QML로 극좌표 차트 사용하기
참고: 이 예제는 QML을 사용한 차트 갤러리 예제의 일부입니다.
임의의 데이터가 포함된 스플라인 계열과 분산형 계열이 있는 차트로 시작합니다. 두 계열 모두 동일한 축을 사용합니다.
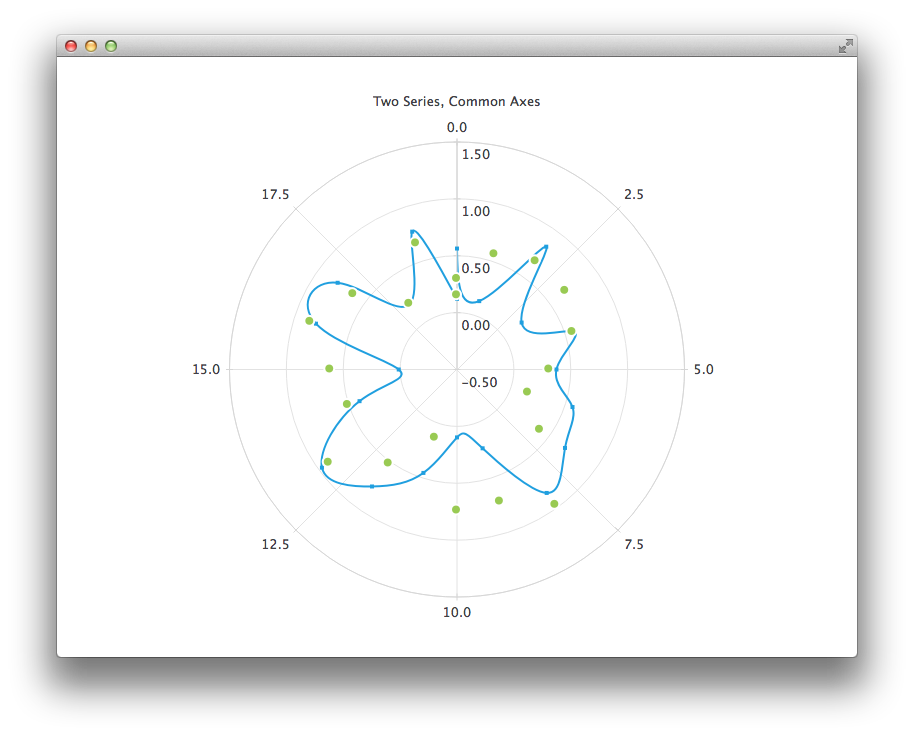
PolarChartView { title: "Two Series, Common Axes" anchors.fill: parent legend.visible: false antialiasing: true ValueAxis { id: axisAngular min: 0 max: 20 tickCount: 9 } ValueAxis { id: axisRadial min: -0.5 max: 1.5 } SplineSeries { id: series1 axisAngular: axisAngular axisRadial: axisRadial pointsVisible: true } ScatterSeries { id: series2 axisAngular: axisAngular axisRadial: axisRadial markerSize: 10 } // Add data dynamically to the series Component.onCompleted: { for (var i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { series1.append(i, Math.random()); series2.append(i, Math.random()); } } }
다음 차트는 DateTimeAxis 및 AreaSeries 을 사용해야 하는 몇 가지 정확한 과거 데이터를 보여줍니다.
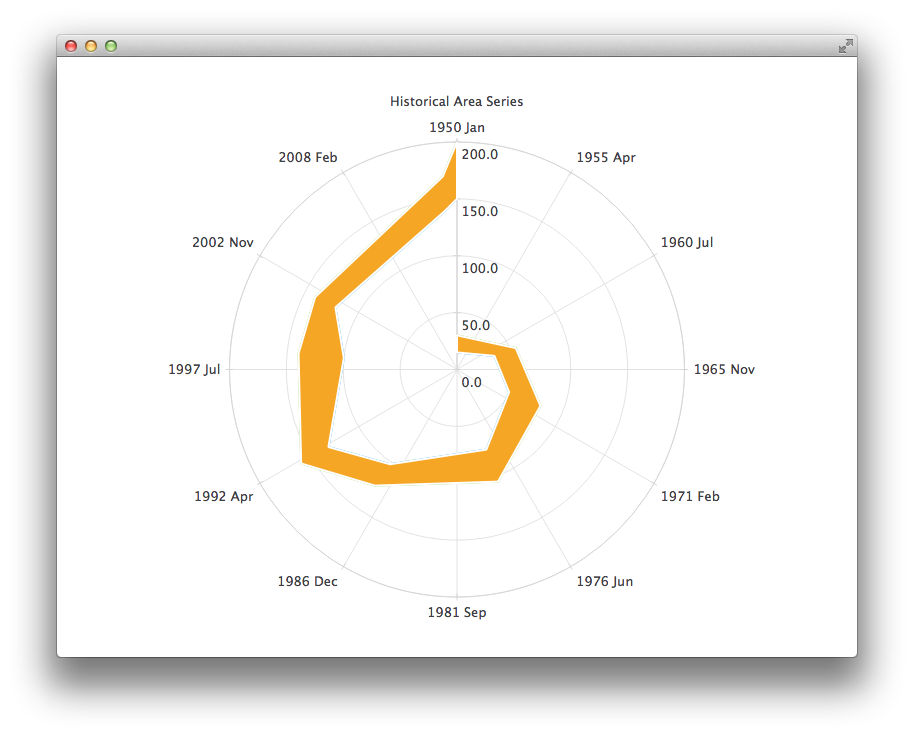
PolarChartView { id: root title: "Historical Area Chart" anchors.fill: parent legend.visible: false antialiasing: true DateTimeAxis { id: axis1 format: "yyyy MMM" tickCount: 13 } ValueAxis { id: axis2 } LineSeries { id: lowerLine axisAngular: axis1 axisRadial: axis2 // Please note that month in JavaScript months are zero based, so 2 means March XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1950, 0, 1)); y: 15 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1962, 4, 1)); y: 35 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1970, 0, 1)); y: 50 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1978, 2, 1)); y: 75 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1987, 11, 1)); y: 102 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1992, 1, 1)); y: 132 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1998, 7, 1)); y: 100 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2002, 4, 1)); y: 120 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2012, 8, 1)); y: 140 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2013, 5, 1)); y: 150 } } LineSeries { id: upperLine axisAngular: axis1 axisRadial: axis2 // Please note that month in JavaScript months are zero based, so 2 means March XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1950, 0, 1)); y: 30 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1962, 4, 1)); y: 55 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1970, 0, 1)); y: 80 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1978, 2, 1)); y: 105 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1987, 11, 1)); y: 125 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1992, 1, 1)); y: 160 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1998, 7, 1)); y: 140 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2002, 4, 1)); y: 140 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2012, 8, 1)); y: 170 } XYPoint { x: root.toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2013, 5, 1)); y: 200 } } AreaSeries { axisAngular: axis1 axisRadial: axis2 lowerSeries: lowerLine upperSeries: upperLine } // DateTimeAxis is based on QDateTimes so we must convert our JavaScript dates to // milliseconds since epoch to make them match the DateTimeAxis values function toMsecsSinceEpoch(date) { var msecs = date.getTime(); return msecs; } }
다음 차트에서는 데이터를 더 쉽게 이해할 수 있도록 CategoryAxis 을 사용합니다.
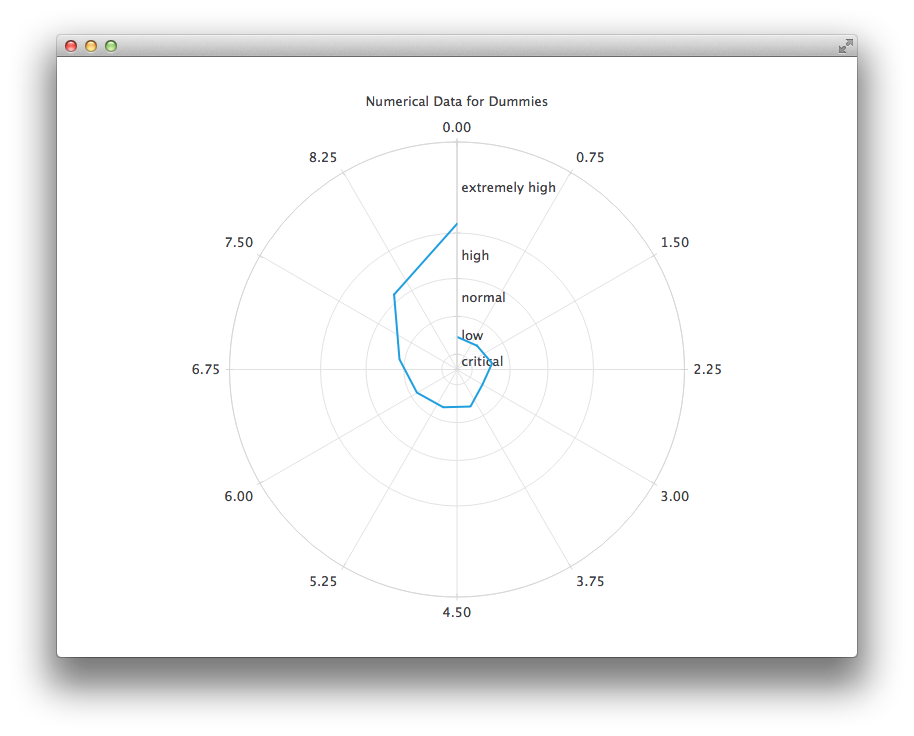
PolarChartView { title: "Numerical Data for Dummies" anchors.fill: parent legend.visible: false antialiasing: true LineSeries { axisRadial: CategoryAxis { min: 0 max: 30 CategoryRange { label: "critical" endValue: 2 } CategoryRange { label: "low" endValue: 7 } CategoryRange { label: "normal" endValue: 12 } CategoryRange { label: "high" endValue: 18 } CategoryRange { label: "extremely high" endValue: 30 } } axisAngular: ValueAxis { tickCount: 13 } XYPoint { x: 0; y: 4.3 } XYPoint { x: 1; y: 4.1 } XYPoint { x: 2; y: 4.7 } XYPoint { x: 3; y: 3.9 } XYPoint { x: 4; y: 5.2 } XYPoint { x: 5; y: 5.3 } XYPoint { x: 6; y: 6.1 } XYPoint { x: 7; y: 7.7 } XYPoint { x: 8; y: 12.9 } XYPoint { x: 9; y: 19.2 } } }
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

