워터 펌프
간단한 워터 펌프 기계를 위한 QML 기반 HMI를 구축하기 위해 OPC UA 서버와 상호 작용합니다.
워터 펌프 예제는 Qt OPC UA 를 사용하여 OPC UA 서버와 상호 작용하여 간단한 기계에 대한 QML 기반 HMI를 구축하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
서버 빌드
워터 펌프 예제를 사용하려면 먼저 워터 펌프 시뮬레이션 서버를 빌드해야 합니다. 평소와 같이 QtCreator 또는 터미널에서 열고 빌드할 수 있습니다.
시뮬레이션
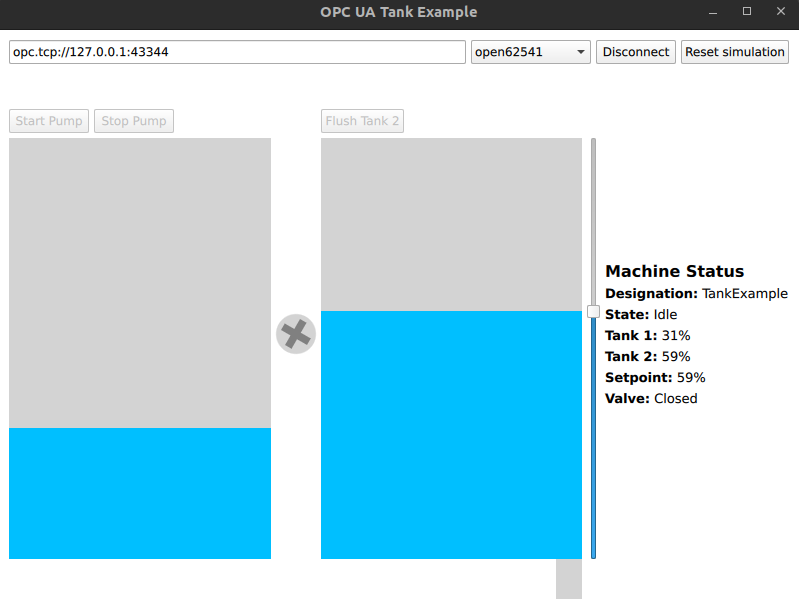
이 예제에 포함된 OPC UA 서버는 두 개의 탱크, 워터 펌프, 밸브가 포함된 기계의 시뮬레이션을 실행합니다. 첫 번째 탱크에서 두 번째 탱크로 물을 펌핑한 다음 밸브를 열어 두 번째 탱크에서 물을 플러시할 수 있습니다. 두 작업 모두 사용자가 구성할 수 있는 설정값이 있어 두 번째 탱크로 펌핑되거나 두 번째 탱크에서 플러시되는 물의 양을 제어할 수 있습니다.
서버에는 다음 노드가 존재합니다:
| NodeId | 함수 |
|---|---|
| ns=2;s=머신 | 머신에 대한 메서드 및 변수 노드가 포함된 폴더 |
| ns=2;s=Machine.State | 머신의 상태 |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Tank1.PercentFilled | 첫 번째 탱크의 현재 충전 상태 |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Tank2.PercentFilled | 두 번째 탱크의 현재 충전 상태 |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Tank2.TargetPercent | 펌핑 및 플러싱을 위한 설정값 |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Tank2.ValveState | 두 번째 탱크의 밸브 상태 |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Designation | 표시 목적으로 사람이 읽을 수 있는 기계의 명칭입니다. |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Start | 펌프를 시작하려면 이 메서드를 호출합니다. |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Stop | 펌프를 중지하려면 이 메서드를 호출합니다. |
| ns=2;s=Machine.FlushTank2 | 탱크 2를 플러시하려면 이 메서드를 호출하세요. |
| ns=2;s=Machine.Reset | 시뮬레이션을 리셋하려면 이 메서드를 호출합니다. |
모든 메서드는 성공할 경우 Good 을 반환하고, 작동이 잘못된 경우(예: 첫 번째 탱크가 비어 있는데 펌프를 시작하려고 시도하는 경우) BadUserAccessDenied 을 반환합니다.
