PySide6.QtWidgets.QMainWindow¶
- class QMainWindow¶
The
QMainWindowclass provides a main application window. More…Synopsis¶
Properties¶
animatedᅟ- Whether manipulating dock widgets and tool bars is animateddockNestingEnabledᅟ- Whether docks can be nesteddockOptionsᅟ- The docking behavior of QMainWindowdocumentModeᅟ- Whether the tab bar for tabbed dockwidgets is set to document modeiconSizeᅟ- Size of toolbar icons in this mainwindowtabShapeᅟ- The tab shape used for tabbed dock widgetstoolButtonStyleᅟ- Style of toolbar buttons in this mainwindowunifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMacᅟ- Whether the window uses the unified title and toolbar look on macOS
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
addDockWidget()def
addToolBar()def
centralWidget()def
corner()def
dockOptions()def
dockWidgetArea()def
documentMode()def
iconSize()def
insertToolBar()def
isAnimated()def
isSeparator()def
menuBar()def
menuWidget()def
removeToolBar()def
resizeDocks()def
restoreState()def
saveState()def
setCorner()def
setDockOptions()def
setIconSize()def
setMenuBar()def
setMenuWidget()def
setStatusBar()def
setTabPosition()def
setTabShape()def
statusBar()def
tabPosition()def
tabShape()def
toolBarArea()def
toolBarBreak()
Virtual methods¶
Slots¶
Signals¶
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Qt Main Window Framework¶
A main window provides a framework for building an application’s user interface. Qt has
QMainWindowand its related classes for main window management.QMainWindowhas its own layout to which you can addQToolBars,QDockWidgets, aQMenuBar, and aQStatusBar. The layout has a center area that can be occupied by any kind of widget. You can see an image of the layout below.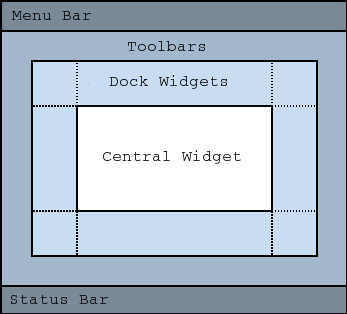
Creating Main Window Components¶
A central widget will typically be a standard Qt widget such as a
QTextEditor aQGraphicsView. Custom widgets can also be used for advanced applications. You set the central widget withsetCentralWidget().Main windows have either a single (SDI) or multiple (MDI) document interface. You create MDI applications in Qt by using a
QMdiAreaas the central widget.We will now examine each of the other widgets that can be added to a main window. We give examples on how to create and add them.
Creating Toolbars¶
Toolbars are implemented in the
QToolBarclass. You add a toolbar to a main window withaddToolBar().You control the initial position of toolbars by assigning them to a specific Qt::ToolBarArea. You can split an area by inserting a toolbar break - think of this as a line break in text editing - with
addToolBarBreak()orinsertToolBarBreak(). You can also restrict placement by the user withsetAllowedAreas()andsetMovable().The size of toolbar icons can be retrieved with
iconSize(). The sizes are platform dependent; you can set a fixed size withsetIconSize(). You can alter the appearance of all tool buttons in the toolbars withsetToolButtonStyle().An example of toolbar creation follows:
def createToolBars(self): fileToolBar = addToolBar(tr("File")) fileToolBar.addAction(newAct)
Creating Dock Widgets¶
Dock widgets are implemented in the
QDockWidgetclass. A dock widget is a window that can be docked into the main window. You add dock widgets to a main window withaddDockWidget().There are four dock widget areas as given by the Qt::DockWidgetArea enum: left, right, top, and bottom. You can specify which dock widget area that should occupy the corners where the areas overlap with
setCorner(). By default each area can only contain one row (vertical or horizontal) of dock widgets, but if you enable nesting withsetDockNestingEnabled(), dock widgets can be added in either direction.Two dock widgets may also be stacked on top of each other. A
QTabBaris then used to select which of the widgets should be displayed.We give an example of how to create and add dock widgets to a main window:
dockWidget = QDockWidget(tr("Dock Widget"), self) dockWidget.setAllowedAreas(Qt.LeftDockWidgetArea | Qt.RightDockWidgetArea) dockWidget.setWidget(dockWidgetContents) addDockWidget(Qt.LeftDockWidgetArea, dockWidget)
The Status Bar¶
You can set a status bar with
setStatusBar(), but one is created the first timestatusBar()(which returns the main window’s status bar) is called. SeeQStatusBarfor information on how to use it.Storing State¶
