Finance Manager Tutorial - Part 1¶
In this tutorial, we will create a finance manager app using QtQuick and PySide6. The app will allow you to add your expenses and visualize them using a pie charts based on the category of spending. The application is designed in a way that it is compatible with Desktop and Android platforms.
To download the complete source code for this tutorial, visit Finance Manager Example - Part 1.
Prerequisites¶
Before we begin, firstly make sure you have Python 3.9+ and PySide6 installed within you Python environment. You can install it using pip:
pip install PySide6
Project Design¶
The finance manager app is a simple app demonstrating the use of PySide6 to integrate QtQuick with Python, allowing for a seamless combination of QML for the user interface and Python for the backend logic. It will have the following components:
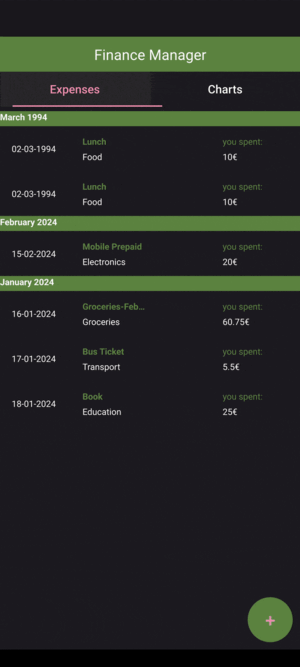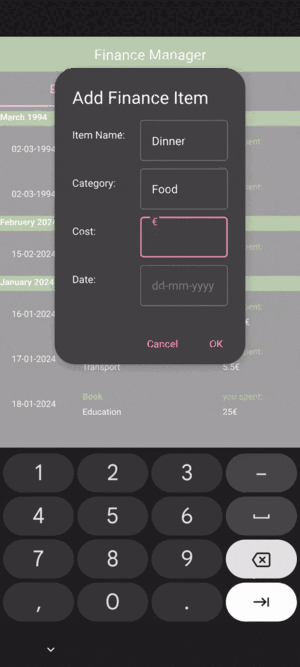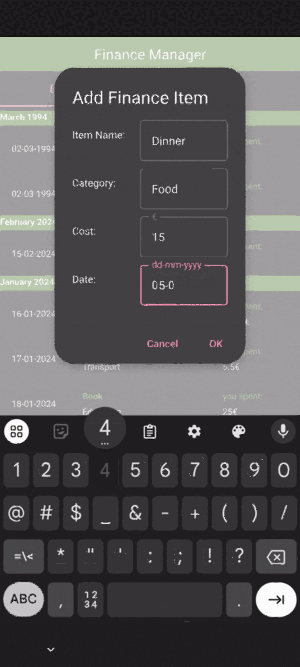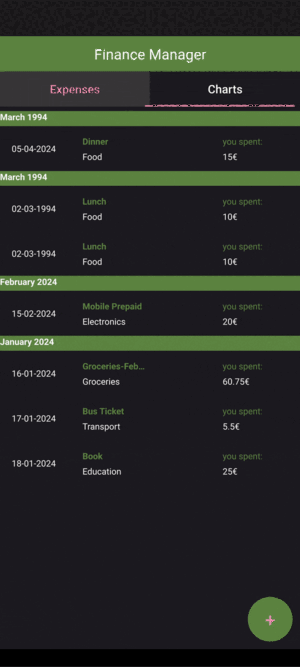
Expense List: This list will display all the entered expenses, showing the expense name, amount, category and date. The expenses are organized by their month and year.
