Qt Quick 안드로이드 스튜디오 프로젝트용
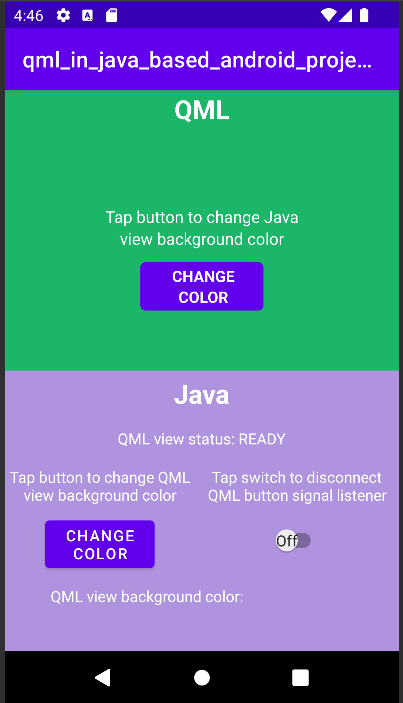
Qt Quick 용 안드로이드 API 예제는 안드로이드 스튜디오 프로젝트
Qt Quick 용 안드로이드 API 예제는 안드로이드 스튜디오 프로젝트로 제공됩니다. 프로젝트 폴더는 Qt 설치 위치에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 기본 Windows 설치 경로 아래에서 찾을 수 있습니다:
C:\Qt\Examples\Qt-<patch-release-number>\platforms\android\<example-name>
이 프로젝트들은 이미 이 Qt 버전과 호환되는 Qt Gradle 플러그인 버전을 사용하도록 구성되어 있습니다.
개요
이 예제에는 안드로이드 스튜디오용 Qt 도구 플러그인을 사용하여 안드로이드 스튜디오로 임포트할 수 있는 QML 프로젝트가 포함되어 있습니다. QtQuickView API를 활용하여 QML 프로젝트를 뷰로 사용하는 Java 및 Kotlin 프로젝트가 있습니다.
QML 작동 방식에 대한 자세한 내용은 Qt Qml. 이 문서는 Java 또는 Kotlin을 사용하여 QML 컴포넌트를 Android 애플리케이션에 임베드하는 방법에 중점을 두고 있습니다.
Android API의 경우 Qt Quick 에서 main() 의 변경이 필요합니다.
일반적인 Qt Quick 애플리케이션의 main.cpp는 다음과 같이 표시됩니다:
#include <QGuiApplication> #include <QQmlApplicationEngine> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QGuiApplication app(argc, argv); QQmlApplicationEngine engine; QObject::connect( &engine, &QQmlApplicationEngine::objectCreationFailed, &app, []() { QCoreApplication::exit(-1); }, Qt::QueuedConnection); engine.loadFromModule("MyQtQuickProject", "Main"); return app.exec(); }
main() 에서는 QML 엔진을 만들거나 나중에 Qt Quick 보기 API에서 처리할 QML을 로드할 필요가 없습니다. main() 에 필요한 모든 것이 있습니다:
#include <QGuiApplication> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QGuiApplication app(argc, argv); return app.exec(); }
레이아웃 설정
Java 및 Kotlin 프로젝트의 경우 모두 app/src/main/res/layout/activity_main.xml 에서 QtQuickViews의레이아웃을 설정해야 합니다.
LinearLayout 에서 각 QtQuickView에 대해 두 개의 프레임레이아웃을 설정합니다.
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/firstQmlFrame"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1">
</FrameLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/secondQmlFrame"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1">
</FrameLayout>id 은 Kotlin 또는 Java 코딩된 메인 액티비티에서 참조하는 것입니다.
자동 생성된 QML 유형 Java 클래스 가져오기
QML 유형에 대한 Java 클래스는 Qt Quick 프로젝트가 빌드될 때 생성됩니다. 이러한 클래스를 메인 액티비티에서 사용하려면 먼저 임포트해야 합니다.
import org.qtproject.example.qtquickview.QmlModule.Main; import org.qtproject.example.qtquickview.QmlModule.Second;
import org.qtproject.example.qtquickview.QmlModule.Main import org.qtproject.example.qtquickview.QmlModule.Second
참고: QML 컴포넌트의 Java 코드 생성에 대한 자세한 내용은 QT_ANDROID_GENERATE_JAVA_QTQUICKVIEW_CONTENTS CMake 변수를 참조하세요.