QMainWindowcan store the state of its layout withsaveState(); it can later be retrieved withrestoreState(). It is the position and size (relative to the size of the main window) of the toolbars and dock widgets that are stored.See also
QMenuBarQToolBarQStatusBarQDockWidgetMenus Example- class DockOption¶
(inherits
enum.Flag) This enum contains flags that specify the docking behavior ofQMainWindow.Constant
Description
QMainWindow.DockOption.AnimatedDocks
Identical to the
animatedproperty.QMainWindow.DockOption.AllowNestedDocks
Identical to the
dockNestingEnabledproperty.QMainWindow.DockOption.AllowTabbedDocks
The user can drop one dock widget “on top” of another. The two widgets are stacked and a tab bar appears for selecting which one is visible.
QMainWindow.DockOption.ForceTabbedDocks
Each dock area contains a single stack of tabbed dock widgets. In other words, dock widgets cannot be placed next to each other in a dock area. If this option is set, AllowNestedDocks has no effect.
QMainWindow.DockOption.VerticalTabs
The two vertical dock areas on the sides of the main window show their tabs vertically. If this option is not set, all dock areas show their tabs at the bottom. Implies AllowTabbedDocks. See also
setTabPosition().QMainWindow.DockOption.GroupedDragging
When dragging the titlebar of a dock, all the tabs that are tabbed with it are going to be dragged. Implies AllowTabbedDocks. Does not work well if some QDockWidgets have restrictions in which area they are allowed. (This enum value was added in Qt 5.6.)
These options only control how dock widgets may be dropped in a
QMainWindow. They do not re-arrange the dock widgets to conform with the specified options. For this reason they should be set before any dock widgets are added to the main window. Exceptions to this are the AnimatedDocks and VerticalTabs options, which may be set at any time.
Note
Properties can be used directly when
from __feature__ import true_propertyis used or via accessor functions otherwise.- property animatedᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether manipulating dock widgets and tool bars is animated.
When a dock widget or tool bar is dragged over the main window, the main window adjusts its contents to indicate where the dock widget or tool bar will be docked if it is dropped. Setting this property causes
QMainWindowto move its contents in a smooth animation. Clearing this property causes the contents to snap into their new positions.By default, this property is set. It may be cleared if the main window contains widgets which are slow at resizing or repainting themselves.
Setting this property is identical to setting the
AnimatedDocksoption usingsetDockOptions().- Access functions:
- property dockNestingEnabledᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether docks can be nested.
If this property is
false, dock areas can only contain a single row (horizontal or vertical) of dock widgets. If this property istrue, the area occupied by a dock widget can be split in either direction to contain more dock widgets.Dock nesting is only necessary in applications that contain a lot of dock widgets. It gives the user greater freedom in organizing their main window. However, dock nesting leads to more complex (and less intuitive) behavior when a dock widget is dragged over the main window, since there are more ways in which a dropped dock widget may be placed in the dock area.
Setting this property is identical to setting the
AllowNestedDocksoption usingsetDockOptions().- Access functions:
- property dockOptionsᅟ: Combination of QMainWindow.DockOption¶
This property holds the docking behavior of
QMainWindow.The default value is
AnimatedDocks|AllowTabbedDocks.- Access functions:
- property documentModeᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether the tab bar for tabbed dockwidgets is set to document mode..
The default is false.
See also
- Access functions:
This property holds size of toolbar icons in this mainwindow..
The default is the default tool bar icon size of the GUI style. Note that the icons used must be at least of this size as the icons are only scaled down.