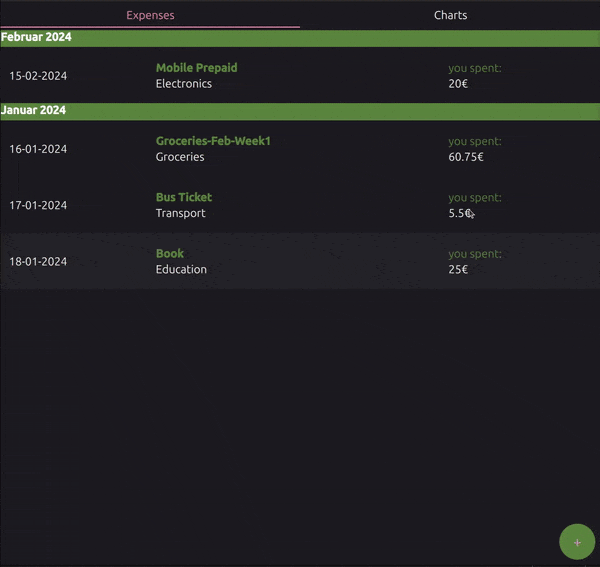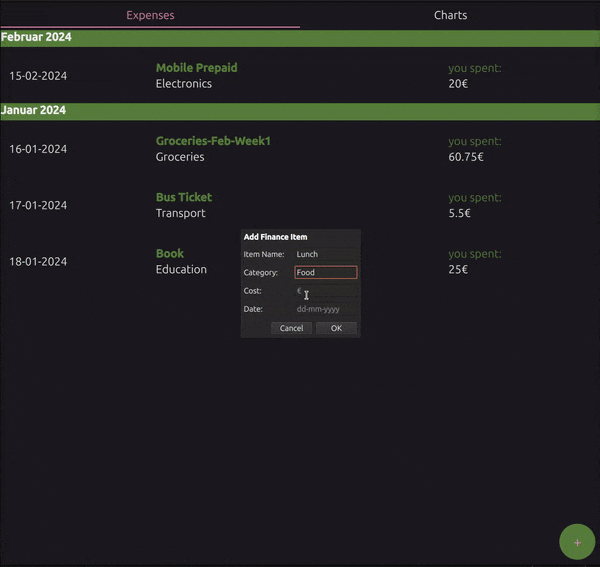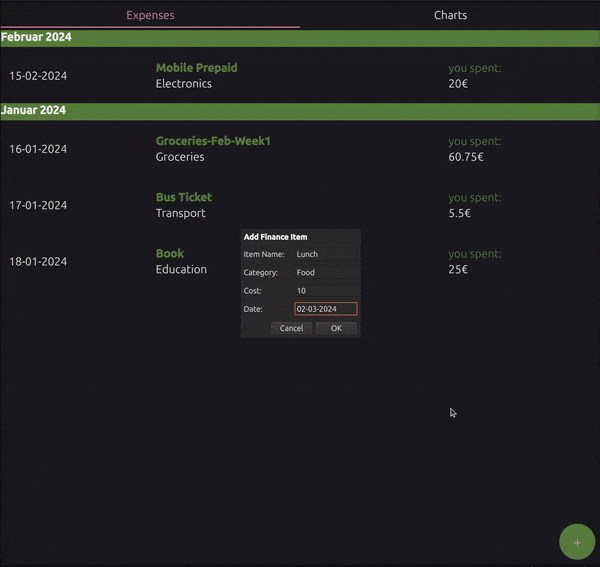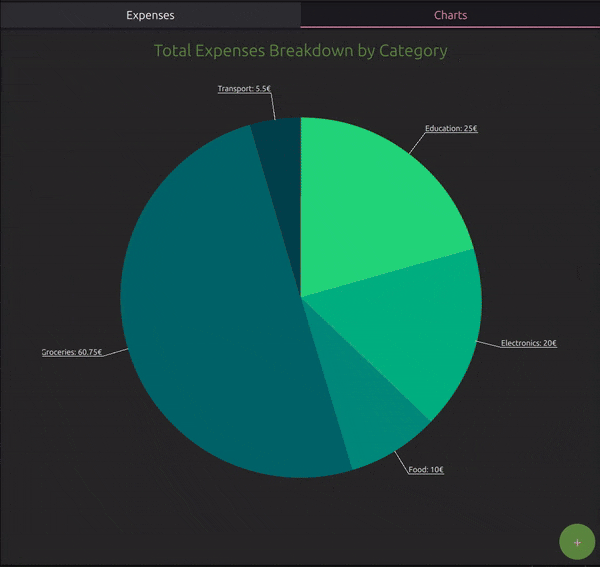
PieChart: This chart will visualize the expenses based on their categories, giving users a clear overview of their spending habits.