메인 액티비티의 onCreate() 메서드
먼저 Java 및 Kotlin 프로젝트의 MainActivity 의 onCreate() 메서드를 살펴봅니다.
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
m_qmlViewBackgroundText = findViewById(R.id.qmlViewBackgroundText);
m_qmlStatus = findViewById(R.id.qmlStatusText);
m_androidControlsLayout = findViewById(R.id.javaRelative);
m_colorBox = findViewById(R.id.qmlColorBox);
m_switch = findViewById(R.id.disconnectQmlListenerSwitch);
m_switch.setOnClickListener(view -> switchListener());
QtQuickView m_firstQuickView = new QtQuickView(this);
QtQuickView m_secondQuickView = new QtQuickView(this);
// Set status change listener for m_qmlView
// listener implemented below in OnStatusChanged
m_firstQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this);
m_secondQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this);
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
FrameLayout m_firstQmlFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.firstQmlFrame);
m_firstQmlFrameLayout.addView(m_firstQuickView, params);
FrameLayout m_secondQmlFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.secondQmlFrame);
m_secondQmlFrameLayout.addView(m_secondQuickView, params);
m_firstQuickView.loadContent(m_firstQmlContent);
m_secondQuickView.loadContent(m_secondQmlContent);
Button m_changeColorButton = findViewById(R.id.changeQmlColorButton);
m_changeColorButton.setOnClickListener(view -> onClickListener());
Button m_rotateQmlGridButton = findViewById(R.id.rotateQmlGridButton);
m_rotateQmlGridButton.setOnClickListener(view -> rotateQmlGrid());
}override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
m_binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
val view = m_binding.root
setContentView(view)
m_binding.disconnectQmlListenerSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener { button, checked ->
switchListener(
button,
checked
)
}
val firstQtQuickView = QtQuickView(this)
val secondQtQuickView = QtQuickView(this)
// Set status change listener for m_qmlView
// listener implemented below in OnStatusChanged
m_firstQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this)
m_secondQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this)
val params: ViewGroup.LayoutParams = FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
)
m_binding.firstQmlFrame.addView(firstQtQuickView, params)
m_binding.secondQmlFrame.addView(secondQtQuickView, params)
firstQtQuickView.loadContent(m_firstQmlContent)
secondQtQuickView.loadContent(m_secondQmlContent)
m_binding.changeQmlColorButton.setOnClickListener { onClickListener() }
m_binding.rotateQmlGridButton.setOnClickListener { rotateQmlGrid() }
}참고: Kotlin 프로젝트에서는 애플리케이션의 UI 구성 요소에 액세스하기 위해 View 바인딩을 사용합니다:
m_binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) val view = m_binding.root setContentView(view)
onCreate() 메서드 내에서 이전에 선언된 변수는 새로운 QtQuickView 인스턴스로 초기화됩니다. 이러한 인스턴스는 Java/Kotlin 활동의 Context 을 인수로 받습니다.
QtQuickView m_firstQuickView = new QtQuickView(this); QtQuickView m_secondQuickView = new QtQuickView(this);
val firstQtQuickView = QtQuickView(this) val secondQtQuickView = QtQuickView(this)
적절한 레이아웃 파라미터를 사용하여 QtQuickView 인스턴스가 안드로이드 레이아웃에 추가됩니다.
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
FrameLayout m_firstQmlFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.firstQmlFrame);
m_firstQmlFrameLayout.addView(m_firstQuickView, params);
FrameLayout m_secondQmlFrameLayout = findViewById(R.id.secondQmlFrame);
m_secondQmlFrameLayout.addView(m_secondQuickView, params);val params: ViewGroup.LayoutParams = FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
)
m_binding.firstQmlFrame.addView(firstQtQuickView, params)
m_binding.secondQmlFrame.addView(secondQtQuickView, params)Main 및 Second Java 클래스는 QtQuickViewContent 클래스에서 상속합니다. 이 클래스는 임포트한 QML 프로젝트에서 생성됩니다.