- Access functions:
- property tabShapeᅟ: QTabWidget.TabShape¶
This property holds the tab shape used for tabbed dock widgets..
The default is
Rounded.See also
- Access functions:
- property toolButtonStyleᅟ: Qt.ToolButtonStyle¶
This property holds style of toolbar buttons in this mainwindow..
To have the style of toolbuttons follow the system settings, set this property to Qt::ToolButtonFollowStyle. On Unix, the user settings from the desktop environment will be used. On other platforms, Qt::ToolButtonFollowStyle means icon only.
The default is Qt::ToolButtonIconOnly.
- Access functions:
- property unifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMacᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether the window uses the unified title and toolbar look on macOS.
Note that the Qt 5 implementation has several limitations compared to Qt 4:
Use in windows with OpenGL content is not supported. This includes QOpenGLWidget.
Using dockable or movable toolbars may result in painting errors and is not recommended
- Access functions:
- __init__([parent=None[, flags=Qt.WindowFlags()]])¶
- Parameters:
parent –
QWidgetflags – Combination of
WindowType
Constructs a
QMainWindowwith the givenparentand the specified widgetflags.QMainWindowsets the Qt::Window flag itself, and will hence always be created as a top-level widget.- addDockWidget(area, dockwidget)¶
- Parameters:
area –
DockWidgetAreadockwidget –
QDockWidget
Adds the given
dockwidgetto the specifiedarea.- addDockWidget(area, dockwidget, orientation)
- Parameters:
area –
DockWidgetAreadockwidget –
QDockWidgetorientation –
Orientation
Adds
dockwidgetinto the givenareain the direction specified by theorientation.Equivalent of calling
addToolBar(Qt::TopToolBarArea,toolbar)- addToolBar(title)
- Parameters:
title – str
- Return type:
Creates a
QToolBarobject, setting its window title totitle, and inserts it into the top toolbar area.See also
setWindowTitle()- addToolBar(area, toolbar)
- Parameters:
area –
ToolBarAreatoolbar –
QToolBar
Adds the
toolbarinto the specifiedareain this main window. Thetoolbaris placed at the end of the current tool bar block (i.e. line). If the main window already managestoolbarthen it will only move the toolbar toarea.- addToolBarBreak([area=Qt.TopToolBarArea])¶
- Parameters:
area –
ToolBarArea
Adds a toolbar break to the given
areaafter all the other objects that are present.Returns the central widget for the main window. This function returns
Noneif the central widget has not been set.See also
Returns the dock widget area that occupies the specified
corner.See also
Returns a popup menu containing checkable entries for the toolbars and dock widgets present in the main window. If there are no toolbars and dock widgets present, this function returns
None.By default, this function is called by the main window when the user activates a context menu, typically by right-clicking on a toolbar or a dock widget.
If you want to create a custom popup menu, reimplement this function and return a newly-created popup menu. Ownership of the popup menu is transferred to the caller.
See also
- dockOptions()¶
- Return type:
Combination of
DockOption
See also
Getter of property
dockOptionsᅟ.- dockWidgetArea(dockwidget)¶
- Parameters:
dockwidget –
QDockWidget- Return type:
Returns the Qt::DockWidgetArea for
dockwidget. Ifdockwidgethas not been added to the main window, this function returnsQt::NoDockWidgetArea.See also
addDockWidget()splitDockWidget()DockWidgetArea- documentMode()¶
- Return type:
bool
See also
Getter of property
documentModeᅟ.- iconSize()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
iconSizeᅟ.This signal is emitted when the size of the icons used in the window is changed. The new icon size is passed in
iconSize.You can connect this signal to other components to help maintain a consistent appearance for your application.
See also
Inserts the
toolbarinto the area occupied by thebeforetoolbar so that it appears before it. For example, in normal left-to-right layout operation, this means thattoolbarwill appear to the left of the toolbar specified bybeforein a horizontal toolbar area.Inserts a toolbar break before the toolbar specified by
before.- isAnimated()¶
- Return type:
bool
Getter of property
animatedᅟ.- isDockNestingEnabled()¶
- Return type:
bool
Getter of property
dockNestingEnabledᅟ.- Return type:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Returns the menu bar for the main window. This function creates and returns an empty menu bar if the menu bar does not exist.