Add Expense: A dialog enabling the user to add new expenses.
The overall project structure will be as follows:
finance_manager/
├── main.py
├── financemodel.py
├── Finance/
│ ├── Main.qml
│ ├── FinanceView.qml
│ ├── FinanceDelegate.qml
│ ├── FinancePieChart.qml
│ ├── AddDialog.qml
│ └── qmldir
Let’s get started!¶
Component Overview¶
In the first part of this tutorial, we will start by creating the Expense List using some
pre-defined expenses. For this, we will create a new Python file financemodel.py that
defines a class FinanceModel that will be used to manage the expenses from Python and expose
it to QML.
financemodel.py
1# Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2# SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4from datetime import datetime
5from dataclasses import dataclass
6from enum import IntEnum
7from collections import defaultdict
8
9from PySide6.QtCore import (QAbstractListModel, QEnum, Qt, QModelIndex, Slot,
10 QByteArray)
11from PySide6.QtQml import QmlElement
12
13QML_IMPORT_NAME = "Finance"
14QML_IMPORT_MAJOR_VERSION = 1
15
16
17@QmlElement
18class FinanceModel(QAbstractListModel):
19
20 @QEnum
21 class FinanceRole(IntEnum):
22 ItemNameRole = Qt.ItemDataRole.DisplayRole
23 CategoryRole = Qt.ItemDataRole.UserRole
24 CostRole = Qt.ItemDataRole.UserRole + 1
25 DateRole = Qt.ItemDataRole.UserRole + 2
26 MonthRole = Qt.ItemDataRole.UserRole + 3
27
28 @dataclass
29 class Finance:
30 item_name: str
31 category: str
32 cost: float
33 date: str
34
35 @property
36 def month(self):
37 return datetime.strptime(self.date, "%d-%m-%Y").strftime("%B %Y")
38
39 def __init__(self, parent=None) -> None:
40 super().__init__(parent)
41 self.m_finances = []
42 self.m_finances.append(self.Finance("Mobile Prepaid", "Electronics", 20.00, "15-02-2024"))
43 self.m_finances.append(self.Finance("Groceries-Feb-Week1", "Groceries", 60.75,
44 "16-01-2024"))
45 self.m_finances.append(self.Finance("Bus Ticket", "Transport", 5.50, "17-01-2024"))
46 self.m_finances.append(self.Finance("Book", "Education", 25.00, "18-01-2024"))
47
48 def rowCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
49 return len(self.m_finances)
50
51 def data(self, index: QModelIndex, role: int):
52 row = index.row()
53 if row < self.rowCount():
54 finance = self.m_finances[row]
55 if role == FinanceModel.FinanceRole.ItemNameRole:
56 return finance.item_name
57 if role == FinanceModel.FinanceRole.CategoryRole:
58 return finance.category
59 if role == FinanceModel.FinanceRole.CostRole:
60 return finance.cost
61 if role == FinanceModel.FinanceRole.DateRole:
62 return finance.date
63 if role == FinanceModel.FinanceRole.MonthRole:
64 return finance.month
65 return None
66
67 @Slot(result=dict)
68 def getCategoryData(self):
69 category_data = defaultdict(float)
70 for finance in self.m_finances:
71 category_data[finance.category] += finance.cost
72 return dict(category_data)
73
74 def roleNames(self):
75 roles = super().roleNames()
76 roles[FinanceModel.FinanceRole.ItemNameRole] = QByteArray(b"item_name")
77 roles[FinanceModel.FinanceRole.CategoryRole] = QByteArray(b"category")
78 roles[FinanceModel.FinanceRole.CostRole] = QByteArray(b"cost")
79 roles[FinanceModel.FinanceRole.DateRole] = QByteArray(b"date")
80 roles[FinanceModel.FinanceRole.MonthRole] = QByteArray(b"month")
81 return roles
82
83 @Slot(int, result='QVariantMap')
84 def get(self, row: int):
85 finance = self.m_finances[row]
86 return {"item_name": finance.item_name, "category": finance.category,
87 "cost": finance.cost, "date": finance.date}
88
89 @Slot(str, str, float, str)
90 def append(self, item_name: str, category: str, cost: float, date: str):
91 finance = self.Finance(item_name, category, cost, date)
92 self.beginInsertRows(QModelIndex(), 0, 0) # Insert at the front
93 self.m_finances.insert(0, finance) # Insert at the front of the list
94 self.endInsertRows()
Here’s a brief overview of the FinanceModel class, its components and methods:
QML type registration
The
FinanceModelclass is registered as a QML type using the@QmlElementdecorator. This decorator is used to define a Python class as a QML type, allowing it to be used in QML files.The
QML_IMPORT_NAMEvariable is used to define the name of the module that will be imported in QML to access theFinanceModelclass.
