PySide6.QtWidgets.QBoxLayout¶
- class QBoxLayout¶
The
QBoxLayoutclass lines up child widgets horizontally or vertically.Details
QBoxLayouttakes the space it gets (from its parent layout or from theparentWidget()), divides it up into a row of boxes, and makes each managed widget fill one box.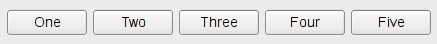
If the
QBoxLayout‘s orientation is Qt::Horizontal the boxes are placed in a row, with suitable sizes. Each widget (or other box) will get at least its minimum size and at most its maximum size. Any excess space is shared according to the stretch factors (more about that below).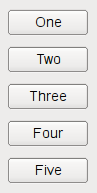
If the
QBoxLayout‘s orientation is Qt::Vertical, the boxes are placed in a column, again with suitable sizes.The easiest way to create a
QBoxLayoutis to use one of the convenience classes, e.g.QHBoxLayout(for Qt::Horizontal boxes) orQVBoxLayout(for Qt::Vertical boxes). You can also use theQBoxLayoutconstructor directly, specifying its direction asLeftToRight,RightToLeft,TopToBottom, orBottomToTop.If the
QBoxLayoutis not the top-level layout (i.e. it is not managing all of the widget’s area and children), you must add it to its parent layout before you can do anything with it. The normal way to add a layout is by calling parentLayout->addLayout().Once you have done this, you can add boxes to the
QBoxLayoutusing one of four functions:addWidget()to add a widget to theQBoxLayoutand set the widget’s stretch factor. (The stretch factor is along the row of boxes.)addSpacing()to create an empty box; this is one of the functions you use to create nice and spacious dialogs. See below for ways to set margins.addStretch()to create an empty, stretchable box.addLayout()to add a box containing anotherQLayoutto the row and set that layout’s stretch factor.
Use
insertWidget(),insertSpacing(),insertStretch()orinsertLayout()to insert a box at a specified position in the layout.QBoxLayoutalso includes two margin widths:setContentsMargins()sets the width of the outer border on each side of the widget. This is the width of the reserved space along each of theQBoxLayout‘s four sides.setSpacing()sets the width between neighboring boxes. (You can useaddSpacing()to get more space at a particular spot.)
The margin default is provided by the style. The default margin most Qt styles specify is 9 for child widgets and 11 for windows. The spacing defaults to the same as the margin width for a top-level layout, or to the same as the parent layout.
To remove a widget from a layout, call
removeWidget(). Callinghide()on a widget also effectively removes the widget from the layout untilshow()is called.You will almost always want to use
QVBoxLayoutandQHBoxLayoutrather thanQBoxLayoutbecause of their convenient constructors.See also
Inherited by:
QVBoxLayout,QHBoxLayoutSynopsis¶
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
addLayout()def
addSpacerItem()def
addSpacing()def
addStretch()def
addStrut()def
addWidget()def
direction()def
insertItem()def
insertLayout()def
insertSpacing()def
insertStretch()def
insertWidget()def
setDirection()def
setStretch()def
stretch()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
- class Direction¶
This type is used to determine the direction of a box layout.
Constant
Description
QBoxLayout.Direction.LeftToRight
Horizontal from left to right.
QBoxLayout.Direction.RightToLeft
Horizontal from right to left.
QBoxLayout.Direction.TopToBottom
Vertical from top to bottom.
QBoxLayout.Direction.BottomToTop
Vertical from bottom to top.