If you want all windows in a Mac application to share one menu bar, don’t use this function to create it, because the menu bar created here will have this
QMainWindowas its parent. Instead, you must create a menu bar that does not have a parent, which you can then share among all the Mac windows. Create a parent-less menu bar this way:menuBar = QMenuBar(None)
See also
- Return type:
Returns the menu bar for the main window. This function returns null if a menu bar hasn’t been constructed yet.
See also
- removeDockWidget(dockwidget)¶
- Parameters:
dockwidget –
QDockWidget
Removes the
dockwidgetfrom the main window layout and hides it. Note that thedockwidgetis not deleted.Removes the
toolbarfrom the main window layout and hides it. Note that thetoolbaris not deleted.Removes a toolbar break previously inserted before the toolbar specified by
before.- resizeDocks(docks, sizes, orientation)¶
- Parameters:
docks – .list of QDockWidget
sizes – .list of int
orientation –
Orientation
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Resizes the dock widgets in the list
docksto the corresponding size in pixels from the listsizes. Iforientationis Qt::Horizontal, adjusts the width, otherwise adjusts the height of the dock widgets. The sizes will be adjusted such that the maximum and the minimum sizes are respected and theQMainWindowitself will not be resized. Any additional/missing space is distributed amongst the widgets according to the relative weight of the sizes.Example:
resizeDocks({blueWidget, yellowWidget}, {20 , 40}, Qt.Horizontal)
If the blue and the yellow widget are nested on the same level they will be resized such that the yellowWidget is twice as big as the blueWidget
If some widgets are grouped in tabs, only one widget per group should be specified. Widgets not in the list might be changed to respect the constraints.
- restoreDockWidget(dockwidget)¶
- Parameters:
dockwidget –
QDockWidget- Return type:
bool
Restores the state of
dockwidgetif it is created after the call torestoreState(). Returnstrueif the state was restored; otherwise returnsfalse.See also
- restoreState(state[, version=0])¶
- Parameters:
state –
QByteArrayversion – int
- Return type:
bool
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Restores the
stateof this mainwindow’s toolbars and dockwidgets. Also restores the corner settings too. Theversionnumber is compared with that stored instate. If they do not match, the mainwindow’s state is left unchanged, and this function returnsfalse; otherwise, the state is restored, and this function returnstrue.To restore geometry saved using QSettings, you can use code like this:
def readSettings(self): settings = QSettings("MyCompany", "MyApp") restoreGeometry(settings.value("myWidget/geometry").toByteArray()) restoreState(settings.value("myWidget/windowState").toByteArray())
- saveState([version=0])¶
- Parameters:
version – int
- Return type:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Saves the current state of this mainwindow’s toolbars and dockwidgets. This includes the corner settings which can be set with
setCorner(). Theversionnumber is stored as part of the data.The objectName property is used to identify each
QToolBarandQDockWidget. You should make sure that this property is unique for eachQToolBarandQDockWidgetyou add to theQMainWindowTo restore the saved state, pass the return value and
versionnumber torestoreState().To save the geometry when the window closes, you can implement a close event like this:
def closeEvent(self, event): settings = QSettings("MyCompany", "MyApp") settings.setValue("geometry", saveGeometry()) settings.setValue("windowState", saveState()) QMainWindow.closeEvent(event)
- setAnimated(enabled)¶
- Parameters:
enabled – bool
See also
Setter of property
animatedᅟ.Sets the given
widgetto be the main window’s central widget.Note:
QMainWindowtakes ownership of thewidgetpointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.See also
- setCorner(corner, area)¶
- Parameters:
corner –
Cornerarea –
DockWidgetArea
Sets the given dock widget
areato occupy the specifiedcorner.See also
- setDockNestingEnabled(enabled)¶
- Parameters:
enabled – bool
See also
Setter of property
dockNestingEnabledᅟ.- setDockOptions(options)¶