클라이언트 기능
이 예제에서는 읽기, 쓰기, 메서드 호출 및 데이터 변경 구독을 사용하며 QOpcUaClient 및 QOpcUaNode 에서 제공하는 비동기 작업에 대한 핸들러를 설정하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
구현
백엔드 클래스는 OPC UA 서버와의 통신을 처리하고 속성 및 Q_INVOKABLE 메서드를 통해 이 서버의 콘텐츠를 노출하는 데 사용되며, OPC UA 메서드 호출을 래핑합니다.
멤버 변수
연결 관리를 위해 QOpcUaClient 포인터가 필요합니다. HMI가 상호 작용하는 각 OPC UA 노드에 대해 QOpcUaNode 객체에 대한 추가 포인터가 필요합니다. 이러한 노드의 값에 대해 서버에서 보고한 마지막 값을 포함하는 멤버 변수가 추가됩니다.
...
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaClient> m_client;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_machineStateNode;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_percentFilledTank1Node;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_percentFilledTank2Node;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_tank2TargetPercentNode;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_tank2ValveStateNode;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_machineNode;
QScopedPointer<QOpcUaNode> m_machineDesignationNode;
double m_percentFilledTank1;
double m_percentFilledTank2;
double m_tank2TargetPercent;
bool m_tank2ValveState;
MachineState m_machineState;
QString m_machineDesignation;
...HMI에서 사용되는 각 값에 대해 게터, 변경된 신호 및 프로퍼티가 추가되어 QML에서 프로퍼티 바인딩을 활성화합니다.
...
Q_PROPERTY(double percentFilledTank1 READ percentFilledTank1 NOTIFY percentFilledTank1Changed)
Q_PROPERTY(double percentFilledTank2 READ percentFilledTank2 NOTIFY percentFilledTank2Changed)
Q_PROPERTY(double tank2TargetPercent READ tank2TargetPercent NOTIFY tank2TargetPercentChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(OpcUaMachineBackend::MachineState machineState READ machineState NOTIFY machineStateChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(bool tank2ValveState READ tank2ValveState NOTIFY tank2ValveStateChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(bool connected READ connected NOTIFY connectedChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString machineDesignation READ machineDesignation NOTIFY machineDesignationChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QString message READ message NOTIFY messageChanged)
...비동기 핸들러
Qt OPC UA 의 비동기 API는 모든 작업에 신호 핸들러가 필요합니다.
데이터 변경 구독은 QOpcUaNode::attributeUpdated 을 사용하여 업데이트를 보고합니다. 이 신호에 연결된 핸들러는 QVariant 으로 새 값을 가져와서 해당 값을 변수에 쓰거나 새 값으로 신호를 보내는 등의 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
void OpcUaMachineBackend::percentFilledTank1Updated(QOpcUa::NodeAttribute attr, const QVariant &value) { Q_UNUSED(attr); m_percentFilledTank1 = value.toDouble(); emit percentFilledTank1Changed(m_percentFilledTank1); }
읽기 작업은 완료 시 QOpcUaNode::attributeRead 신호를 내보냅니다. 클라이언트는 상태 코드를 확인한 다음 노드에서 결과를 가져와야 합니다.
void OpcUaMachineBackend::machineDesignationRead(QOpcUa::NodeAttributes attr) { if (attr & QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value) { // Make sure the value attribute has been read if (m_machineDesignationNode->attributeError(QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value) == QOpcUa::UaStatusCode::Good) { // Make sure there was no error m_machineDesignation = m_machineDesignationNode->attribute(QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value).toString(); // Get the attribute from the cache emit machineDesignationChanged(m_machineDesignation); } } }
서버와의 상호 작용
생성자에서 QOpcUaProvider 이 생성되고 사용 가능한 백엔드가 저장되어 백엔드 선택 드롭다운 메뉴에 대한 모델을 제공합니다.
