Qt Quick 3D - Beispiel für benutzerdefinierte Shader
Demonstriert die Verwendung von benutzerdefinierten Vertex- und Fragment-Shadern.
Dieses Beispiel demonstriert die Verwendung eines Materials mit vollständig benutzerdefiniertem Vertex- und Fragment-Shader-Code.
Dieses Beispiel ist das Gegenstück zum custommaterials-Beispiel, das die andere Gruppe von benutzerdefinierten Materialien demonstriert: shaded Materialien, bei denen der Shader-Code-Schnipsel ein PrincipledMaterial ergänzt, anstatt es zu ersetzen.
Implementieren eines benutzerdefinierten Materials
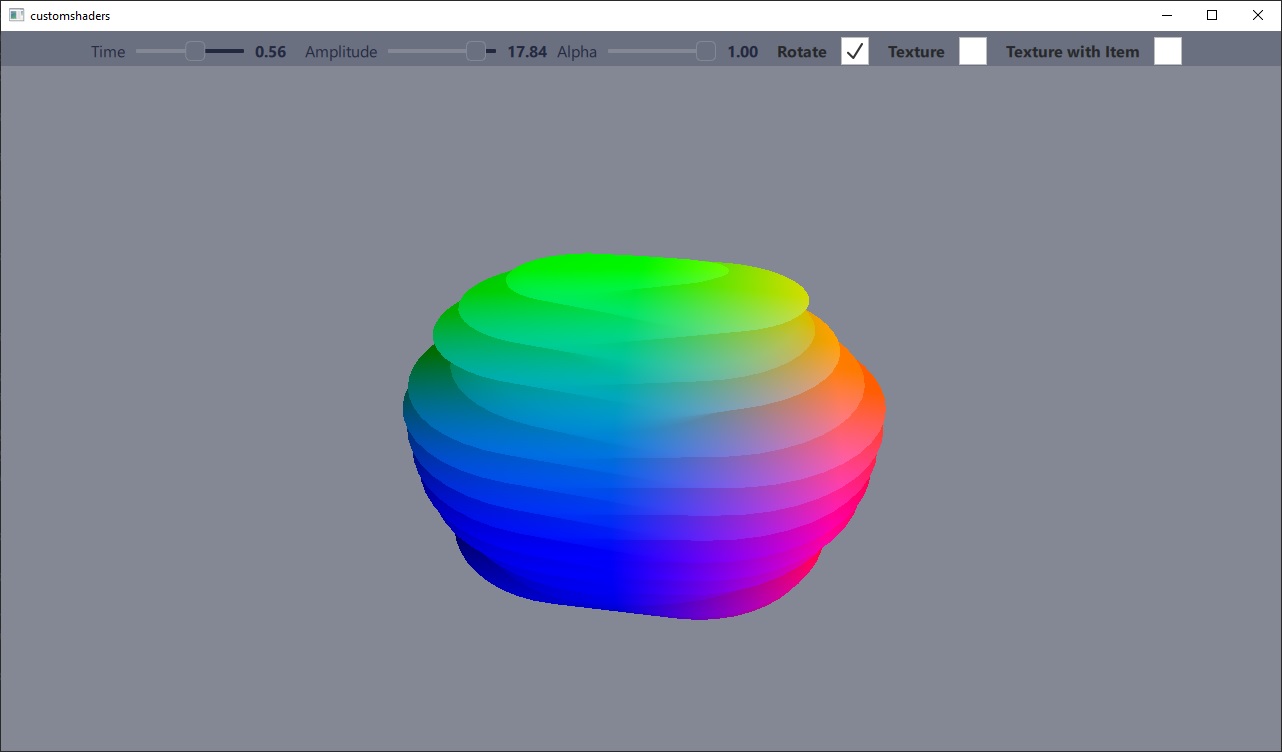
In diesem Beispiel wird ein Mesh durch den Vertex-Shader gemäß einer Sinusfunktion verformt. Das Endergebnis wird durch zwei Schieberegler gesteuert, die den Zeit- und Amplitudenwerten der Sinusfunktion entsprechen.
Der Fragment-Shader wird verwendet, um das Netz entsprechend den Positionswerten der Scheitelpunkte zu färben. Es sind zwei Fragment-Shader enthalten: einer mit und einer ohne Texturierung. Die texturierte Version sampelt eine Textur, die entweder aus einer Bilddatei oder aus einer Live-Ebene Qt Quick stammt.
Das Material nimmt nicht am standardmäßigen Beleuchtungs- oder Schattensystem teil und hat daher die Eigenschaft shadingMode auf CustomMaterial.Unshaded gesetzt.
Unter CustomMaterial finden Sie eine ausführliche Beschreibung der Funktionen für benutzerdefinierte Materialien.
CustomMaterial { id: root property real time: 0.0 property real amplitude: 5.0 property real alpha: 1.0 property bool texturing: false property bool textureFromItem: false property Item texSrc Texture { id: texFromFile source: "qt_logo.png" } Texture { id: texFromItem sourceItem: root.texSrc } property TextureInput tex: TextureInput { enabled: root.texturing texture: root.textureFromItem ? texFromItem : texFromFile } shadingMode: CustomMaterial.Unshaded sourceBlend: root.alpha < 1.0 ? CustomMaterial.SrcAlpha : CustomMaterial.NoBlend destinationBlend: root.alpha < 1.0 ? CustomMaterial.OneMinusSrcAlpha : CustomMaterial.NoBlend cullMode: CustomMaterial.BackFaceCulling vertexShader: "example.vert" fragmentShader: root.texturing ? "example_tex.frag" : "example.frag" }
Verwenden eines benutzerdefinierten Materials
Ein benutzerdefiniertes Material, das benutzerdefinierte Shader verwendet, wird auf die gleiche Weise wie jedes andere Material verwendet. Die Uniformen im Shader können einfach durch QML-Eigenschaftsbindungen aktualisiert werden.
Model { position: Qt.vector3d(0, 0, 0) NumberAnimation on eulerRotation.y { from: 0 to: 360 duration: 3000 loops: -1 running: control.animateRotation } scale: Qt.vector3d(2, 2, 2) source: "#Sphere" materials: [ ExampleMaterial { id: exampleMaterial time: control.time amplitude: control.amplitude alpha: control.alpha texturing: control.texturing textureFromItem: control.textureFromItem texSrc: Rectangle { layer.enabled: true layer.textureMirroring: ShaderEffectSource.NoMirroring visible: false SequentialAnimation on color { ColorAnimation { from: "black"; to: "yellow"; duration: 2000 } ColorAnimation { from: "yellow"; to: "cyan"; duration: 1000 } ColorAnimation { from: "cyan"; to: "black"; duration: 500 } loops: -1 } width: 512 height: 512 Image { source: "qt_logo.png" anchors.centerIn: parent } } } ] }
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

