PySide6.QtWidgets.QGridLayout¶
- class QGridLayout¶
The
QGridLayoutclass lays out widgets in a grid. More…Synopsis¶
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
addItem()def
addLayout()def
addWidget()def
cellRect()def
columnCount()def
columnStretch()def
itemAtPosition()def
originCorner()def
rowCount()def
rowStretch()def
setRowStretch()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description¶
QGridLayouttakes the space made available to it (by its parent layout or by theparentWidget()), divides it up into rows and columns, and puts each widget it manages into the correct cell.Columns and rows behave identically; we will discuss columns, but there are equivalent functions for rows.
Each column has a minimum width and a stretch factor. The minimum width is the greatest of that set using
setColumnMinimumWidth()and the minimum width of each widget in that column. The stretch factor is set usingsetColumnStretch()and determines how much of the available space the column will get over and above its necessary minimum.Normally, each managed widget or layout is put into a cell of its own using
addWidget(). It is also possible for a widget to occupy multiple cells using the row and column spanning overloads ofaddItem()andaddWidget(). If you do this,QGridLayoutwill guess how to distribute the size over the columns/rows (based on the stretch factors).To remove a widget from a layout, call
removeWidget(). Callinghide()on a widget also effectively removes the widget from the layout untilshow()is called.This illustration shows a fragment of a dialog with a five-column, three-row grid (the grid is shown overlaid in magenta):
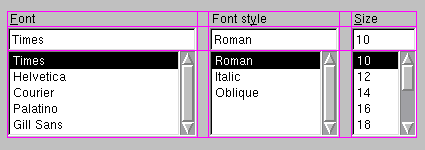
Columns 0, 2 and 4 in this dialog fragment are made up of a
QLabel, aQLineEdit, and a QListBox. Columns 1 and 3 are placeholders made withsetColumnMinimumWidth(). Row 0 consists of threeQLabelobjects, row 1 of threeQLineEditobjects and row 2 of three QListBox objects. We used placeholder columns (1 and 3) to get the right amount of space between the columns.Note that the columns and rows are not equally wide or tall. If you want two columns to have the same width, you must set their minimum widths and stretch factors to be the same yourself. You do this using
setColumnMinimumWidth()andsetColumnStretch().If the
QGridLayoutis not the top-level layout (i.e. does not manage all of the widget’s area and children), you must add it to its parent layout when you create it, but before you do anything with it. The normal way to add a layout is by callingaddLayout()on the parent layout.Once you have added your layout you can start putting widgets and other layouts into the cells of your grid layout using
addWidget(),addItem(), andaddLayout().QGridLayoutalso includes two margin widths: thecontents marginand thespacing(). The contents margin is the width of the reserved space along each of theQGridLayout‘s four sides. Thespacing()is the width of the automatically allocated spacing between neighboring boxes.The default contents margin values are provided by the
style. The default value Qt styles specify is 9 for child widgets and 11 for windows. The spacing defaults to the same as the margin width for a top-level layout, or to the same as the parent layout.See also
QBoxLayoutQStackedLayoutLayout Management Basic Layouts ExampleConstructs a new
QGridLayoutwith parent widget,parent. The layout has one row and one column initially, and will expand when new items are inserted.The layout is set directly as the top-level layout for
parent. There can be only one top-level layout for a widget. It is returned bylayout().If
parentisNone, then you must insert this grid layout into another layout, or set it as a widget’s layout usingsetLayout().See also
- addItem(item, row, column[, rowSpan=1[, columnSpan=1[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()]]])¶
- Parameters:
item –
QLayoutItemrow – int
column – int
rowSpan – int
columnSpan – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
Adds
itemat positionrow,column, spanningrowSpanrows andcolumnSpancolumns, and aligns it according toalignment. IfrowSpanand/orcolumnSpanis -1, then the item will extend to the bottom and/or right edge, respectively. The layout takes ownership of theitem.Warning
Do not use this function to add child layouts or child widget items. Use
addLayout()oraddWidget()instead.- addLayout(layout, row, column[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()])¶
- Parameters:
layout –
QLayoutrow – int
column – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
Places the
layoutat position (row,column) in the grid. The top-left position is (0, 0).The alignment is specified by
alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.A non-zero alignment indicates that the layout should not grow to fill the available space but should be sized according to
sizeHint().layoutbecomes a child of the grid layout.- addLayout(layout, row, column, rowSpan, columnSpan[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()])
- Parameters:
layout –
QLayoutrow – int
column – int
rowSpan – int
columnSpan – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
This is an overloaded function.
