QWizard¶
Synopsis¶
Functions¶
def
addPage(page)def
button(which)def
buttonText(which)def
currentId()def
currentPage()def
field(name)def
hasVisitedPage(id)def
options()def
page(id)def
pageIds()def
pixmap(which)def
removePage(id)def
setButton(which, button)def
setButtonLayout(layout)def
setButtonText(which, text)def
setDefaultProperty(className, property, changedSignal)def
setField(name, value)def
setOption(option[, on=true])def
setOptions(options)def
setPage(id, page)def
setPixmap(which, pixmap)def
setSideWidget(widget)def
setStartId(id)def
setSubTitleFormat(format)def
setTitleFormat(format)def
setWizardStyle(style)def
sideWidget()def
startId()def
subTitleFormat()def
testOption(option)def
titleFormat()def
visitedIds()def
visitedPages()def
wizardStyle()
Virtual functions¶
def
cleanupPage(id)def
initializePage(id)def
nextId()def
validateCurrentPage()
Slots¶
Signals¶
def
currentIdChanged(id)def
customButtonClicked(which)def
helpRequested()def
pageAdded(id)def
pageRemoved(id)
Detailed Description¶
A wizard (also called an assistant on macOS) is a special type of input dialog that consists of a sequence of pages. A wizard’s purpose is to guide the user through a process step by step. Wizards are useful for complex or infrequent tasks that users may find difficult to learn.
QWizardinheritsQDialogand represents a wizard. Each page is aQWizardPage(aQWidgetsubclass). To create your own wizards, you can use these classes directly, or you can subclass them for more control.Topics:
A Trivial Example¶
The following example illustrates how to create wizard pages and add them to a wizard. For more advanced examples, see Class Wizard and License Wizard .
QWizardPage *createIntroPage() { QWizardPage *page = new QWizardPage; page->setTitle("Introduction"); QLabel *label = new QLabel("This wizard will help you register your copy " "of Super Product Two."); label->setWordWrap(true); QVBoxLayout *layout = new QVBoxLayout; layout->addWidget(label); page->setLayout(layout); return page; } QWizardPage *createRegistrationPage() { ... } QWizardPage *createConclusionPage() { ... } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_UseHighDpiPixmaps); QApplication app(argc, argv); #ifndef QT_NO_TRANSLATION QString translatorFileName = QLatin1String("qtbase_"); translatorFileName += QLocale::system().name(); QTranslator *translator = new QTranslator(&app); if (translator->load(translatorFileName, QLibraryInfo::location(QLibraryInfo::TranslationsPath))) app.installTranslator(translator); #endif QWizard wizard; wizard.addPage(createIntroPage()); wizard.addPage(createRegistrationPage()); wizard.addPage(createConclusionPage()); wizard.setWindowTitle("Trivial Wizard"); wizard.show(); return app.exec(); }
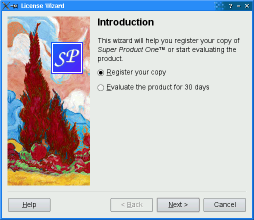
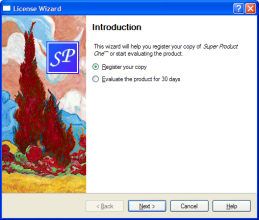
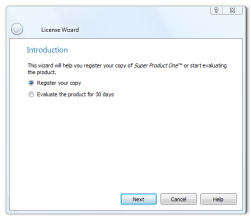
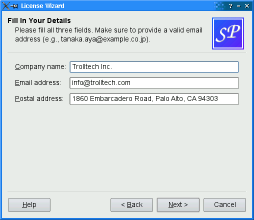
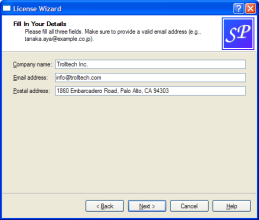
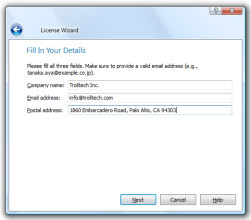
Wizard Look and Feel¶
QWizardsupports four wizard looks:
ClassicStyle
ModernStyle
MacStyle
AeroStyleYou can explicitly set the look to use using
setWizardStyle()(e.g., if you want the same look on all platforms).