...
QOpcUaProvider provider;
setBackends(provider.availableBackends());
...연결을 시도하기 전에 선택한 백엔드가 있는 QOpcUaClient 이 생성됩니다. QOpcUaClient::endpointsRequestFinished 신호는 백엔드의 requestEndpointsFinished 슬롯에 연결됩니다. QOpcUaClient::stateChanged 신호는 백엔드의 clientStateHandler 슬롯에 연결해야 합니다.
void OpcUaMachineBackend::connectToEndpoint(const QString&url, qint32 index) { if (m_connected) return; QOpcUaProvider provider; if (index < 0 || index >= m_backends.size()) return; // Invalid index if (!m_client || (m_client && m_client->backend() != m_backends.at(index))) { m_client.reset(provider.createClient(m_backends.at(index))); if (m_client) { QObject::connect(m_client.data(), &QOpcUaClient::endpointsRequestFinished, this, &OpcUaMachineBackend::requestEndpointsFinished); QObject::connect(m_client.data(), &QOpcUaClient::stateChanged, this, &OpcUaMachineBackend::clientStateHandler); } } if (!m_client) { qWarning() << "Could not create client"; m_successfullyCreated = false; return; } m_successfullyCreated = true; m_client->requestEndpoints(url); }
OpcUaMachineBackend::requestEndpointsFinished 슬롯은 서버에서 사용 가능한 엔드포인트 목록을 수신하고 목록의 첫 번째 항목에 대한 연결을 시작합니다. 사용 가능한 엔드포인트가 없으면 연결 설정이 중단됩니다.
void OpcUaMachineBackend::requestEndpointsFinished(const QList<QOpcUaEndpointDescription> &endpoints) { if (endpoints.isEmpty()) { qWarning() << "The server did not return any endpoints"; clientStateHandler(QOpcUaClient::ClientState::Disconnected); return; } m_client->connectToEndpoint(endpoints.at(0)); }
clientStateHandler 는 QOpcUaClient 의 연결 또는 연결 해제에 따라 작동합니다. 연결에 성공하면 이전에 생성된 노드 멤버 변수가 노드 객체로 채워집니다.
...
if (state == QOpcUaClient::ClientState::Connected) {
setMessage(u"Connected"_s);
// Create node objects for reading, writing and subscriptions
m_machineNode.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine"_s));
m_machineStateNode.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine.State"_s));
m_percentFilledTank1Node.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine.Tank1.PercentFilled"_s));
m_percentFilledTank2Node.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine.Tank2.PercentFilled"_s));
m_tank2TargetPercentNode.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine.Tank2.TargetPercent"_s));
m_tank2ValveStateNode.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine.Tank2.ValveState"_s));
m_machineDesignationNode.reset(m_client->node(u"ns=2;s=Machine.Designation"_s));
...모든 노드 객체가 생성되면 데이터 변경 핸들러가 노드 객체에 연결되고 모니터링이 활성화됩니다.
...
