C
Launching Android Emulator
Android Emulator allows you to emulate Android devices on Windows, macOS or Linux machines. The Android Emulator runs the Android operating system in a virtual machine called an AVD. The AVD contains the full Android software stack and it runs as if it were on a physical device. Below is the diagram of the Android Emulator's high-level architecture.
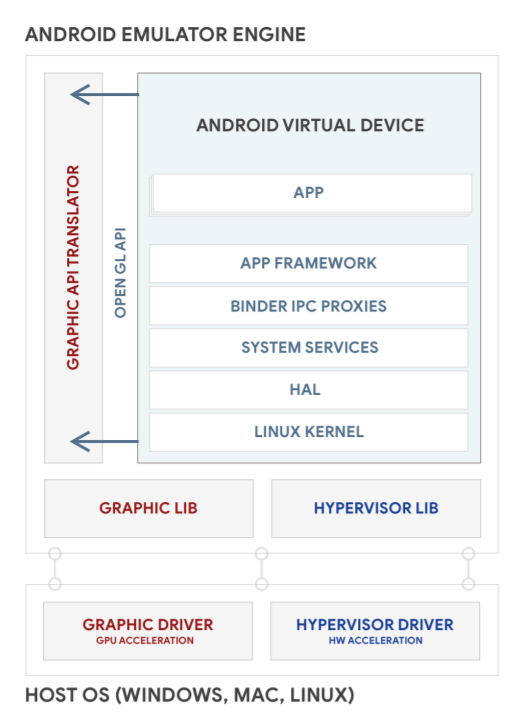
Prerequisites
- Android Studio 4 or newer installed
- Android SDK 29 and Android Tools installed
- Find
<ANDROID_SDK_ROOT>, usually it's in one of the following directories, depending on the machine's OS:- Windows:
<User>/AppData/Local/Android/sdk. - Linux:
~/Android/Sdk. - macOS:
