a region that contains no points.Example:
r1 = QRegion(10, 10, 20, 20) r1.isEmpty() # false r3 = QRegion() r3.isEmpty() # true r2 = QRegion(40, 40, 20, 20) r3 = r1.intersected(r2) # r3: intersection of r1 and r2 r3.isEmpty() # true r3 = r1.united(r2) # r3: union of r1 and r2 r3.isEmpty() # false
- isNull()¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the region is empty; otherwise returnsfalse. An empty region is a region that contains no points. This function is the same asisEmptySee also
Returns
trueif this region is different from theotherregion; otherwise returnsfalse.This is an overloaded function.
Applies the
intersected()function to this region andr.r1&r2is equivalent tor1.intersected(r2).See also
- __mul__(m)¶
- Parameters:
m –
QTransform- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Applies the
united()function to this region andr.r1+r2is equivalent tor1.united(r2).See also
united()operator|()Returns a region that is the union of this region with the specified
rect.See also
Applies the
united()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1+=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.united(r2).See also
Applies the
subtracted()function to this region andr.r1-r2is equivalent tor1.subtracted(r2).See also
Applies the
subtracted()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1-=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.subtracted(r2).See also
Returns
trueif the region is equal tor; otherwise returns false.Applies the
xored()function to this region andr.r1^r2is equivalent tor1.xored(r2).See also
Applies the
xored()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1^=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.xored(r2).See also
Applies the
united()function to this region andr.r1|r2is equivalent tor1.united(r2).See also
united()operator+()Applies the
united()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1|=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.united(r2).See also
- rectCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of rectangles that this region is composed of. Same as
end() - begin().This is an overloaded function.
Use the QSpan overload instead.
Returns a region which is
rsubtracted from this region.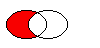
The figure shows the result when the ellipse on the right is subtracted from the ellipse on the left (
left - right).See also
Swaps this region with
other. This operation is very fast and never fails.This is an overloaded function.
Translates the region
point.x() along the x axis andpoint.y() along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.Translates to the given
point.- translate(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – int
dy – int
Translates (moves) the region
dxalong the X axis anddyalong the Y axis.This is an overloaded function.
Returns a copy of the regtion that is translated
p.x() along the x axis andp.y() along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the rectangle to the right and down.See also
- translated(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – int
dy – int
- Return type:
Returns a copy of the region that is translated
dxalong the x axis anddyalong the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.See also
Returns a region which is the union of this region and the given
rect.See also
Returns a region which is the union of this region and
r.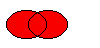
The figure shows the union of two elliptical regions.
See also
Returns a region which is the exclusive or (XOR) of this region and
r.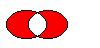
The figure shows the exclusive or of two elliptical regions.
See also