Members
FinanceRole Enum: Defines custom roles for the model data, such as
ItemNameRole,CategoryRole,CostRole,DateRoleandMonthRole.Finance Dataclass: Represents an individual expense with the attributes
item_name,category,cost,dateandmonth.init Method: Initializes the model with some pre-defined expenses.
rowCount Method: Returns the number of items in the model.
data Method: Returns the data for a given role and index in the model.
getCategoryData Method: Returns a dictionary the total cost for each category in the model. This method has the
@Slotdecorator to make it accessible from QML.roleNames Method: Maps role names to their
QByteArrayvalues.get Method: A
@Slotmethod to get the expense data at a given index.append Method: A
@Slotmethod to append a new expense to the model.
For using as a data model in the ListView component in QML, the methods rowCount, data, and
roleNames are required.
Now that we have defined the FinanceModel class, let’s create the QML components to display the
expenses. First, we create Finance/Main.qml file that will be the main QML file for our app.
Main.qml
1// Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2// SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4import QtQuick
5import QtQuick.Controls
6import QtQuick.Layouts
7import QtQuick.Controls.Material
8import Finance
9
10ApplicationWindow {
11 id: window
12 Material.theme: Material.Dark
13 Material.accent: Material.Gray
14 width: Screen.width * 0.3
15 height: Screen.height * 0.5
16 visible: true
17 title: qsTr("Finance Manager")
18
19 // Add a toolbar for the application, only visible on mobile
20 header: ToolBar {
21 Material.primary: "#5c8540"
22 visible: Qt.platform.os == "android"
23 RowLayout {
24 anchors.fill: parent
25 Label {
26 text: qsTr("Finance Manager")
27 font.pixelSize: 20
28 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignCenter
29 }
30 }
31 }
32
33 ColumnLayout {
34 anchors.fill: parent
35
36 TabBar {
37 id: tabBar
38 Layout.fillWidth: true
39
40 TabButton {
41 text: qsTr("Expenses")
42 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
43 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.04 :
44 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
45 onClicked: stackView.currentIndex = 0
46 }
47
48 TabButton {
49 text: qsTr("Charts")
50 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
51 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.04 :
52 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
53 onClicked: stackView.currentIndex = 1
54 }
55 }
56
57 StackLayout {
58 id: stackView
59 Layout.fillWidth: true
60 Layout.fillHeight: true
61
62 Item {
63 id: expensesView
64 Layout.fillWidth: true
65 Layout.fillHeight: true
66
67 FinanceView {
68 id: financeView
69 anchors.fill: parent
70 financeModel: finance_model
71 }
72 }
73
74 Item {
75 id: chartsView
76 Layout.fillWidth: true
77 Layout.fillHeight: true
78
79 FinancePieChart {
80 id: financePieChart
81 anchors.fill: parent
82 Component.onCompleted: {
83 var categoryData = finance_model.getCategoryData()
84 updateChart(categoryData)
85 }
86 }
87 }
88 }
89 }
90
91 // Model to store the finance data. Created from Python.