ClassicStyle
ModernStyle
MacStyle
AeroStyle
Note:
AeroStylehas effect only on a Windows Vista system with alpha compositing enabled.ModernStyleis used as a fallback when this condition is not met.In addition to the wizard style, there are several options that control the look and feel of the wizard. These can be set using
setOption()orsetOptions(). For example,HaveHelpButtonmakesQWizardshow a Help button along with the other wizard buttons.You can even change the order of the wizard buttons to any arbitrary order using
setButtonLayout(), and you can add up to three custom buttons (e.g., a Print button) to the button row. This is achieved by callingsetButton()orsetButtonText()withCustomButton1,CustomButton2, orCustomButton3to set up the button, and by enabling theHaveCustomButton1,HaveCustomButton2, orHaveCustomButton3options. Whenever the user clicks a custom button,customButtonClicked()is emitted. For example:wizard()->setButtonText(QWizard::CustomButton1, tr("&Print")); wizard()->setOption(QWizard::HaveCustomButton1, true); connect(wizard(), &QWizard::customButtonClicked, this, &ConclusionPage::printButtonClicked);
Elements of a Wizard Page¶
Wizards consist of a sequence of
QWizardPages. At any time, only one page is shown. A page has the following attributes:The diagram belows shows how
QWizardrenders these attributes, assuming they are all present andModernStyleis used: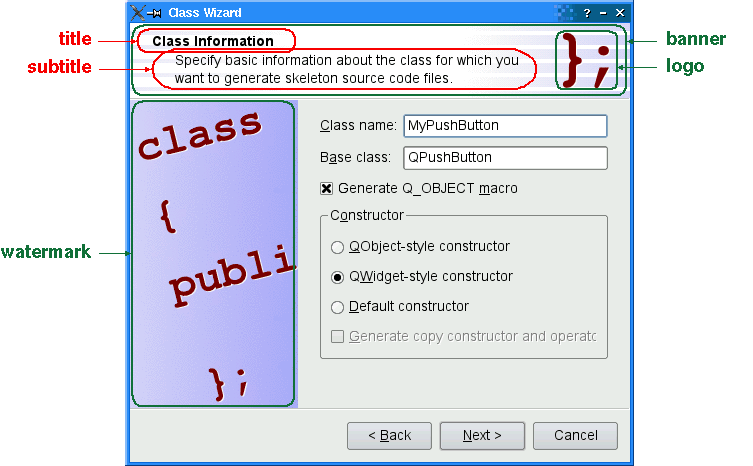
When a
subTitleis set,QWizarddisplays it in a header, in which case it also uses theBannerPixmapand theLogoPixmapto decorate the header. TheWatermarkPixmapis displayed on the left side, below the header. At the bottom, there is a row of buttons allowing the user to navigate through the pages.The page itself (the
QWizardPagewidget) occupies the area between the header, the watermark, and the button row. Typically, the page is aQWizardPageon which aQGridLayoutis installed, with standard child widgets (QLabels,QLineEdits, etc.).If the wizard’s style is
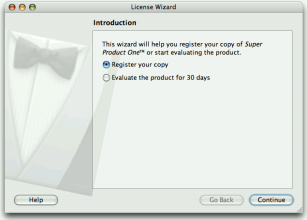
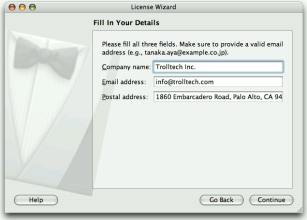
MacStyle, the page looks radically different: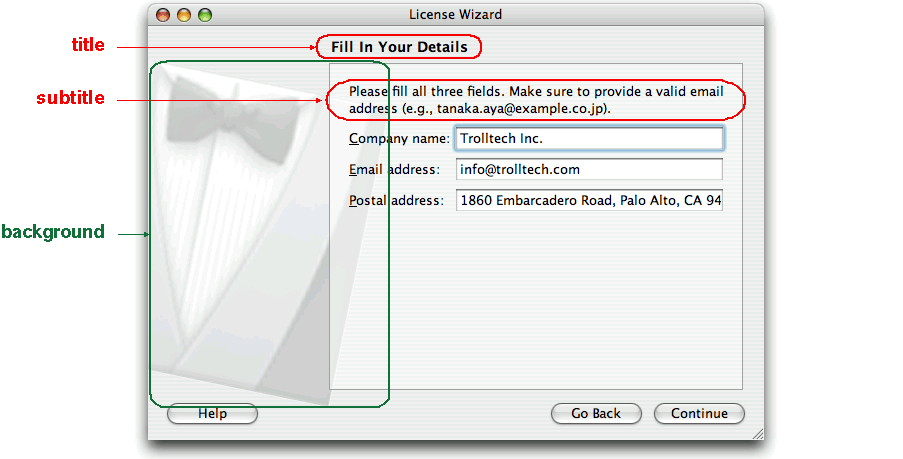
The watermark, banner, and logo pixmaps are ignored by the
MacStyle. If theBackgroundPixmapis set, it is used as the background for the wizard; otherwise, a default “assistant” image is used.The title and subtitle are set by calling
setTitle()andsetSubTitle()on the individual pages. They may be plain text or HTML (seetitleFormatandsubTitleFormat). The pixmaps can be set globally for the entire wizard usingsetPixmap(), or on a per-page basis usingsetPixmap().
Registering and Using Fields¶
