C
Multiscreen Launcher
Demonstrates usage of the Qt Android Apps Utils API with multi-screen support.
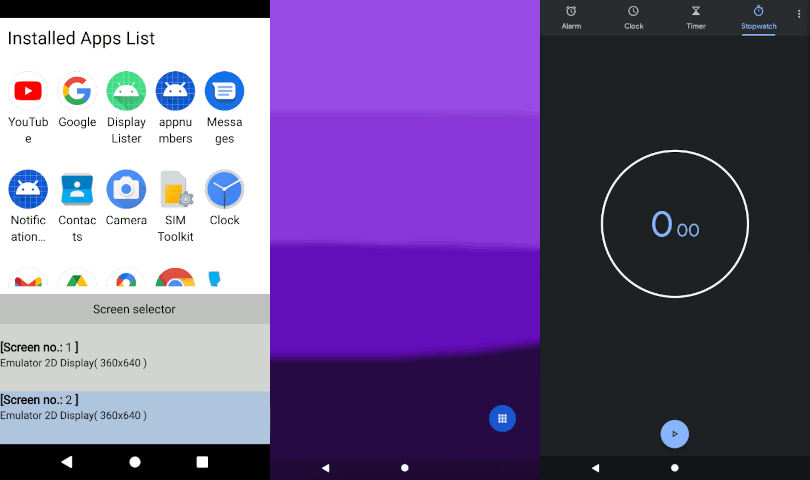
This example demonstrates how to use Qt Android Automotive Base to show a list of installed apps in an Android or Android Automotive device and how to run particular application on the chosen screen. The application UI is created by using Qt Quick.
When starting the app, a list of all installed apps, excluding system apps, is shown as GridView. Pressing the icon starts the app. Below the applications grid, is the list of available screens. Selected application will run on the screen chosen from the list.
Running the Example
To run the example from Qt Creator, open the Welcome mode and select the example from Examples. For more information, see Qt Creator: Tutorial: Build and run.
Using the Model
The installed apps model is based on a QAbstractListModel from C++ and it is extended to QML. The model can be used with ListView or GridView as needed in a same way like in App Lister example.
In this example, a ListView is used to present available screens. The model is attached to the list of the screens as follows:
ListView { id: screensListView anchors.left: parent.left anchors.right: parent.right anchors.bottom: parent.bottom height: 200 model: Application.screens
Now, we set the list's delegate to show the available screens information, and choose the preffered one. The chosen screen will be the target for running the app.
id: screenItemDelegate Rectangle { color: ListView.isCurrentItem ? "lightsteelblue" : "lightgrey" width: window.width height: 80 - window.marginSize Column { Text { id: screenItemIdLabel font.pointSize: 16 text: "<b>[Screen no.:</b> " + index + " <b>]</b>" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignLeft maximumLineCount: 1 } Text { id: screenItemNameLabel font.pointSize: 14 text: modelData.name + "( " + modelData.width + "x" + modelData.height + " )" } } MouseArea { id: screenItemArea anchors.fill: parent onClicked: { screensListView.currentIndex = index } } } }
Using the API Calls
Inside the ListView delegate, we can access some information from Android Apps Utils, and use them to start an app for example:
AndroidAppsUtils.startAppOnScreen(model.packageName, screen) } } } Text { id: appName text: model.appName width: delegate.width anchors.top: appIcon.bottom anchors.topMargin: window.marginSize / 3 horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter elide: Text.ElideRight wrapMode: Text.Wrap maximumLineCount: 2 } } } ListView { id: screensListView anchors.left: parent.left anchors.right: parent.right anchors.bottom: parent.bottom height: 200 model: Application.screens headerPositioning: ListView.OverlayHeader header: screensListHeader delegate: screenItemDelegate focus: true clip: true } Component { id: screensListHeader Rectangle { z: 2 width: window.width height: 40 visible: true color: "silver" Text { anchors.centerIn: parent text: qsTr("Screen selector") } } } Component { id: screenItemDelegate Rectangle { color: ListView.isCurrentItem ? "lightsteelblue" : "lightgrey" width: window.width height: 80 - window.marginSize Column { Text { id: screenItemIdLabel font.pointSize: 16 text: "<b>[Screen no.:</b> " + index + " <b>]</b>" horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignLeft maximumLineCount: 1 } Text { id: screenItemNameLabel font.pointSize: 14 text: modelData.name + "( " + modelData.width + "x" + modelData.height + " )" } } MouseArea { id: screenItemArea anchors.fill: parent onClicked: { screensListView.currentIndex = index
See also Qt for Android.
Available under certain Qt licenses.
Find out more.