92 FinanceModel {
93 id: finance_model
94 }
95
96 // Add a dialog to add new entries
97 AddDialog {
98 id: addDialog
99 onFinished: function(item_name, category, cost, date) {
100 finance_model.append(item_name, category, cost, date)
101 var categoryData = finance_model.getCategoryData()
102 financePieChart.updateChart(categoryData)
103 }
104 }
105
106 // Add a button to open the dialog
107 ToolButton {
108 id: roundButton
109 text: qsTr("+")
110 highlighted: true
111 Material.elevation: 6
112 width: Qt.platform.os === "android" ?
113 Math.min(parent.width * 0.2, Screen.width * 0.15) :
114 Math.min(parent.width * 0.060, Screen.width * 0.05)
115 height: width // Keep the button circular
116 anchors.margins: 10
117 anchors.right: parent.right
118 anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
119 background: Rectangle {
120 color: "#5c8540"
121 radius: roundButton.width / 2
122 }
123 font.pixelSize: width * 0.4
124 onClicked: {
125 addDialog.createEntry()
126 }
127 }
128}
In the Main.qml we import the created Finance QML module file and the file has the following components:
ApplicationWindow:
The main window of the application.
Sets the theme to
Material.Darkand accent color toMaterial.Gray.Adjusts the window size to the screen dimensions.
Contains the title “Finance Manager”.
ToolBar:
A toolbar that is only visible on mobile platforms (Android and iOS). Note that PySide6 supports only Android, but you can use the same code with Qt C++ for iOS.
Contains a
Labelwith the text “Finance Manager”.
ColumnLayout:
A layout that arranges its children in a column.
Fills the entire window.
TabBar:
Contains two
TabButtoncomponents for switching between Expense and Charts views.
StackLayout:
A layout that stacks its children on top of each other.
Contains two
Itemcomponents for the “Expenses” and “Charts” views.
FinanceView:
A custom component to display the list of expenses.
Binds to the
finance_model.This component is defined in the
FinanceView.qmlfile.
FinancePieChart:
A custom component to display a pie chart of expenses by category.
Updates the chart with data from
finance_model.getCategoryData()when the component is completed.This component is defined in the
FinancePieChart.qmlfile.
FinanceModel:
The data model created from Python to store finance data. This is imported by import the QML module
Financein theMain.qmlfile.
AddDialog:
A dialog for adding new expense entries.
Appends new entries to
finance_modeland updates the pie chart.
RoundButton:
A circular button to open the
AddDialog.qml.Positioned at the bottom-right corner of the window.
Contains a “+” symbol and has a highlighted appearance.
Now that we have the basic structure of the main QML file, let’s create the FinanceView.qml file:
FinanceView.qml
1// Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2// SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4import QtQuick
5import QtQuick.Controls
6import QtQuick.Controls.Material
7
8ListView {
9 id: listView
10 anchors.fill: parent
11 height: parent.height
12 property var financeModel
13
14 delegate: FinanceDelegate {
15 id: delegate
16 width: listView.width
17 }
18
19 model: financeModel
20
21 section.property: "month" // Group items by the "month" property
22 section.criteria: ViewSection.FullString
23 section.delegate: Component {
24 id: sectionHeading
25 Rectangle {
26 width: listView.width
27 height: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
28 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.05 :
29 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03
30 color: "#5c8540"
31
32 required property string section
33
34 Text {
35 text: parent.section
36 font.bold: true
37 // depending on the screen density, adjust the font size
38 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
39 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03 :
40 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
41 color: Material.primaryTextColor
42 }
43 }
44 }
45
46 ScrollBar.vertical: ScrollBar { }
47}
FinanceView.qml contains the following components:
ListView:
The main container for displaying a list of items.