In many wizards, the contents of a page may affect the default values of the fields of a later page. To make it easy to communicate between pages,
QWizardsupports a “field” mechanism that allows you to register a field (e.g., aQLineEdit) on a page and to access its value from any page. It is also possible to specify mandatory fields (i.e., fields that must be filled before the user can advance to the next page).To register a field, call
registerField()field. For example:class ClassInfoPage(QWizardPage): def __init__(self, parent): QWizardPage.__init__(self, parent) ... classNameLabel = QLabel(self.tr("&Class name:")) classNameLineEdit = QLineEdit() classNameLabel.setBuddy(classNameLineEdit) baseClassLabel = QLabel(self.tr("B&ase class:")) baseClassLineEdit = QLineEdit() baseClassLabel.setBuddy(baseClassLineEdit) qobjectMacroCheckBox = QCheckBox(self.tr("Generate Q_OBJECT ¯o")) registerField("className*", classNameLineEdit) registerField("baseClass", baseClassLineEdit) registerField("qobjectMacro", qobjectMacroCheckBox) ...The above code registers three fields,
className,baseClass, andqobjectMacro, which are associated with three child widgets. The asterisk (*) next toclassNamedenotes a mandatory field.The fields of any page are accessible from any other page. For example:
def initializePage(self): className = field("className") self.headerLineEdit.setText(className.lower() + ".h") self.implementationLineEdit.setText(className.lower() + ".cpp") self.outputDirLineEdit.setText(QDir.convertSeparators(QDir.tempPath()))Here, we call
field()to access the contents of theclassNamefield (which was defined in theClassInfoPage) and use it to initialize theOutputFilePage. The field’s contents is returned as aQVariant.When we create a field using
registerField(), we pass a unique field name and a widget. We can also provide a Qt property name and a “changed” signal (a signal that is emitted when the property changes) as third and fourth arguments; however, this is not necessary for the most common Qt widgets, such asQLineEdit,QCheckBox, andQComboBox, becauseQWizardknows which properties to look for.If an asterisk (
*) is appended to the name when the property is registered, the field is a mandatory field . When a page has mandatory fields, the Next and/or Finish buttons are enabled only when all mandatory fields are filled.To consider a field “filled”,
QWizardsimply checks that the field’s current value doesn’t equal the original value (the value it had wheninitializePage()was called). ForQLineEditandQAbstractSpinBoxsubclasses,QWizardalso checks thathasAcceptableInput()returns true, to honor any validator or mask.