~/Library/Android/sdk.
- Windows:
- Extract
sdk-repo-linux-system-images-eng.ziparchive from the version you choose to<ANDROID_SDK_ROOT>/system-images/android-29/android-automotive - You should have following folder structure:
<ANDROID_SDK_ROOT>/system-images/android-29/android-automotive/x86 - Remember to keep correct ABI names across apps, paths and configuration files like
x86orx86_64.
Step-by-step guide to start emulator with AVD Manager
For AVD management in Qt Creator see Create an Android Virtual Device (AVD).
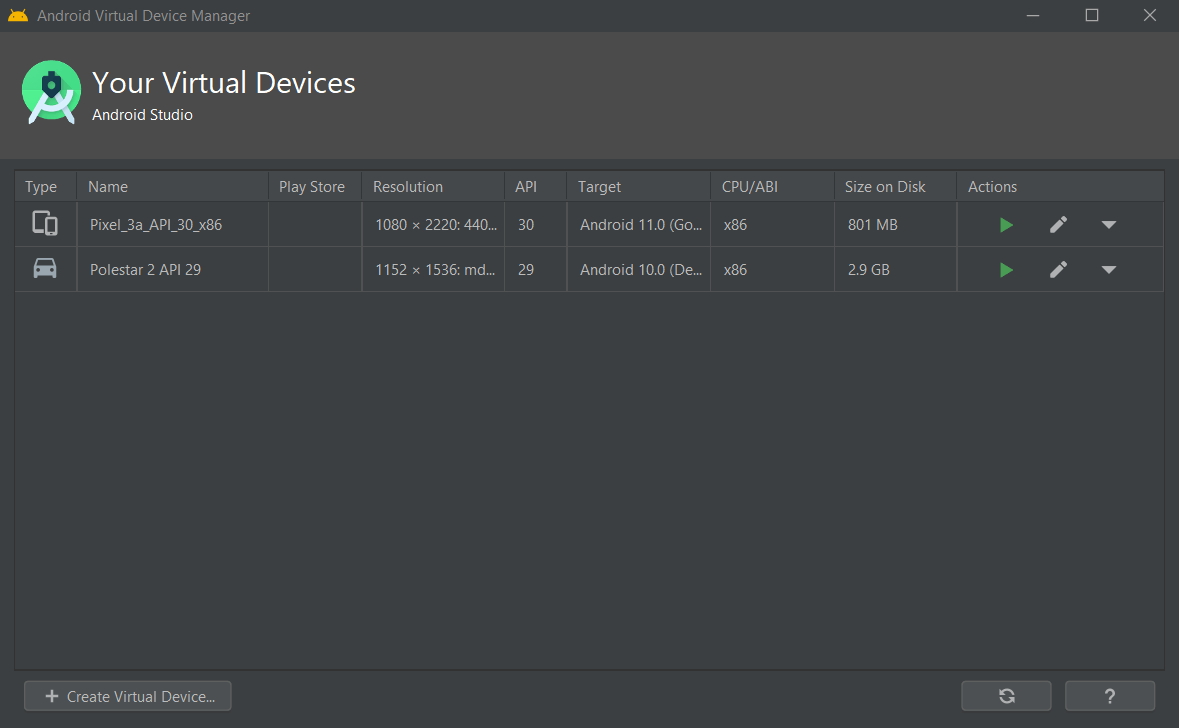
- Start AVD Manager, select Create Virtual Device
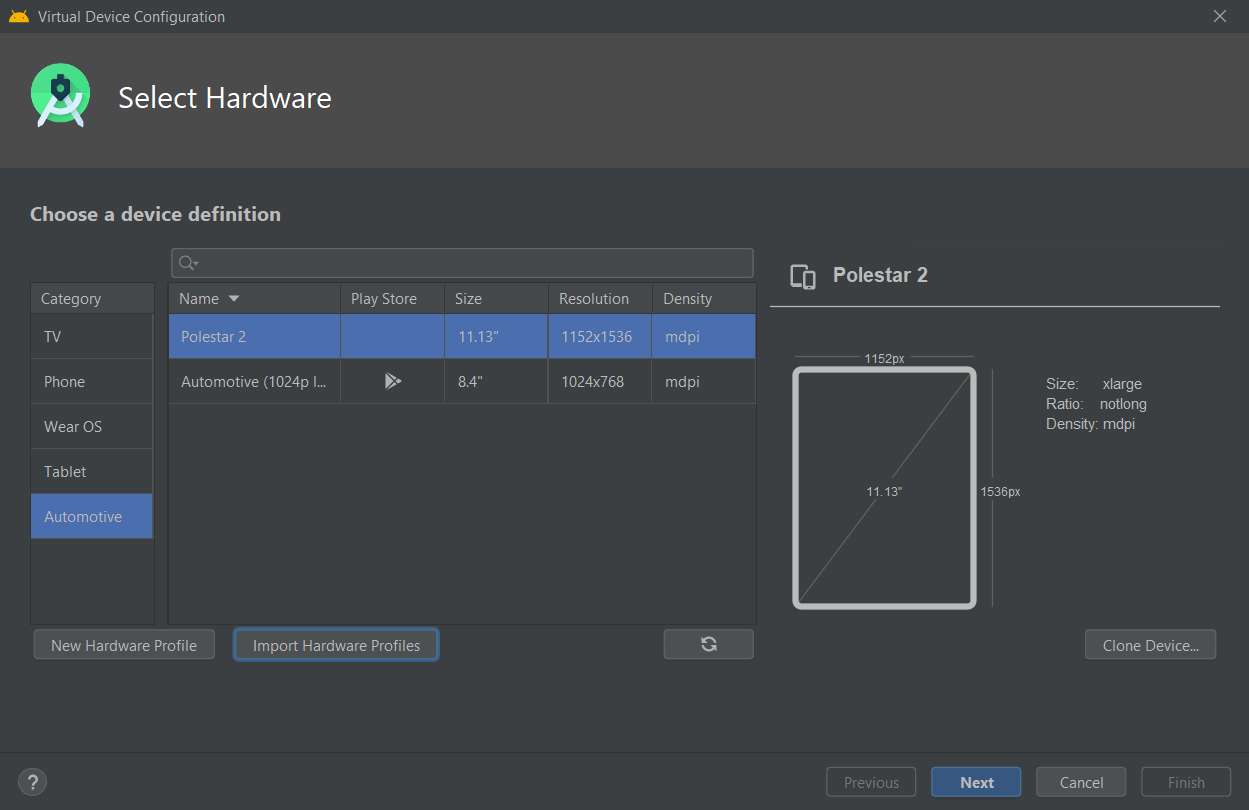
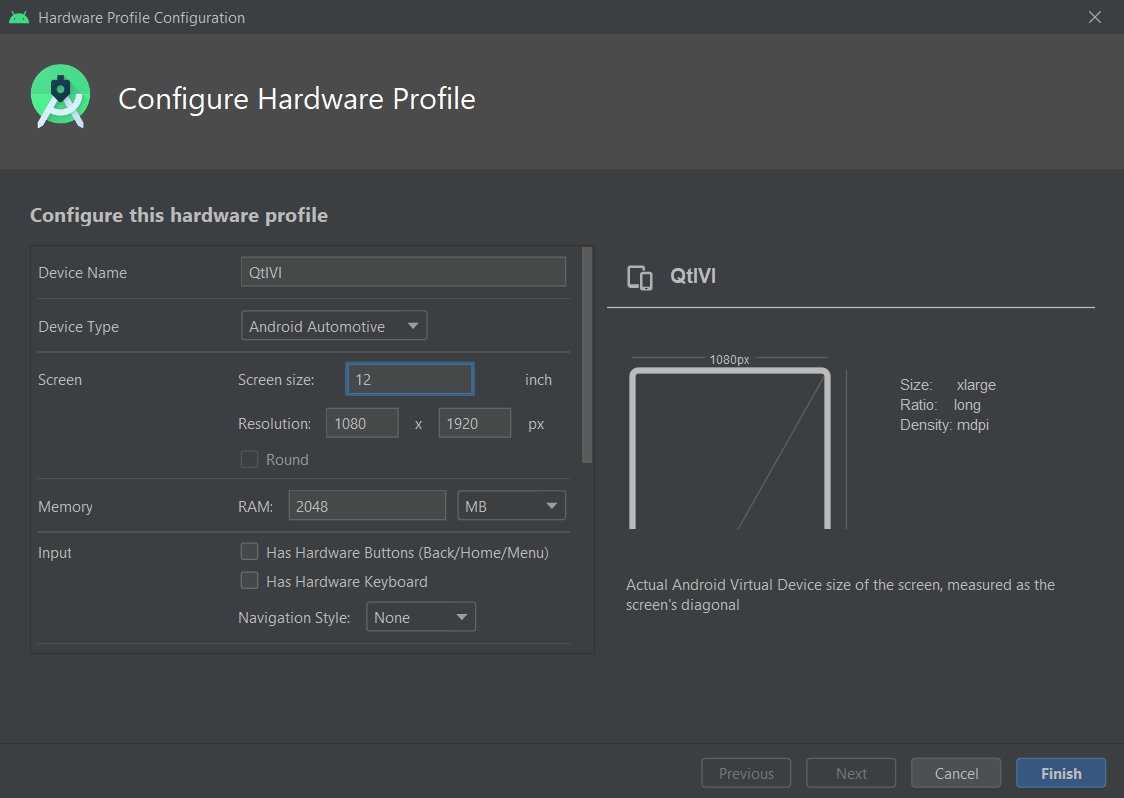