// Connect signal handlers for subscribed values
QObject::connect(m_machineStateNode.data(),
&QOpcUaNode::dataChangeOccurred,
this,
&OpcUaMachineBackend::machineStateUpdated);
QObject::connect(m_percentFilledTank1Node.data(),
&QOpcUaNode::dataChangeOccurred,
this,
&OpcUaMachineBackend::percentFilledTank1Updated);
QObject::connect(m_percentFilledTank2Node.data(),
&QOpcUaNode::dataChangeOccurred,
this,
&OpcUaMachineBackend::percentFilledTank2Updated);
QObject::connect(m_tank2TargetPercentNode.data(),
&QOpcUaNode::dataChangeOccurred,
this,
&OpcUaMachineBackend::tank2TargetPercentUpdated);
QObject::connect(m_tank2ValveStateNode.data(),
&QOpcUaNode::dataChangeOccurred,
this,
&OpcUaMachineBackend::tank2ValveStateUpdated);
// Subscribe to data changes
m_machineStateNode->enableMonitoring(
QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value, QOpcUaMonitoringParameters(100));
m_percentFilledTank1Node->enableMonitoring(
QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value, QOpcUaMonitoringParameters(100));
m_percentFilledTank2Node->enableMonitoring(
QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value, QOpcUaMonitoringParameters(100));
m_tank2TargetPercentNode->enableMonitoring(
QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value, QOpcUaMonitoringParameters(100));
m_tank2ValveStateNode->enableMonitoring(
...머신 지정은 변경되지 않아야 하며 시작 시 한 번만 읽습니다.
...
// Connect the handler for async reading
QObject::connect(m_machineDesignationNode.data(),
&QOpcUaNode::attributeRead,
this,
&OpcUaMachineBackend::machineDesignationRead);
// Request the value attribute of the machine designation node
m_machineDesignationNode->readAttributes(QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value);
...설정값에 대한 설정자가 백엔드에 추가됩니다.
void OpcUaMachineBackend::machineWriteTank2TargetPercent(double value) { if (m_tank2TargetPercentNode) m_tank2TargetPercentNode->writeAttribute(QOpcUa::NodeAttribute::Value, value); }
메소드의 경우 OPC UA 서버 메소드를 호출하는 래퍼가 생성됩니다.
void OpcUaMachineBackend::startPump() { m_machineNode->callMethod(u"ns=2;s=Machine.Start"_s); }
HMI
백엔드 인스턴스가 생성되어 uaBackend 이라는 컨텍스트 프로퍼티로 QML 파트에 전달됩니다.
...
OpcUaMachineBackend backend;
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("uaBackend", &backend);
...이제 uaBackend의 속성, 신호 및 Q_INVOKABLE 메서드에 QML 코드로 액세스할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 두 번째 탱크를 세척하는 버튼은 백엔드가 서버에 연결되어 있고 기계가 유휴 상태이며 탱크 레벨이 설정값 이상인 경우에만 활성화됩니다. 클릭하면 서버에서 flushTank2() 메서드가 호출됩니다.
Button { id: flushButton text: "Flush" enabled: uaBackend.connected && uaBackend.machineState === OpcUaMachineBackend.MachineState.Idle && uaBackend.percentFilledTank2 > uaBackend.tank2TargetPercent onClicked: { uaBackend.flushTank2() } }
백엔드의 신호는 QML 코드에서 직접 사용할 수도 있습니다.
Connections { target: uaBackend function onPercentFilledTank2Changed(value) { if (uaBackend.machineState === OpcUaMachineBackend.MachineState.Pumping) rotation += 15 } }
사용법
서버는 HMI 애플리케이션에 의해 자동으로 시작됩니다. Connect 버튼을 클릭하여 서버에 연결한 후 슬라이더를 드래그하여 설정값을 설정합니다. 그런 다음 Start 을 클릭하여 첫 번째 탱크에서 두 번째 탱크로 물을 펌핑하기 시작합니다. 두 번째 탱크의 현재 값보다 낮은 설정값을 설정한 경우 Flush 을 클릭하면 밸브가 열립니다.
물이 남지 않은 경우 Reset simulation 을 클릭하여 첫 번째 탱크를 다시 채웁니다.
파일:
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/CMakeLists.txt
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/Pump.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/ServerControl.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/Tank.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/Tank1Unit.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/Tank2Unit.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/TankSimulation.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/ValueDisplay.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/main.cpp
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/main.qml
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/opcuamachinebackend.cpp
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/opcuamachinebackend.h
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/qml.qrc
- waterpump/waterpump-qmlcpp/waterpump-qmlcpp.pro
Qt Quick 워터 펌프도참조하세요 .
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