QWizard‘s mandatory field mechanism is provided for convenience. A more powerful (but also more cumbersome) alternative is to reimplementisComplete()and to emit thecompleteChanged()signal whenever the page becomes complete or incomplete.The enabled/disabled state of the Next and/or Finish buttons is one way to perform validation on the user input. Another way is to reimplement
validateCurrentPage()(orvalidatePage()) to perform some last-minute validation (and show an error message if the user has entered incomplete or invalid information). If the function returnstrue, the next page is shown (or the wizard finishes); otherwise, the current page stays up.
Creating Linear Wizards¶
Most wizards have a linear structure, with page 1 followed by page 2 and so on until the last page. The Class Wizard example is such a wizard. With
QWizard, linear wizards are created by instantiating theQWizardPages and inserting them usingaddPage(). By default, the pages are shown in the order in which they were added. For example:def __init__(self, parent): QWizard.__init__(self, parent): self.addPage(IntroPage()) self.addPage(ClassInfoPage()) self.addPage(CodeStylePage()) self.addPage(OutputFilesPage()) self.addPage(ConclusionPage()) ...When a page is about to be shown,
QWizardcallsinitializePage()(which in turn callsinitializePage()) to fill the page with default values. By default, this function does nothing, but it can be reimplemented to initialize the page’s contents based on other pages’ fields (see theexample above).If the user presses Back,
cleanupPage()is called (which in turn callscleanupPage()). The default implementation resets the page’s fields to their original values (the values they had beforeinitializePage()was called). If you want the Back button to be non-destructive and keep the values entered by the user, simply enable theIndependentPagesoption.
Creating Non-Linear Wizards¶
Some wizards are more complex in that they allow different traversal paths based on the information provided by the user. The License Wizard example illustrates this. It provides five wizard pages; depending on which options are selected, the user can reach different pages.
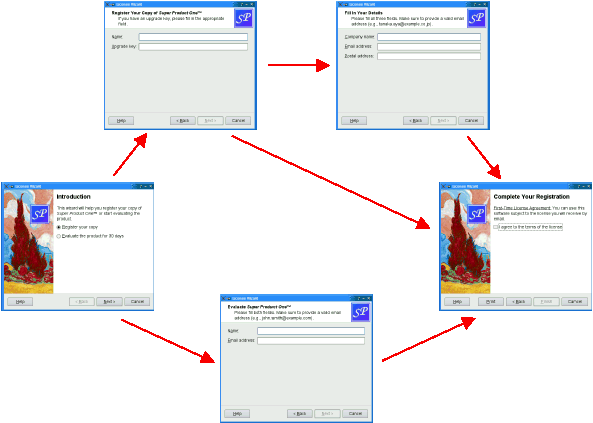
In complex wizards, pages are identified by IDs. These IDs are typically defined using an enum. For example:
class LicenseWizard (QWizard): ... Page_Intro = 1 Page_Evaluate = 2 Page_Register = 3 Page_Details = 4 Page_Conclusion = 5 ...The pages are inserted using
setPage(), which takes an ID and an instance ofQWizardPage(or of a subclass):LicenseWizard::LicenseWizard(QWidget *parent) : QWizard(parent) { setPage(Page_Intro, new IntroPage); setPage(Page_Evaluate, new EvaluatePage); setPage(Page_Register, new RegisterPage); setPage(Page_Details, new DetailsPage); setPage(Page_Conclusion, new ConclusionPage); ... }By default, the pages are shown in increasing ID order. To provide a dynamic order that depends on the options chosen by the user, we must reimplement
nextId(). For example:int IntroPage::nextId() const { if (evaluateRadioButton->isChecked()) { return LicenseWizard::Page_Evaluate; } else { return LicenseWizard::Page_Register; } } int EvaluatePage::nextId() const { return LicenseWizard::Page_Conclusion; } int RegisterPage::nextId() const { if (upgradeKeyLineEdit->text().isEmpty()) { return LicenseWizard::Page_Details; } else { return LicenseWizard::Page_Conclusion; } } int DetailsPage::nextId() const { return LicenseWizard::Page_Conclusion; } int ConclusionPage::nextId() const { return -1; }It would also be possible to put all the logic in one place, in a