private final Main m_firstQmlContent = new Main(); private final Second m_secondQmlContent = new Second();
private val m_firstQmlContent: Main = Main() private val m_secondQmlContent: Second = Second()
QtQuickView.loadContent() 메서드를 통해 Qt Quick 콘텐츠가 로드되며, 이 메서드는 QtQuickViewContent를 인수로 받습니다.
m_firstQuickView.loadContent(m_firstQmlContent); m_secondQuickView.loadContent(m_secondQmlContent);
firstQtQuickView.loadContent(m_firstQmlContent) secondQtQuickView.loadContent(m_secondQmlContent)
QML 컴포넌트와 상호작용하기
임베디드 QML 컴포넌트와 상호 작용하기 위해 QtQmlStatusChangeListener 인터페이스를 구현하고 onStatusChanged 메서드를 재정의하여 현재 QtQuickView에 로드 중인 QtQuickViewContent의 로드 상태를 가져옵니다.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements QtQmlStatusChangeListener { ... }
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), QtQmlStatusChangeListener { ... }
onStatusChanged 구현:
@Override
public void onStatusChanged(QtQmlStatus qtQmlStatus, QtQuickViewContent content) {
Log.i(TAG, "Status of QtQuickView: " + qtQmlStatus);
// Show current QML View status in a textview
m_qmlStatus.setText(getString(R.string.qml_view_status, m_statusNames.get(qtQmlStatus)));
updateColorDisplay();
if (content == m_firstQmlContent) {
// Connect signal listener to "onClicked" signal from main.qml
// addSignalListener returns int which can be used later to identify the listener
if (qtQmlStatus == QtQmlStatus.READY && m_switch.isChecked()) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId = m_firstQmlContent.connectOnClickedListener(
(String name, Void v) -> {
Log.i(TAG, "QML button clicked");
m_androidControlsLayout.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(
m_colors.getColor()
));
});
}
}
}override fun onStatusChanged(status: QtQmlStatus?, content: QtQuickViewContent?) {
Log.v(TAG, "Status of QtQuickView: $status")
// Show current QML View status in a textview
m_binding.qmlStatusText.text = getString(R.string.qml_view_status, m_statusNames[status])
updateColorDisplay()
if (content == m_firstQmlContent) {
// Connect signal listener to "onClicked" signal from main.qml
// addSignalListener returns int which can be used later to identify the listener
if (status == QtQmlStatus.READY && m_binding.disconnectQmlListenerSwitch.isChecked) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId =
m_firstQmlContent.connectOnClickedListener { _: String, _: Void? ->
Log.i(TAG, "QML button clicked")
m_binding.kotlinRelative.setBackgroundColor(
Color.parseColor(
m_colors.getColor()
)
)
}
}
}
}MainActivity statusChangeListener 은 , 은 방식으로 설정합니다. m_mainQmlContent m_secondQmlContent QtQuickViewContent.setStatusChangeListener
m_firstQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this); m_secondQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this);
m_firstQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this) m_secondQmlContent.setStatusChangeListener(this)
재정의된 콜백 함수 onStatusChanged() 는 현재 QtQuickViewContent 로딩의 현재 상태, QtQmlStatus Enum을 포함하는 StatusChanged() 신호를 QtQuickView로 받습니다. 이 QtQmlStatus 이 QtQmlStatus.READY 으로 확인되면 QML 뷰와 상호작용을 시작할 수 있습니다.
QML 컴포넌트 속성 값 가져오기 및 설정하기
QML 컴포넌트 속성 값을 가져오고 설정하는 것은 Main.java 클래스에 설명된 메서드를 통해 이루어집니다. 이 경우 m_mainQmlContent.setColorStringProperty() 및 m_mainQmlContent.getColorStringProperty() 메서드를 사용합니다. 이러한 메서드는 QML 컴포넌트에 포함된 프로퍼티에 따라 생성됩니다.