Constructs a new
QBoxLayoutwith directiondirand parent widgetparent.The layout is set directly as the top-level layout for
parent. There can be only one top-level layout for a widget. It is returned bylayout().See also
Adds
layoutto the end of the box, with serial stretch factorstretch.layoutbecomes a child of the box layout.See also
insertLayout()addItem()addWidget()- addSpacerItem(spacerItem)¶
- Parameters:
spacerItem –
QSpacerItem
Adds
spacerItemto the end of this box layout.The ownership of
spacerItemis passed to this layout.See also
- addSpacing(size)¶
- Parameters:
size – int
Adds a non-stretchable space (a
QSpacerItem) with sizesizeto the end of this box layout.QBoxLayoutprovides default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.See also
insertSpacing()addItem()QSpacerItem- addStretch([stretch=0])¶
- Parameters:
stretch – int
Adds a stretchable space (a
QSpacerItem) with zero minimum size and stretch factorstretchto the end of this box layout.See also
insertStretch()addItem()QSpacerItem- addStrut(size)¶
- Parameters:
size – int
Limits the perpendicular dimension of the box (e.g. height if the box is
LeftToRight) to a minimum ofsize. Other constraints may increase the limit.See also
addItem()- addWidget(widget[, stretch=0[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()]])¶
- Parameters:
widget –
QWidgetstretch – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
Adds
widgetto the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor ofstretchand alignmentalignment.The stretch factor applies only in the
directionof theQBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in thisQBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the
QBoxLayouthas a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to thesizePolicy()of each widget that’s involved.The alignment is specified by
alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.widgetbecomes a child of theparentWidget().See also
insertWidget()addItem()addLayout()addStretch()addSpacing()addStrut()Returns the direction of the box.
addWidget()andaddSpacing()work in this direction; the stretch stretches in this direction.See also
- insertItem(index, item)¶
- Parameters:
index – int
item –
QLayoutItem
Inserts
iteminto this box layout at positionindex. Index must be either negative or within the range 0 tocount(), inclusive. Ifindexis negative orcount(), the item is added at the end.The ownership of
itemis passed to this layout.See also
addItem()insertWidget()insertLayout()insertStretch()insertSpacing()Inserts
layoutat positionindex, with stretch factorstretch. Ifindexis negative, the layout is added at the end.layoutbecomes a child of the box layout.See also
- insertSpacerItem(index, spacerItem)¶
- Parameters:
index – int
spacerItem –
QSpacerItem
Inserts
spacerItemat positionindex, with zero minimum size and stretch factor. Ifindexis negative the space is added at the end.The ownership of
spacerItemis passed to this layout.- insertSpacing(index, size)¶
- Parameters:
index – int
size – int
Inserts a non-stretchable space (a
QSpacerItem) at positionindex, with sizesize. Ifindexis negative the space is added at the end.The box layout has default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.
See also
- insertStretch(index[, stretch=0])¶
- Parameters:
index – int
stretch – int
Inserts a stretchable space (a
QSpacerItem) at positionindex, with zero minimum size and stretch factorstretch. Ifindexis negative the space is added at the end.See also
- insertWidget(index, widget[, stretch=0[, alignment=Qt.Alignment()]])¶
- Parameters:
index – int
widget –
QWidgetstretch – int
alignment – Combination of
AlignmentFlag
Inserts
widgetat positionindex, with stretch factorstretchand alignmentalignment. Ifindexis negative, the widget is added at the end.The stretch factor applies only in the
directionof theQBoxLayout, and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in thisQBoxLayout. Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the
QBoxLayouthas a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to thesizePolicy()of each widget that’s involved.The alignment is specified by
alignment. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.widgetbecomes a child of theparentWidget().See also
Sets the direction of this layout to
direction.See also
- setStretch(index, stretch)¶
- Parameters:
index – int
stretch – int
Sets the stretch factor at position
index. tostretch.See also
Sets the stretch factor for the layout
layouttostretchand returnstrueiflayoutis found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returnsfalse.- setStretchFactor(w, stretch)
- Parameters:
w –
QWidgetstretch – int
- Return type:
bool
Sets the stretch factor for
widgettostretchand returns true ifwidgetis found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returnsfalse.See also
setAlignment()- stretch(index)¶
- Parameters:
index – int
- Return type:
int
Returns the stretch factor at position
index.See also