nextId()reimplementation. For example:def nextId(self): id = self.currentId() if id == Page_Intro: if field("intro.evaluate").toBool(): return Page_Evaluate else: return Page_Register elif id == Page_Evaluate: return Page_Conclusion elif id == Page_Register: if field("register.upgradeKey").toString().isEmpty(): return Page_Details else: return Page_Conclusion elif id == Page_Details: return Page_Conclusion else: return -1To start at another page than the page with the lowest ID, call
setStartId().To test whether a page has been visited or not, call
hasVisitedPage(). For example:void ConclusionPage::initializePage() { QString licenseText; if (wizard()->hasVisitedPage(LicenseWizard::Page_Evaluate)) { licenseText = tr("<u>Evaluation License Agreement:</u> " "You can use this software for 30 days and make one " "backup, but you are not allowed to distribute it."); } else if (wizard()->hasVisitedPage(LicenseWizard::Page_Details)) { licenseText = tr("<u>First-Time License Agreement:</u> " "You can use this software subject to the license " "you will receive by email."); } else { licenseText = tr("<u>Upgrade License Agreement:</u> " "This software is licensed under the terms of your " "current license."); } bottomLabel->setText(licenseText); }
- class PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard([parent=None[, flags=Qt.WindowFlags()]])¶
- param parent:
- param flags:
WindowFlags
Constructs a wizard with the given
parentand windowflags.See also
parent()windowFlags()
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.WizardButton¶
This enum specifies the buttons in a wizard.
Constant
Description
QWizard.BackButton
The Back button (Go Back on macOS)
QWizard.NextButton
The Next button (Continue on macOS)
QWizard.CommitButton
The Commit button
QWizard.FinishButton
The Finish button (Done on macOS)
QWizard.CancelButton
The Cancel button (see also
NoCancelButton)QWizard.HelpButton
The Help button (see also
HaveHelpButton)QWizard.CustomButton1
The first user-defined button (see also
HaveCustomButton1)QWizard.CustomButton2
The second user-defined button (see also
HaveCustomButton2)QWizard.CustomButton3
The third user-defined button (see also
HaveCustomButton3)The following value is only useful when calling
setButtonLayout():Constant
Description
QWizard.Stretch
A horizontal stretch in the button layout
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.WizardPixmap¶
This enum specifies the pixmaps that can be associated with a page.
Constant
Description
QWizard.WatermarkPixmap
The tall pixmap on the left side of a
ClassicStyleorModernStylepageQWizard.LogoPixmap
The small pixmap on the right side of a
ClassicStyleorModernStylepage headerQWizard.BannerPixmap
The pixmap that occupies the background of a
ModernStylepage headerQWizard.BackgroundPixmap
The pixmap that occupies the background of a
MacStylewizardSee also
setPixmap()setPixmap()Elements of a Wizard Page
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.WizardStyle¶
This enum specifies the different looks supported by
QWizard.Constant
Description
QWizard.ClassicStyle
Classic Windows look
QWizard.ModernStyle
Modern Windows look
QWizard.MacStyle
macOS look
QWizard.AeroStyle
Windows Aero look
See also
setWizardStyle()WizardOptionWizard Look and Feel
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.WizardOption¶
This enum specifies various options that affect the look and feel of a wizard.
Constant
Description
QWizard.IndependentPages
The pages are independent of each other (i.e., they don’t derive values from each other).