- Parameters:
options – Combination of
DockOption
See also
Setter of property
dockOptionsᅟ.- setDocumentMode(enabled)¶
- Parameters:
enabled – bool
See also
Setter of property
documentModeᅟ.Setter of property
iconSizeᅟ.Sets the menu bar for the main window to
menuBar.Note:
QMainWindowtakes ownership of themenuBarpointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.See also
Sets the menu bar for the main window to
menuBar.QMainWindowtakes ownership of themenuBarpointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.See also
- setStatusBar(statusbar)¶
- Parameters:
statusbar –
QStatusBar
Sets the status bar for the main window to
statusbar.Setting the status bar to
Nonewill remove it from the main window. Note thatQMainWindowtakes ownership of thestatusbarpointer and deletes it at the appropriate time.See also
- setTabPosition(areas, tabPosition)¶
- Parameters:
areas – Combination of
DockWidgetAreatabPosition –
TabPosition
Sets the tab position for the given dock widget
areasto the specifiedtabPosition. By default, all dock areas show their tabs at the bottom.Setter of property
tabShapeᅟ.- setToolButtonStyle(toolButtonStyle)¶
- Parameters:
toolButtonStyle –
ToolButtonStyle
See also
Setter of property
toolButtonStyleᅟ.- setUnifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac(set)¶
- Parameters:
set – bool
See also
Setter of property
unifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMacᅟ.- splitDockWidget(after, dockwidget, orientation)¶
- Parameters:
after –
QDockWidgetdockwidget –
QDockWidgetorientation –
Orientation
Splits the space covered by the
firstdock widget into two parts, moves thefirstdock widget into the first part, and moves theseconddock widget into the second part.The
orientationspecifies how the space is divided: A Qt::Horizontal split places the second dock widget to the right of the first; a Qt::Vertical split places the second dock widget below the first.Note: if
firstis currently in a tabbed docked area,secondwill be added as a new tab, not as a neighbor offirst. This is because a single tab can contain only one dock widget.Note: The Qt::LayoutDirection influences the order of the dock widgets in the two parts of the divided area. When right-to-left layout direction is enabled, the placing of the dock widgets will be reversed.
- statusBar()¶
- Return type:
Returns the status bar for the main window. This function creates and returns an empty status bar if the status bar does not exist.
See also
- tabPosition(area)¶
- Parameters:
area –
DockWidgetArea- Return type:
Returns the tab position for
area.- tabShape()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
tabShapeᅟ.- tabifiedDockWidgetActivated(dockWidget)¶
- Parameters:
dockWidget –
QDockWidget
This signal is emitted when the tabified dock widget is activated by selecting the tab. The activated dock widget is passed in
dockWidget.See also
- tabifiedDockWidgets(dockwidget)¶
- Parameters:
dockwidget –
QDockWidget- Return type:
.list of QDockWidget
Returns the dock widgets that are tabified together with
dockwidget.See also
- tabifyDockWidget(first, second)¶
- Parameters:
first –
QDockWidgetsecond –
QDockWidget
Moves
seconddock widget on top offirstdock widget, creating a tabbed docked area in the main window.See also
Removes the central widget from this main window.
The ownership of the removed widget is passed to the caller.
Returns the Qt::ToolBarArea for
toolbar. Iftoolbarhas not been added to the main window, this function returnsQt::NoToolBarArea.See also
addToolBar()addToolBarBreak()ToolBarAreaReturns whether there is a toolbar break before the
toolbar.See also
- toolButtonStyle()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
toolButtonStyleᅟ.- toolButtonStyleChanged(toolButtonStyle)¶
- Parameters:
toolButtonStyle –
ToolButtonStyle
This signal is emitted when the style used for tool buttons in the window is changed. The new style is passed in
toolButtonStyle.You can connect this signal to other components to help maintain a consistent appearance for your application.
See also
- unifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMac()¶
- Return type:
bool
See also
Getter of property
unifiedTitleAndToolBarOnMacᅟ.