PySide6.QtGui.QPen¶
- class QPen¶
The
QPenclass defines how aQPaintershould draw lines and outlines of shapes. More…Synopsis¶
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
brush()def
capStyle()def
color()def
dashOffset()def
dashPattern()def
isCosmetic()def
isSolid()def
joinStyle()def
miterLimit()def
__ne__()def
operator=()def
__eq__()def
setBrush()def
setCapStyle()def
setColor()def
setCosmetic()def
setDashOffset()def
setDashPattern()def
setJoinStyle()def
setMiterLimit()def
setStyle()def
setWidth()def
setWidthF()def
style()def
swap()def
width()def
widthF()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
A pen has a
style(),width(),brush(),capStyle()andjoinStyle().The pen style defines the line type. The brush is used to fill strokes generated with the pen. Use the
QBrushclass to specify fill styles. The cap style determines the line end caps that can be drawn usingQPainter, while the join style describes how joins between two lines are drawn. The pen width can be specified in both integer (width()) and floating point (widthF()) precision. A line width of zero indicates a cosmetic pen. This means that the pen width is always drawn one pixel wide, independent of thetransformationset on the painter.The various settings can easily be modified using the corresponding
setStyle(),setWidth(),setBrush(),setCapStyle()andsetJoinStyle()functions (note that the painter’s pen must be reset when altering the pen’s properties).For example:
painter = QPainter(self) pen = QPen(Qt.GlobalColor.green, 3, Qt.DashDotLine, Qt.RoundCap, Qt.RoundJoin) painter.setPen(pen)
which is equivalent to
painter = QPainter(self) QPen pen # creates a default pen pen.setStyle(Qt.DashDotLine) pen.setWidth(3) pen.setBrush(Qt.GlobalColor.green) pen.setCapStyle(Qt.RoundCap) pen.setJoinStyle(Qt.RoundJoin) painter.setPen(pen)
The default pen is a solid black brush with 1 width, square cap style (Qt::SquareCap), and bevel join style (Qt::BevelJoin).
In addition
QPenprovides thecolor()andsetColor()convenience functions to extract and set the color of the pen’s brush, respectively. Pens may also be compared and streamed.For more information about painting in general, see the Paint System documentation.
Pen Style¶
Qt provides several built-in styles represented by the Qt::PenStyle enum:


Qt::SolidLine
Qt::DashLine
Qt::DotLine



Qt::DashDotLine
Qt::DashDotDotLine
Qt::CustomDashLine
Simply use the
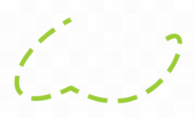
setStyle()function to convert the pen style to either of the built-in styles, except the Qt::CustomDashLine style which we will come back to shortly. Setting the style to Qt::NoPen tells the painter to not draw lines or outlines. The default pen style is Qt::SolidLine.Since Qt 4.1 it is also possible to specify a custom dash pattern using the
setDashPattern()function which implicitly converts the style of the pen to Qt::CustomDashLine. The pattern argument, a QList, must be specified as an even number of qreal entries where the entries 1, 3, 5… are the dashes and 2, 4, 6… are the spaces. For example, the custom pattern shown above is created using the following code:pen = QPen() dashes = QList() space = 4 dashes << 1 << space << 3 << space << 9 << space << 27 << space << 9 << space pen.setDashPattern(dashes)
Note that the dash pattern is specified in units of the pens width, e.g. a dash of length 5 in width 10 is 50 pixels long.
The currently set dash pattern can be retrieved using the
dashPattern()function. Use theisSolid()function to determine whether the pen has a solid fill, or not.Cap Style¶
The cap style defines how the end points of lines are drawn using
QPainter. The cap style only apply to wide lines, i.e. when the width is 1 or greater. The Qt::PenCapStyle enum provides the following styles:


Qt::SquareCap
Qt::FlatCap
Qt::RoundCap
The Qt::SquareCap style is a square line end that covers the end point and extends beyond it by half the line width. The Qt::FlatCap style is a square line end that does not cover the end point of the line. And the Qt::RoundCap style is a rounded line end covering the end point.
The default is Qt::SquareCap.
Whether or not end points are drawn when the pen width is 0 or 1 depends on the cap style. Using Qt::SquareCap or Qt::RoundCap they are drawn, using Qt::FlatCap they are not drawn.
Join Style¶
The join style defines how joins between two connected lines can be drawn using
QPainter. The join style only apply to wide lines, i.e. when the width is 1 or greater. The Qt::PenJoinStyle enum provides the following styles:


Qt::BevelJoin
Qt::MiterJoin
Qt::RoundJoin
The Qt::BevelJoin style fills the triangular notch between the two lines. The Qt::MiterJoin style extends the lines to meet at an angle. And the Qt::RoundJoin style fills a circular arc between the two lines.
The default is Qt::BevelJoin.
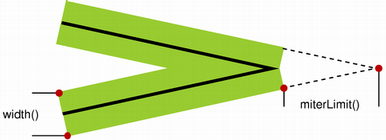
When the Qt::MiterJoin style is applied, it is possible to use the
setMiterLimit()function to specify how far the miter join can extend from the join point. ThemiterLimit()is used to reduce artifacts between line joins where the lines are close to parallel.The
miterLimit()must be specified in units of the pens width, e.g. a miter limit of 5 in width 10 is 50 pixels long. The default miter limit is 2, i.e. twice the pen width in pixels.- __init__()¶
Constructs a default black solid line pen with 1 width.
- __init__(style)
- Parameters:
style –
PenStyle
Constructs a black pen with 1 width and the given
style.See also
- __init__(color)
- Parameters:
color –
QColor
Constructs a solid line pen with 1 width and the given
color.See also
- __init__(pen)
- Parameters:
pen –
QPen
Constructs a pen that is a copy of the given
pen.- __init__(brush, width[, s=Qt.SolidLine[, c=Qt.SquareCap[, j=Qt.BevelJoin]]])
- Parameters:
brush –
QBrushwidth – float
s –
PenStylec –
PenCapStylej –
PenJoinStyle
Constructs a pen with the specified
brush,width, penstyle,capstyle andjoinstyle.Returns the brush used to fill strokes generated with this pen.
See also
- capStyle()¶
- Return type:
Returns the pen’s cap style.
See also
setCapStyle()Cap StyleReturns the color of this pen’s brush.
See also
- dashOffset()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the dash offset for the pen.
See also
- dashPattern()¶
- Return type:
.list of qreal
Returns the dash pattern of this pen.
See also
- isCosmetic()¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the pen is cosmetic; otherwise returnsfalse.Cosmetic pens are used to draw strokes that have a constant width regardless of any transformations applied to the
QPainterthey are used with. Drawing a shape with a cosmetic pen ensures that its outline will have the same thickness at different scale factors.A zero width pen is cosmetic by default.
See also
- isSolid()¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the pen has a solid fill, otherwise false.See also
- joinStyle()¶
- Return type:
Returns the pen’s join style.
See also
setJoinStyle()Join Style- miterLimit()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the miter limit of the pen. The miter limit is only relevant when the join style is set to Qt::MiterJoin.
See also
setMiterLimit()Join Style- __ne__(p)
- Parameters:
p –
QPen- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the pen is different from the givenpen; otherwise false. Two pens are different if they have different styles, widths or colors.See also
operator==()- __ne__(lhs)
- Parameters:
lhs –
PenStyle- Return type:
bool
- __ne__(rhs)
- Parameters:
rhs –
PenStyle- Return type:
bool
Makes this pen a solid pen with the given color, and default cap and join styles, and returns a reference to this pen.
Makes this pen a solid, black pen with default cap and join styles, and returns a reference to this pen.
- __eq__(p)
- Parameters:
p –
QPen- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the pen is equal to the givenpen; otherwise false. Two pens are equal if they have equal styles, widths and colors.See also
operator!=()- __eq__(lhs)
- Parameters:
lhs –
PenStyle- Return type:
bool
- __eq__(rhs)
- Parameters:
rhs –
PenStyle- Return type:
bool
Sets the brush used to fill strokes generated with this pen to the given
brush.See also
- setCapStyle(pcs)¶
- Parameters:
pcs –
PenCapStyle
Sets the pen’s cap style to the given
style. The default value is Qt::SquareCap.See also
capStyle()Cap StyleSets the color of this pen’s brush to the given
color.See also
- setCosmetic(cosmetic)¶
- Parameters:
cosmetic – bool
Sets this pen to cosmetic or non-cosmetic, depending on the value of
cosmetic.See also
- setDashOffset(doffset)¶
- Parameters:
doffset – float
Sets the dash offset (the starting point on the dash pattern) for this pen to the
offsetspecified. The offset is measured in terms of the units used to specify the dash pattern.
For example, a pattern where each stroke is four units long, followed by a gap of two units, will begin with the stroke when drawn as a line.
However, if the dash offset is set to 4.0, any line drawn will begin with the gap. Values of the offset up to 4.0 will cause part of the stroke to be drawn first, and values of the offset between 4.0 and 6.0 will cause the line to begin with part of the gap.
- setDashPattern(pattern)¶
- Parameters:
pattern – .list of qreal
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Sets the dash pattern for this pen to the given
pattern. This implicitly converts the style of the pen to Qt::CustomDashLine.The pattern must be specified as an even number of positive entries where the entries 1, 3, 5… are the dashes and 2, 4, 6… are the spaces. For example:

pen = QPen() dashes = QList() space = 4 dashes << 1 << space << 3 << space << 9 << space << 27 << space << 9 << space pen.setDashPattern(dashes)
The dash pattern is specified in units of the pens width; e.g. a dash of length 5 in width 10 is 50 pixels long. Note that a pen with zero width is equivalent to a cosmetic pen with a width of 1 pixel.
Each dash is also subject to cap styles so a dash of 1 with square cap set will extend 0.5 pixels out in each direction resulting in a total width of 2.
Note that the default cap style is Qt::SquareCap, meaning that a square line end covers the end point and extends beyond it by half the line width.
- setJoinStyle(pcs)¶
- Parameters:
pcs –
PenJoinStyle
Sets the pen’s join style to the given
style. The default value is Qt::BevelJoin.See also
joinStyle()Join Style- setMiterLimit(limit)¶
- Parameters:
limit – float
Sets the miter limit of this pen to the given
limit.
The miter limit describes how far a miter join can extend from the join point. This is used to reduce artifacts between line joins where the lines are close to parallel.
This value does only have effect when the pen style is set to Qt::MiterJoin. The value is specified in units of the pen’s width, e.g. a miter limit of 5 in width 10 is 50 pixels long. The default miter limit is 2, i.e. twice the pen width in pixels.
See also
miterLimit()setJoinStyle()Join StyleSets the pen style to the given
style.See the Qt::PenStyle documentation for a list of the available styles. Since Qt 4.1 it is also possible to specify a custom dash pattern using the
setDashPattern()function which implicitly converts the style of the pen to Qt::CustomDashLine.- setWidth(width)¶
- Parameters:
width – int
Sets the pen width to the given
widthin pixels with integer precision.A line width of zero indicates a cosmetic pen. This means that the pen width is always drawn one pixel wide, independent of the
transformationset on the painter.Setting a pen width with a negative value is not supported.
See also
- setWidthF(width)¶
- Parameters:
width – float
Sets the pen width to the given
widthin pixels with floating point precision.A line width of zero indicates a cosmetic pen. This means that the pen width is always drawn one pixel wide, independent of the
transformationon the painter.Setting a pen width with a negative value is not supported.
See also
Returns the pen style.
See also
setStyle()Pen StyleSwaps this pen with
other. This operation is very fast and never fails.- width()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the pen width with integer precision.
See also
- widthF()¶
- Return type:
float
Returns the pen width with floating point precision.
See also