QWizard.IgnoreSubTitles
Don’t show any subtitles, even if they are set.
QWizard.ExtendedWatermarkPixmap
Extend any
WatermarkPixmapall the way down to the window’s edge.QWizard.NoDefaultButton
Don’t make the Next or Finish button the dialog’s
default button.QWizard.NoBackButtonOnStartPage
Don’t show the Back button on the start page.
QWizard.NoBackButtonOnLastPage
Don’t show the Back button on the last page.
QWizard.DisabledBackButtonOnLastPage
Disable the Back button on the last page.
QWizard.HaveNextButtonOnLastPage
Show the (disabled) Next button on the last page.
QWizard.HaveFinishButtonOnEarlyPages
Show the (disabled) Finish button on non-final pages.
QWizard.NoCancelButton
Don’t show the Cancel button.
QWizard.CancelButtonOnLeft
Put the Cancel button on the left of Back (rather than on the right of Finish or Next).
QWizard.HaveHelpButton
Show the Help button.
QWizard.HelpButtonOnRight
Put the Help button on the far right of the button layout (rather than on the far left).
QWizard.HaveCustomButton1
Show the first user-defined button (
CustomButton1).QWizard.HaveCustomButton2
Show the second user-defined button (
CustomButton2).QWizard.HaveCustomButton3
Show the third user-defined button (
CustomButton3).QWizard.NoCancelButtonOnLastPage
Don’t show the Cancel button on the last page.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.addPage(page)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
int
Adds the given
pageto the wizard, and returns the page’s ID.The ID is guaranteed to be larger than any other ID in the
QWizardso far.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.back()¶
Goes back to the previous page.
This is equivalent to pressing the Back button.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.button(which)¶
- Parameters:
which –
WizardButton- Return type:
Returns the button corresponding to role
which.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.buttonText(which)¶
- Parameters:
which –
WizardButton- Return type:
str
Returns the text on button
which.If a text has ben set using
setButtonText(), this text is returned.By default, the text on buttons depends on the
wizardStyle. For example, on macOS, the Next button is called Continue.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.cleanupPage(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
This virtual function is called by
QWizardto clean up pageidjust before the user leaves it by clicking Back (unless theIndependentPagesoption is set).The default implementation calls
cleanupPage()on page(id).See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.currentId()¶
- Return type:
int
This property holds the ID of the current page.
This property cannot be set directly. To change the current page, call
next(),back(), orrestart().By default, this property has a value of -1, indicating that no page is currently shown.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.currentIdChanged(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.currentPage()¶
- Return type:
Returns a pointer to the current page, or
Noneif there is no current page (e.g., before the wizard is shown).This is equivalent to calling page(
currentId()).See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.customButtonClicked(which)¶
- Parameters:
which – int
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.field(name)¶
- Parameters:
name – str
- Return type:
object
Returns the value of the field called
name.This function can be used to access fields on any page of the wizard.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.hasVisitedPage(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the page history contains pageid; otherwise, returnsfalse.Pressing Back marks the current page as “unvisited” again.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.helpRequested()¶
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.initializePage(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
This virtual function is called by
QWizardto prepare pageidjust before it is shown either as a result ofrestart()being called, or as a result of the user clicking Next. (However, if theIndependentPagesoption is set, this function is only called the first time the page is shown.)By reimplementing this function, you can ensure that the page’s fields are properly initialized based on fields from previous pages.
The default implementation calls
initializePage()on page(id).See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.next()¶
Advances to the next page.
This is equivalent to pressing the Next or Commit button.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.nextId()¶
- Return type:
int
This virtual function is called by
QWizardto find out which page to show when the user clicks the Next button.The return value is the ID of the next page, or -1 if no page follows.
The default implementation calls
nextId()on thecurrentPage().By reimplementing this function, you can specify a dynamic page order.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.options()¶
- Return type:
WizardOptions
This property holds the various options that affect the look and feel of the wizard.