public void onClickListener() {
// Set the QML view root object property "colorStringFormat" value to
// color from Colors.getColor()
m_firstQmlContent.setColorStringFormat(m_colors.getColor());
updateColorDisplay();
}
private void updateColorDisplay() {
String qmlBackgroundColor = m_firstQmlContent.getColorStringFormat();
// Display the QML View background color code
m_qmlViewBackgroundText.setText(qmlBackgroundColor);
// Display the QML View background color in a view
// if qmlBackGroundColor is not null
if (qmlBackgroundColor != null) {
m_colorBox.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(qmlBackgroundColor));
}
}private fun onClickListener() {
// Set the QML view root object property "colorStringFormat" value to
// color from Colors.getColor()
m_firstQmlContent.colorStringFormat = m_colors.getColor()
updateColorDisplay()
}
private fun updateColorDisplay() {
val qmlBackgroundColor = m_firstQmlContent.colorStringFormat
// Display the QML View background color code
m_binding.qmlViewBackgroundText.text = qmlBackgroundColor
// Display the QML View background color in a view
// if qmlBackgroundColor is not null
if (qmlBackgroundColor != null) {
m_binding.qmlColorBox.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(qmlBackgroundColor))
}
}m_mainQmlContent.setColorStringProperty() 메서드를 사용하여 m_mainQmlContent 의 colorStringFormat 속성 값을 Colors.java (또는 Colors.kt) 클래스에서 가져온 임의의 색상 값으로 설정합니다.
m_mainQmlContent.getColorStringProperty() 메서드는 여기서 m_mainQmlContent의 루트 객체의 현재 배경색을 가져온 다음 애플리케이션의 Java/Kotlin Android 측에서 사용자에게 표시하는 데 사용됩니다.
m_secondQmlContent 에는 생성된 m_secondQmlContent.setGridRotation() 메서드를 사용하여 Java 측에서 회전할 수 있는 Grid QML 컴포넌트가 있습니다.
private void rotateQmlGrid() {
Integer previousGridRotation = m_secondQmlContent.getGridRotation();
if (previousGridRotation != null) {
m_secondQmlContent.setGridRotation(previousGridRotation + 45);
}
}private fun rotateQmlGrid() {
val previousGridRotation = m_secondQmlContent.gridRotation
if (previousGridRotation != null) {
m_secondQmlContent.gridRotation = previousGridRotation + 45
}
}신호 리스너
QtQuickViewContent 클래스는 QML 컴포넌트 루트 객체에 선언된 신호 간에 신호 리스너를 연결하고 연결을 끊는 데 사용되는 connectSignalListener() 및 disconnectSignalListener() 메서드를 제공합니다. QtQuickViewContent.connectSignalListener() 메서드는 고유한 신호 리스너 ID를 반환하며, 이 ID는 나중에 리스너를 식별하고 연결을 끊을 때 저장하고 사용합니다.
여기서는 신호 리스너를 QML 컴포넌트의 onClicked() 신호에 연결합니다:
if (qtQmlStatus == QtQmlStatus.READY && m_switch.isChecked()) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId = m_firstQmlContent.connectOnClickedListener(
(String name, Void v) -> {
Log.i(TAG, "QML button clicked");
m_androidControlsLayout.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor(
m_colors.getColor()
));
});
}if (status == QtQmlStatus.READY && m_binding.disconnectQmlListenerSwitch.isChecked) {
m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId =
m_firstQmlContent.connectOnClickedListener { _: String, _: Void? ->
Log.i(TAG, "QML button clicked")
m_binding.kotlinRelative.setBackgroundColor(
Color.parseColor(
m_colors.getColor()
)
)
}
}QML 컴포넌트의 버튼이 클릭될 때마다 onClicked() 신호가 방출됩니다. 그러면 이 리스너가 해당 신호를 수신하고 애플리케이션의 안드로이드 쪽을 유지하는 레이아웃의 배경색이 Colors.java 클래스에서 가져온 임의의 색상 값으로 설정됩니다.
그런 다음 QtQuickViewContent.disconnectSignalListener() 메서드를 사용하여 고유한 신호 리스너 ID를 부여하여 신호 리스너의 연결을 끊습니다.
m_firstQmlContent.disconnectSignalListener(m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId);
m_firstQmlContent.disconnectSignalListener(m_qmlButtonSignalListenerId)
아직 확인하지 않으셨다면 Qt 아카데미를 확인해 보세요 : 이 예제에서 참조한 도구와 API를 소개하는 안드로이드 앱에 콘텐츠 임베딩하기 Qt Quick 3D 강좌를 참고하세요.
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