Fills the entire parent container using
anchors.fill: parent.Uses the
financeModelproperty as its data model.
property var financeModel:
A property to hold the data model for the list.
This model is expected to be passed from the parent component. In this case, it is passed from the
Main.qmlfile.
delegate:
Defines how each item in the
ListViewshould be displayed.Uses a custom component
FinanceDelegateto render each item. This component is defined in theFinanceDelegate.qmlfile.Sets the width of each delegate to match the width of the
ListView.
model:
Binds the
ListViewto thefinanceModelproperty.The
ListViewwill display items based on the data infinanceModel.
section:
The section property is used to group the items in the list view based on the month of the expense.
ScrollBar.vertical:
Adds a vertical scrollbar to the
ListView.Ensures that users can scroll through the list if the content exceeds the visible area.
These components together create a scrollable list view for displaying financial data, with each
item rendered using the FinanceDelegate component.
Next, let’s create the FinanceDelegate.qml file:
FinanceDelegate.qml
1// Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2// SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4import QtQuick
5import QtQuick.Layouts
6import QtQuick.Controls
7import QtQuick.Controls.Material
8
9ItemDelegate {
10 id: delegate
11 checkable: true
12 width: parent.width
13 height: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
14 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.15 :
15 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.1
16
17 contentItem:
18 RowLayout {
19 Label {
20 id: dateLabel
21 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
22 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03 :
23 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
24 text: date
25 elide: Text.ElideRight
26 Layout.fillWidth: true
27 Layout.preferredWidth: 1
28 color: Material.primaryTextColor
29 }
30
31 ColumnLayout {
32 spacing: 5
33 Layout.fillWidth: true
34 Layout.preferredWidth: 1
35
36 Label {
37 text: item_name
38 color: "#5c8540"
39 font.bold: true
40 elide: Text.ElideRight
41 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
42 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03 :
43 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
44 Layout.fillWidth: true
45 }
46
47 Label {
48 text: category
49 elide: Text.ElideRight
50 Layout.fillWidth: true
51 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
52 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03 :
53 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
54 }
55 }
56
57 Item {
58 Layout.fillWidth: true // This item will take up the remaining space
59 }
60
61 ColumnLayout {
62 spacing: 5
63 Layout.fillWidth: true
64 Layout.preferredWidth: 1
65
66 Label {
67 text: "you spent:"
68 color: "#5c8540"
69 elide: Text.ElideRight
70 Layout.fillWidth: true
71 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
72 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03 :
73 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
74 }
75
76 Label {
77 text: cost + "€"
78 elide: Text.ElideRight
79 Layout.fillWidth: true
80 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
81 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03 :
82 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.02
83 }
84 }
85 }
86}
FinanceDelegate.qml contains the following components:
ItemDelegate:
The root element of the delegate.
Represents a single item in the
ListView.
RowLayout:
A layout that arranges its children horizontally.
Contains multiple elements to display different parts of the financial data.
Label (dateLabel):
Displays the date of the expense.
ColumnLayout:
A layout that arranges its children vertically.
Contains labels for the item name and category.
Label (item_name):
Displays the name of the item.
Label (category):
Displays the category of the transaction.
Item:
A spacer item to take up the remaining space in the
RowLayoutso that the last label is aligned to the right.
ColumnLayout (cost section):
A layout that arranges its children vertically.
Contains labels for the cost description and the actual cost.
Label (“you spent:”):
Displays the static text “you spent:”
Label (cost):
Displays the cost of the transaction.
These components together create a detailed and structured visual representation of each financial
transaction in the ListView, displaying the date, item name, category, and cost in a readable format.
