使用 GDB 进行远程调试
通常情况下,远程机器或容器已经安装了 GDBserver,并且应用程序的远程执行已经设置好,可以通过选择Run 按钮(或Ctrl+R)来运行,这时可以通过选择Debug 按钮(或F5)来启动远程调试。
在这种情况下,Qt Creator 会按正确顺序自动启动和连接远程计算机上的调试服务器和应用程序以及开发主机上的实际调试器。
这是首选方法。
如果不符合这种自动设置的要求,但远程机器能够运行 GDB 服务器(或任何使用 GDB 串行协议的兼容探针),则仍可使用Qt Creator 调试应用程序。
应用程序正在运行,可通过 SSH 访问远程机器
如果要连接到远程计算机上已运行的应用程序,并且可以通过 SSH 从本地计算机主机启动调试服务器,请访问Debug >Start Debugging >Attach to running applications 。
应用程序未运行,终端可访问远程计算机
如果无法通过 SSH 从本地计算机启动调试服务器,请查阅设备文档,了解启动调试服务器的其他方法。
如果可以通过终端访问远程机器,并在远程机器上安装了 GDB 服务器,则可以手动将可执行文件传输到远程机器,然后通过端口号和可执行文件启动gdbserver :
gdbserver :1234 /path/to/executable
它通常会做出响应:
Process /path/to/executable created; pid = 5159 Listening on port 1234
在运行Qt Creator 的本地计算机上:
- 转到Debug >Start Debugging >Attach to Running Debug Server 。
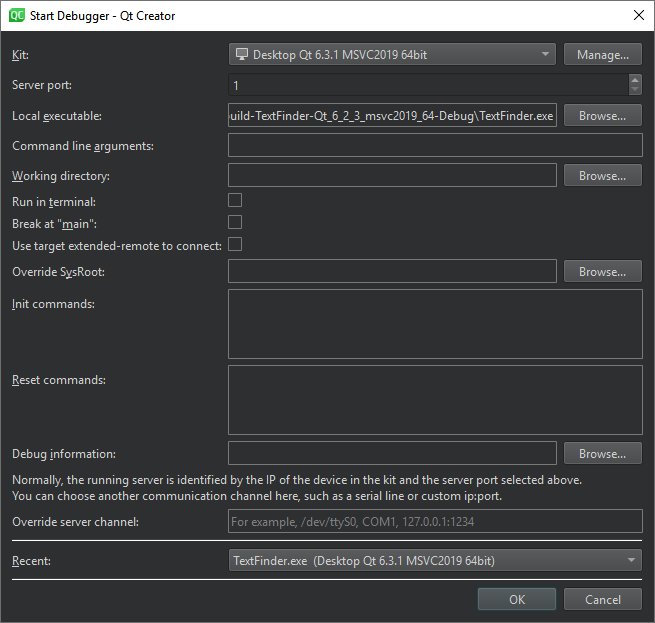
- 在Kit 中,选择用于构建项目的构建和运行工具包。
- 在Server port 中,输入远程机器的名称和要使用的端口号。
- 在Local executable 中,指定本地计算机上应用程序可执行文件的路径。
- 在Command line arguments 中,指定要传递给可执行文件的命令行参数。
- 在Working directory 中,指定工作目录。默认为构建结果的目录。
- 为控制台应用程序选择Run in terminal 。
- 选择Break at "main" 可在主函数处停止调试器。
- 选择Use target extended-remote to connect ,在
target extended-remote mode中创建连接。在此模式下,当调试程序退出或您从程序中脱离时,调试器仍与目标相连。您可以重新运行应用程序,附加到正在运行的应用程序,或使用目标机专用的监控命令。例如,除非使用--once选项调用,否则 GDB 不会退出,但可以使用monitor exit命令使其退出。 - 在Override SysRoot 中,指定要使用的
sysroot的路径,而不是默认的sysroot。 - 在Init commands 中,输入与目标建立连接后立即执行的命令。
- 在Reset commands 中,输入重置与目标的连接时要执行的命令。
- 在Debug information 中,指定存储调试信息的位置。不能使用空路径。
- 在Override server channel 中,指定要使用的通信通道,如串行线路或自定义端口。
- 在Recent 中,选择要使用的最新配置。
- 选择OK 开始调试。
默认情况下,无响应的 GDB 进程会在 40 秒后终止。要增加GDB timeout 中的超时时间,请访问首选项>Debugger >GDB 。
有关在 GDB 中以target extended-remote 模式连接的更多信息,请参阅《使用 GDB 调试:连接到远程目标》。
应用程序正在运行,终端可访问远程机器和 gdbserver
这种情况与上一节几乎相同,只是启动gdbserver 的方式不同:
gdbserver --attach :1234 <PID of running application>
使用 SSH 端口转发
要在无法暴露 GDB 服务器端口的远程目标机上进行调试,可使用 SSH 隧道将远程端口映射到本地端口。Qt Creator 会自动检测本地和远程端口。
打开 SSH 端口转发:
- 转到首选项>Devices 。
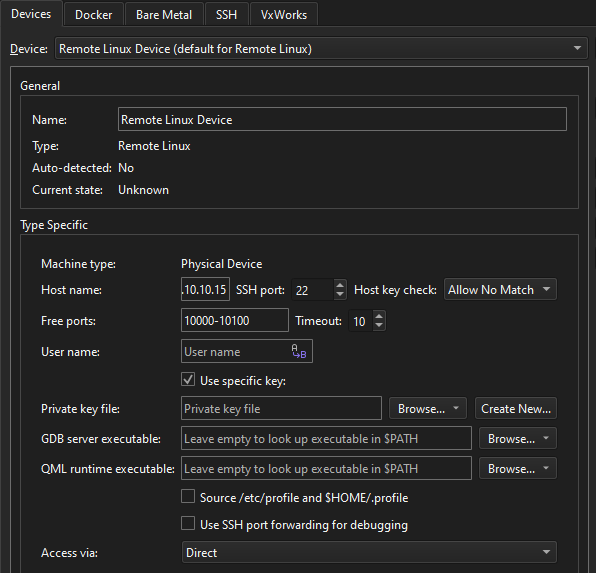
- 在Device 中,选择Remote Linux Device 。
- 选择Use SSH port forwarding for debugging 。
- 选择OK 。
Copyright © The Qt Company Ltd. and other contributors. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