By default, the following options are set (depending on the platform):
Windows:
HelpButtonOnRight.macOS:
NoDefaultButtonandNoCancelButton.X11 and QWS (Qt for Embedded Linux): none.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.page(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
- Return type:
Returns the page with the given
id, orNoneif there is no such page.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.pageAdded(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.pageIds()¶
- Return type:
Returns the list of page IDs.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.pageRemoved(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.pixmap(which)¶
- Parameters:
which –
WizardPixmap- Return type:
Returns the pixmap set for role
which.By default, the only pixmap that is set is the
BackgroundPixmapon macOS version 10.13 and earlier.See also
setPixmap()pixmap()Elements of a Wizard Page
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.removePage(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
Removes the page with the given
id.cleanupPage()will be called if necessary.Note
Removing a page may influence the value of the
startIdproperty.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.restart()¶
Restarts the wizard at the start page. This function is called automatically when the wizard is shown.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setButton(which, button)¶
- Parameters:
which –
WizardButtonbutton –
PySide2.QtWidgets.QAbstractButton
Sets the button corresponding to role
whichtobutton.To add extra buttons to the wizard (e.g., a Print button), one way is to call with
CustomButton1toCustomButton3, and make the buttons visible using theHaveCustomButton1toHaveCustomButton3options.See also
button()setButtonText()setButtonLayout()options
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setButtonLayout(layout)¶
- Parameters:
layout –
Sets the order in which buttons are displayed to
layout, wherelayoutis a list ofWizardButtons.The default layout depends on the options (e.g., whether
HelpButtonOnRight) that are set. You can call this function if you need more control over the buttons’ layout than what options already provides.You can specify horizontal stretches in the layout using
Stretch.Example:
class MyWizard(QWizard): def __init__(self, parent): QWizard.__ini__(self, parent) ... layout = [QWizard.Stretch, QWizard.BackButton, QWizard.CancelButton, QWizard.NextButton, QWizard.FinishButton] setButtonLayout(layout); ...
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setButtonText(which, text)¶
- Parameters:
which –
WizardButtontext – str
Sets the text on button
whichto betext.By default, the text on buttons depends on the
wizardStyle. For example, on macOS, the Next button is called Continue.To add extra buttons to the wizard (e.g., a Print button), one way is to call with
CustomButton1,CustomButton2, orCustomButton3to set their text, and make the buttons visible using theHaveCustomButton1,HaveCustomButton2, and/orHaveCustomButton3options.Button texts may also be set on a per-page basis using
setButtonText().
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setDefaultProperty(className, property, changedSignal)¶
- Parameters:
className – str
property – str
changedSignal – str
Sets the default property for
classNameto beproperty, and the associated change signal to bechangedSignal.The default property is used when an instance of
className(or of one of its subclasses) is passed toregisterField()and no property is specified.QWizardknows the most common Qt widgets. For these (or their subclasses), you don’t need to specify apropertyor achangedSignal. The table below lists these widgets:Widget
Property
Change Notification Signal
bool
checkedint
valueint
currentIndexQDateTimedateTimeQStringtextint
currentRowint
valueSee also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setField(name, value)¶
- Parameters:
name – str
value – object
Sets the value of the field called
nametovalue.This function can be used to set fields on any page of the wizard.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setOption(option[, on=true])¶
- Parameters:
option –
WizardOptionon – bool
Sets the given
optionto be enabled ifonis true; otherwise, clears the givenoption.See also
options
testOption()setWizardStyle()
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setOptions(options)¶
- Parameters:
options –
WizardOptions
This property holds the various options that affect the look and feel of the wizard.