- Choose a existing hardware profile, import or create new one
- Select a system image
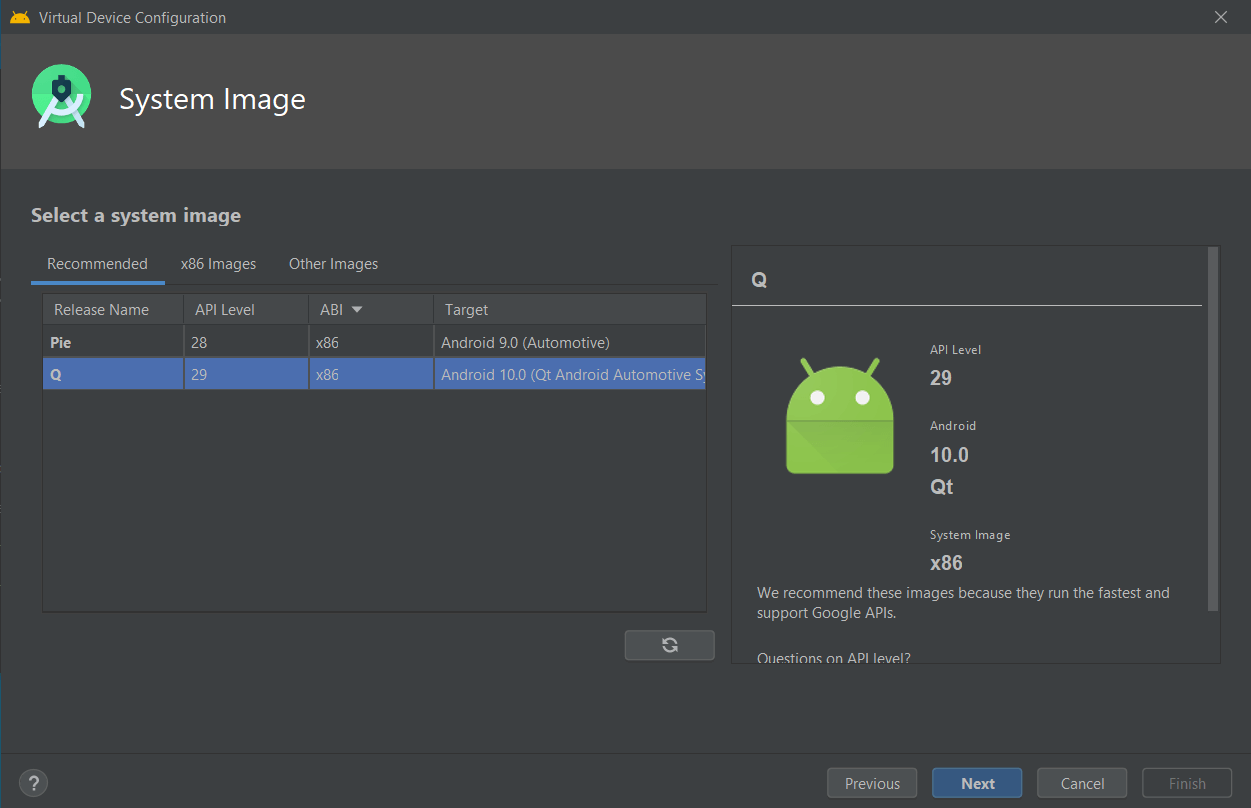
- Verify a emulator configuration
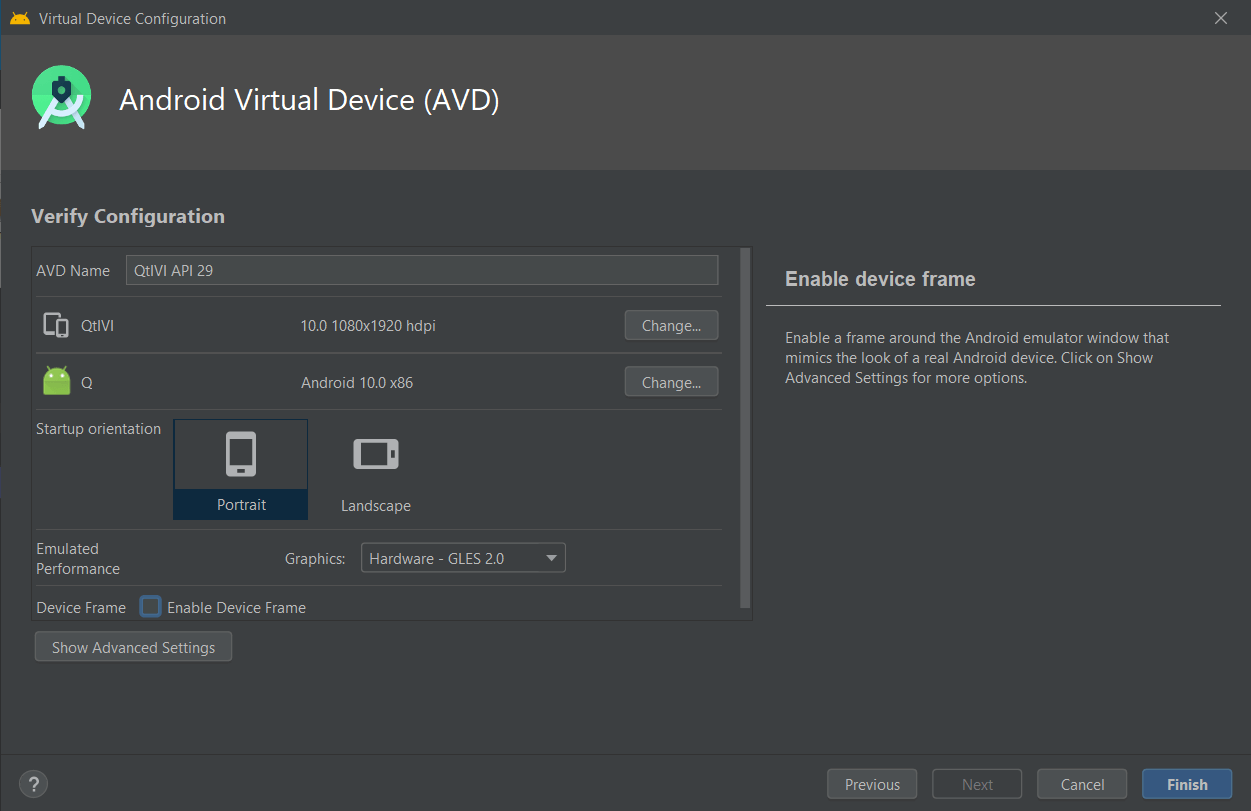
- Start emulator
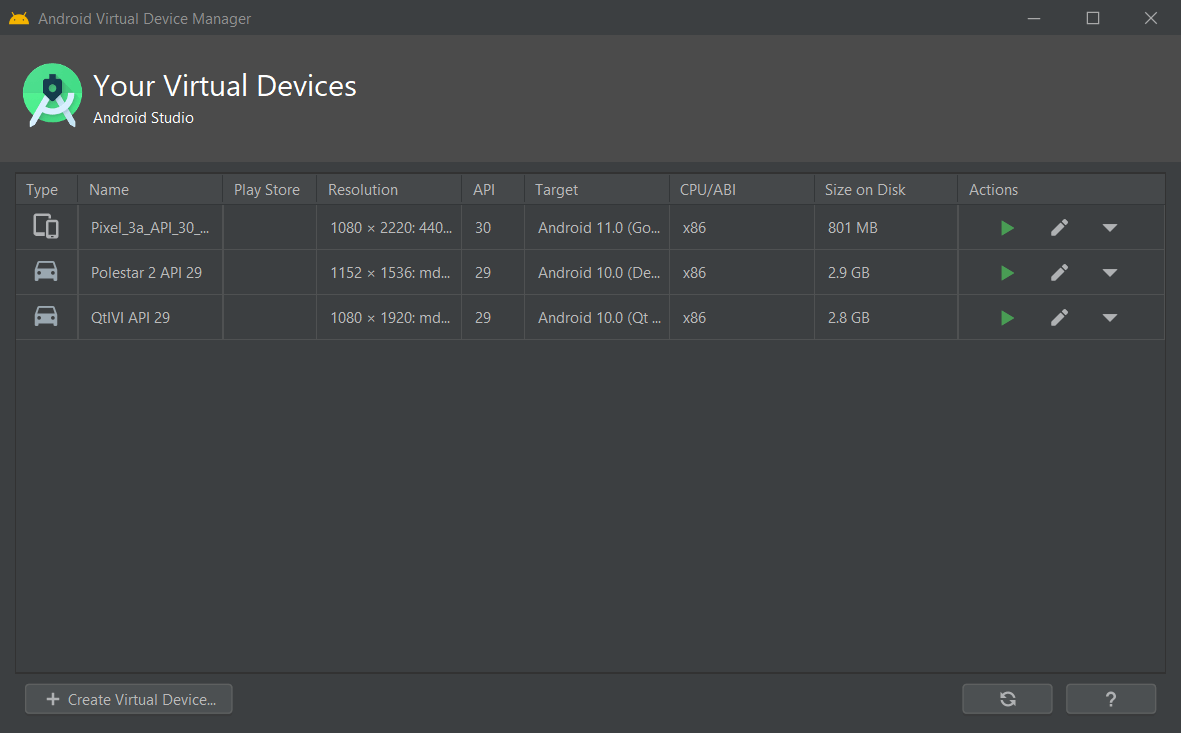
See also Android Emulator requirements.
Available under certain Qt licenses.
Find out more.