This version adds the layout
layoutto the cell grid, spanning multiple rows/columns. The cell will start atrow,columnspanningrowSpanrows andcolumnSpancolumns.If
rowSpanand/orcolumnSpanis -1, then the layout will extend to the bottom and/or right edge, respectively.- addWidget(widget, row, column[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()])¶
- Parameters:
widget –
QWidgetrow – int
column – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
Adds the given
widgetto the cell grid atrow,column. The top-left position is (0, 0) by default.The alignment is specified by
alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.- addWidget(widget, row, column, rowSpan, columnSpan[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()])
- Parameters:
widget –
QWidgetrow – int
column – int
rowSpan – int
columnSpan – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
This is an overloaded function.
This version adds the given
widgetto the cell grid, spanning multiple rows/columns. The cell will start atfromRow,fromColumnspanningrowSpanrows andcolumnSpancolumns. Thewidgetwill have the givenalignment.If
rowSpanand/orcolumnSpanis -1, then the widget will extend to the bottom and/or right edge, respectively.Returns the geometry of the cell with row
rowand columncolumnin the grid. Returns an invalid rectangle ifroworcolumnis outside the grid.Warning
in the current version of Qt this function does not return valid results until
setGeometry()has been called, i.e. after theparentWidget()is visible.- columnCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of columns in this grid.
- columnMinimumWidth(column)¶
- Parameters:
column – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the column spacing for column
column.See also
- columnStretch(column)¶
- Parameters:
column – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the stretch factor for column
column.See also
- getItemPosition(idx)¶
- Parameters:
idx – int
- Return type:
PyObject*
Returns the position information of the item with the given
index.The variables passed as
rowandcolumnare updated with the position of the item in the layout, and therowSpanandcolumnSpanvariables are updated with the vertical and horizontal spans of the item.See also
itemAtPosition()itemAt()- horizontalSpacing()¶
- Return type:
int
See also
- itemAtPosition(row, column)¶
- Parameters:
row – int
column – int
- Return type:
Returns the layout item that occupies cell (
row,column), orNoneif the cell is empty.See also
Returns the corner that’s used for the grid’s origin, i.e. for position (0, 0).
See also
- rowCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of rows in this grid.
- rowMinimumHeight(row)¶
- Parameters:
row – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the minimum width set for row
row.See also
- rowStretch(row)¶
- Parameters:
row – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the stretch factor for row
row.See also
- setColumnMinimumWidth(column, minSize)¶
- Parameters:
column – int
minSize – int
Sets the minimum width of column
columntominSizepixels.- setColumnStretch(column, stretch)¶
- Parameters:
column – int
stretch – int
Sets the stretch factor of column
columntostretch. The first column is number 0.The stretch factor is relative to the other columns in this grid. Columns with a higher stretch factor take more of the available space.
The default stretch factor is 0. If the stretch factor is 0 and no other column in this table can grow at all, the column may still grow.
An alternative approach is to add spacing using
addItem()with aQSpacerItem.See also
- setDefaultPositioning(n, orient)¶
- Parameters:
n – int
orient –
Orientation
- setHorizontalSpacing(spacing)¶
- Parameters:
spacing – int
See also
Sets the grid’s origin corner, i.e. position (0, 0), to
corner.See also
- setRowMinimumHeight(row, minSize)¶
- Parameters:
row – int
minSize – int
Sets the minimum height of row
rowtominSizepixels.- setRowStretch(row, stretch)¶
- Parameters:
row – int
stretch – int
Sets the stretch factor of row
rowtostretch. The first row is number 0.The stretch factor is relative to the other rows in this grid. Rows with a higher stretch factor take more of the available space.
The default stretch factor is 0. If the stretch factor is 0 and no other row in this table can grow at all, the row may still grow.
- setVerticalSpacing(spacing)¶
- Parameters:
spacing – int
See also
- verticalSpacing()¶
- Return type:
int
See also