Then we create the FinancePieChart.qml file:
FinancePieChart.qml
1// Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2// SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4pragma ComponentBehavior: Bound
5import QtQuick
6import QtGraphs
7import QtQuick.Controls.Material
8
9Item {
10 width: Screen.width
11 height: Screen.height
12
13 GraphsView {
14 id: chart
15 anchors.fill: parent
16 antialiasing: true
17
18 theme: GraphsTheme {
19 colorScheme: Qt.Dark
20 theme: GraphsTheme.Theme.QtGreenNeon
21 }
22
23 PieSeries {
24 id: pieSeries
25 }
26 }
27
28 Text {
29 id: chartTitle
30 text: "Total Expenses Breakdown by Category"
31 color: "#5c8540"
32 font.pixelSize: Qt.platform.os == "android" ?
33 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.04 :
34 Math.min(window.width, window.height) * 0.03
35 anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
36 anchors.top: parent.top
37 anchors.topMargin: 20
38 }
39
40 function updateChart(data) {
41 pieSeries.clear()
42 for (var category in data) {
43 var slice = pieSeries.append(category, data[category])
44 slice.label = category + ": " + data[category] + "€"
45 slice.labelVisible = true
46 }
47 }
48}
FinancePieChart.qml contains the following components:
Item:
The root element of the QML file.
Sets the width and height to match the screen dimensions.
GraphsView:
A container for displaying charts. This was introduced with Qt 6.8 with Qt Graphs module.
PieSeries:
A series type for creating pie charts. This is also a part of the Qt Graphs module.
Text
A title for the pie chart.
updateChart(data):
A JavaScript function to update the pie chart with new data.
Clears existing slices in the PieSeries.
Iterates over the provided data to create new slices.
Each slice is labeled with the category name and value in euros.
These components together create a responsive pie chart that can be dynamically updated with new data.
Finally, we create the AddDialog.qml file:
AddDialog.qml
1// Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2// SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4import QtQuick
5import QtQuick.Controls
6import QtQuick.Layouts
7
8Dialog {
9 id: dialog
10
11 signal finished(string itemName, string category, real cost, string date)
12
13 contentItem: ColumnLayout {
14 id: form
15 spacing: 10
16 property alias itemName: itemName
17 property alias category: category
18 property alias cost: cost
19 property alias date: date
20
21 GridLayout {
22 columns: 2
23 columnSpacing: 20
24 rowSpacing: 10
25 Layout.fillWidth: true
26
27 Label {
28 text: qsTr("Item Name:")
29 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
30 }
31
32 TextField {
33 id: itemName
34 focus: true
35 Layout.fillWidth: true
36 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
37 }
38
39 Label {
40 text: qsTr("Category:")
41 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
42 }
43
44 TextField {
45 id: category
46 focus: true
47 Layout.fillWidth: true
48 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
49 }
50
51 Label {
52 text: qsTr("Cost:")
53 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
54 }
55
56 TextField {
57 id: cost
58 focus: true
59 Layout.fillWidth: true
60 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
61 placeholderText: qsTr("€")
62 inputMethodHints: Qt.ImhFormattedNumbersOnly
63 }
64
65 Label {
66 text: qsTr("Date:")
67 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
68 }
69
70 TextField {
71 id: date
72 Layout.fillWidth: true
73 Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBaseline
74 // placeholderText: qsTr("dd-mm-yyyy")
75 validator: RegularExpressionValidator { regularExpression: /^[0-3]?\d-[01]?\d-\d{4}$/ }
76 // code to add the - automatically
77 onTextChanged: {
78 if (date.text.length === 2 || date.text.length === 5) {
79 date.text += "-"
80 }
81 }
82 Component.onCompleted: {
83 var today = new Date();
84 var day = String(today.getDate()).padStart(2, '0');
85 var month = String(today.getMonth() + 1).padStart(2, '0'); // Months are zero-based
86 var year = today.getFullYear();
87 date.placeholderText = day + "-" + month + "-" + year;
88 }
89 }
90 }
91 }
92
93 function createEntry() {
94 form.itemName.clear()
95 form.category.clear()
96 form.cost.clear()
97 form.date.clear()
98 dialog.title = qsTr("Add Finance Item")
99 dialog.open()
100 }
101
102 x: parent.width / 2 - width / 2
103 y: parent.height / 2 - height / 2
104
105 focus: true
106 modal: true
107 title: qsTr("Add Finance Item")
108 standardButtons: Dialog.Ok | Dialog.Cancel
109
110 Component.onCompleted: {
111 dialog.visible = false
112 Qt.inputMethod.visibleChanged.connect(adjustDialogPosition)
113 }
114
115 function adjustDialogPosition() {
116 if (Qt.inputMethod.visible) {
117 // If the keyboard is visible, move the dialog up
118 dialog.y = parent.height / 4 - height / 2
119 } else {
120 // If the keyboard is not visible, center the dialog
121 dialog.y = parent.height / 2 - height / 2
122 }
123 }
124
125 onAccepted: {
126 finished(form.itemName.text, form.category.text, parseFloat(form.cost.text), form.date.text)
127 }
128}
AddDialog.qml contains the following components:
Dialog:
Root element for the dialog.: Identifier for the dialog.