By default, the following options are set (depending on the platform):
Windows:
HelpButtonOnRight.macOS:
NoDefaultButtonandNoCancelButton.X11 and QWS (Qt for Embedded Linux): none.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setPage(id, page)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
Adds the given
pageto the wizard with the givenid.Note
Adding a page may influence the value of the
startIdproperty in case it was not set explicitly.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setPixmap(which, pixmap)¶
- Parameters:
which –
WizardPixmappixmap –
PySide2.QtGui.QPixmap
Sets the pixmap for role
whichtopixmap.The pixmaps are used by
QWizardwhen displaying a page. Which pixmaps are actually used depend on thewizard style.Pixmaps can also be set for a specific page using
setPixmap().See also
pixmap()setPixmap()Elements of a Wizard Page
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setSideWidget(widget)¶
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide2.QtWidgets.QWidget
Sets the given
widgetto be shown on the left side of the wizard. For styles which use theWatermarkPixmap(ClassicStyleandModernStyle) the side widget is displayed on top of the watermark, for other styles or when the watermark is not provided the side widget is displayed on the left side of the wizard.Passing
Noneshows no side widget.When the
widgetis notNonethe wizard reparents it.Any previous side widget is hidden.
You may call with the same widget at different times.
All widgets set here will be deleted by the wizard when it is destroyed unless you separately reparent the widget after setting some other side widget (or
None).By default, no side widget is present.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setStartId(id)¶
- Parameters:
id – int
This property holds the ID of the first page.
If this property isn’t explicitly set, this property defaults to the lowest page ID in this wizard, or -1 if no page has been inserted yet.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setSubTitleFormat(format)¶
- Parameters:
format –
TextFormat
This property holds the text format used by page subtitles.
The default format is
AutoText.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setTitleFormat(format)¶
- Parameters:
format –
TextFormat
This property holds the text format used by page titles.
The default format is
AutoText.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.setWizardStyle(style)¶
- Parameters:
style –
WizardStyle
This property holds the look and feel of the wizard.
By default,
QWizarduses theAeroStyleon a Windows Vista system with alpha compositing enabled, regardless of the current widget style. If this is not the case, the default wizard style depends on the current widget style as follows:MacStyleis the default if the current widget style is QMacStyle,ModernStyleis the default if the current widget style is QWindowsStyle, andClassicStyleis the default in all other cases.See also
Wizard Look and Feeloptions
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.sideWidget()¶
- Return type:
Returns the widget on the left side of the wizard or
None.By default, no side widget is present.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.startId()¶
- Return type:
int
This property holds the ID of the first page.
If this property isn’t explicitly set, this property defaults to the lowest page ID in this wizard, or -1 if no page has been inserted yet.
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.subTitleFormat()¶
- Return type:
This property holds the text format used by page subtitles.
The default format is
AutoText.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.testOption(option)¶
- Parameters:
option –
WizardOption- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the givenoptionis enabled; otherwise, returns false.See also
options
setOption()setWizardStyle()
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.titleFormat()¶
- Return type:
This property holds the text format used by page titles.
The default format is
AutoText.See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.validateCurrentPage()¶
- Return type:
bool
This virtual function is called by
QWizardwhen the user clicks Next or Finish to perform some last-minute validation. If it returnstrue, the next page is shown (or the wizard finishes); otherwise, the current page stays up.The default implementation calls
validatePage()on thecurrentPage().When possible, it is usually better style to disable the Next or Finish button (by specifying
mandatory fieldsor by reimplementingisComplete()) than to reimplement .See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.visitedIds()¶
- Return type:
Returns the list of IDs of visited pages, in the order in which the pages were visited.
See also
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.visitedPages()¶
- Return type:
Note
This function is deprecated.
Use
visitedIds()instead
- PySide2.QtWidgets.QWizard.wizardStyle()¶
- Return type:
This property holds the look and feel of the wizard.
By default,
QWizarduses theAeroStyleon a Windows Vista system with alpha compositing enabled, regardless of the current widget style. If this is not the case, the default wizard style depends on the current widget style as follows:MacStyleis the default if the current widget style is QMacStyle,ModernStyleis the default if the current widget style is QWindowsStyle, andClassicStyleis the default in all other cases.See also
Wizard Look and Feeloptions
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.