signal finished(...): Custom signal emitted when the dialog is accepted. In this case, it is emitted when the user adds a new expense.
ColumnLayout:
Container for the dialog fields.
TextField:
Input fields for the item name, category, cost and date.
Function
createEntry():Clears the form fields.
Sets the dialog title.
Opens the dialog.
Dialog Properties:
title: qsTr("Add Finance Item"): Sets the dialog title.standardButtons: Dialog.Ok | Dialog.Cancel: Adds standard OK and Cancel buttons.Component.onCompleted: Hides the dialog when the component is first completed.onAccepted: Calls thefinishedfunction with the form data when the dialog is accepted.
Function
adjustDialogPosition:Adjusts the dialog position to move slightly up when the virtual keyboard is shown. This is only applicable for mobile platforms.
Main Python file¶
Now that we have created the main QML file and the necessary components, we can run the application
to see the expense list view in action. Create a new Python file main.py and add the following
code:
main.py
1# Copyright (C) 2024 The Qt Company Ltd.
2# SPDX-License-Identifier: LicenseRef-Qt-Commercial OR BSD-3-Clause
3
4import sys
5from pathlib import Path
6from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication
7from PySide6.QtQml import QQmlApplicationEngine
8
9from financemodel import FinanceModel # noqa: F401
10
11if __name__ == '__main__':
12 app = QApplication(sys.argv)
13 QApplication.setOrganizationName("QtProject")
14 QApplication.setApplicationName("Finance Manager")
15 engine = QQmlApplicationEngine()
16
17 engine.addImportPath(Path(__file__).parent)
18 engine.loadFromModule("Finance", "Main")
19
20 if not engine.rootObjects():
21 sys.exit(-1)
22
23 exit_code = app.exec()
24 del engine
25 sys.exit(exit_code)
In the main.py file, we create a QApplication instance, load the Main.qml file. The Python
import statement from financemodel import FinanceModel registers the FinanceModel class as a QML
type, allowing it to be used in QML files.
Running the Application¶
To run the application, execute the main.py file using Python:
python main.py
Deploying the Application¶
To deploy the application on Desktop, you can use the pyside6-deploy: the deployment tool for Qt for Python tool. Run the following command from the project directory:
pyside6-deploy --name FinanceManager
This will create a standalone executable for the application in the project directory.
For deploying to Android, you can use the pyside6-android-deploy: the Android deployment tool for Qt for Python tool. Run the following command from the project directory:
pyside6-android-deploy --name FinanceManager --wheel-pyside=<path_to_pyside6_wheel>
--wheel-shiboken=<path_to_shiboken_wheel>
This will create an APK file that can be installed on an Android device in the project directory.
Summary¶
In this part of the tutorial, we have created a basic finance manager app, including the expense
list view categorized by month and year, the pie chart, and the add expense dialog. We have also
defined the FinanceModel class in Python to manage the financial data and expose it to QML.
In the next part of the tutorial, we will continue to build on this foundation by moving the
expense data into a database based on the sqlalchemy Python
package.