PySide6.QtWidgets.QColorDialog¶
- class QColorDialog¶
The
QColorDialogclass provides a dialog widget for specifying colors.Details
The color dialog’s function is to allow users to choose colors. For example, you might use this in a drawing program to allow the user to set the brush color.
The static functions provide modal color dialogs.
The static
getColor()function shows the dialog, and allows the user to specify a color. This function can also be used to let users choose a color with a level of transparency: pass theShowAlphaChanneloption as an additional argument.The user can store
customCount()different custom colors. The custom colors are shared by all color dialogs, and remembered during the execution of the program. UsesetCustomColor()to set the custom colors, and usecustomColor()to get them.When pressing the “Pick Screen Color” button, the cursor changes to a haircross and the colors on the screen are scanned. The user can pick up one by clicking the mouse or the Enter button. Pressing Escape restores the last color selected before entering this mode.
The Standard Dialogs example shows how to use
QColorDialogas well as other built-in Qt dialogs.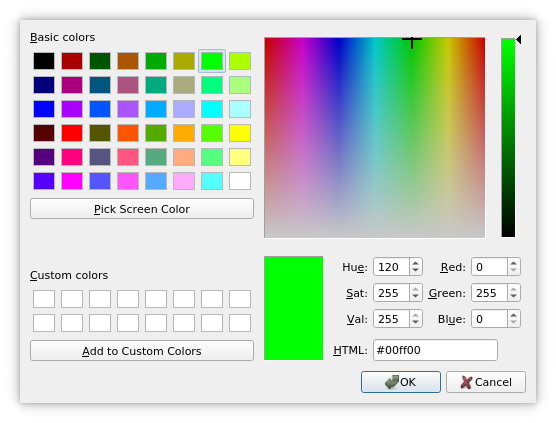
See also
QFileDialogQFontDialogStandard Dialogs ExampleSynopsis¶
Properties¶
currentColorᅟ- The currently selected color in the dialogoptionsᅟ- The various options that affect the look and feel of the dialog
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
currentColor()def
open()def
options()def
selectedColor()def
setOption()def
setOptions()def
testOption()
Signals¶
def
colorSelected()
Static functions¶
def
customColor()def
customCount()def
getColor()def
setCustomColor()def
standardColor()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
- class ColorDialogOption¶
(inherits
enum.Flag) This enum specifies various options that affect the look and feel of a color dialog.Constant
Description
QColorDialog.ColorDialogOption.ShowAlphaChannel
Allow the user to select the alpha component of a color.
QColorDialog.ColorDialogOption.NoButtons
Don’t display OK and Cancel buttons. (Useful for “live dialogs”.)
QColorDialog.ColorDialogOption.NoEyeDropperButton
Hide the Eye Dropper button. This value was added in Qt 6.6.
QColorDialog.ColorDialogOption.DontUseNativeDialog
Use Qt’s standard color dialog instead of the operating system native color dialog.
See also
optionssetOption()testOption()windowModality()
Note
Properties can be used directly when
from __feature__ import true_propertyis used or via accessor functions otherwise.This property holds the currently selected color in the dialog.
- Access functions:
- property optionsᅟ: Combination of QColorDialog.ColorDialogOption¶
This property holds the various options that affect the look and feel of the dialog.
By default, all options are disabled.
Options should be set before showing the dialog. Setting them while the dialog is visible is not guaranteed to have an immediate effect on the dialog (depending on the option and on the platform).
See also
- Access functions:
Constructs a color dialog with the given
parent.Constructs a color dialog with the given
parentand specifiedinitialcolor.This signal is emitted just after the user has clicked OK to select a color to use. The chosen color is specified by
color.See also
- currentColor()¶
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property
currentColorᅟ.This signal is emitted whenever the current color changes in the dialog. The current color is specified by
color.See also
Notification signal of property
currentColorᅟ.Returns the custom color at the given
indexas a QColor value.See also
- static customCount()¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of custom colors supported by
QColorDialog. All color dialogs share the same custom colors.- static getColor([initial=Qt.white[, parent=None[, title=""[, options=QColorDialog.ColorDialogOptions()]]]])¶
- Parameters:
initial –
QColorparent –
QWidgettitle – str
options – Combination of
ColorDialogOption
- Return type:
Pops up a modal color dialog with the given window
title(or “Select Color” if none is specified), lets the user choose a color, and returns that color. The color is initially set toinitial. The dialog is a child ofparent. It returns an invalid (see QColor::isValid()) color if the user cancels the dialog.The
optionsargument allows you to customize the dialog.Opens the dialog and connects its
colorSelected()signal to the slot specified byreceiverandmember.The signal will be disconnected from the slot when the dialog is closed.
- options()¶
- Return type:
Combination of
ColorDialogOption
See also
Getter of property
optionsᅟ.Returns the color that the user selected by clicking the OK or equivalent button.
Note
This color is not always the same as the color held by the
currentColorproperty since the user can choose different colors before finally selecting the one to use.Setter of property
currentColorᅟ.Sets the custom color at
indexto the QColorcolorvalue.Note
This function does not apply to the Native Color Dialog on the macOS platform. If you still require this function, use the
DontUseNativeDialogoption.See also
- setOption(option[, on=true])¶
- Parameters:
option –
ColorDialogOptionon – bool
Sets the given
optionto be enabled ifonis true; otherwise, clears the givenoption.See also
- setOptions(options)¶
- Parameters:
options – Combination of
ColorDialogOption
See also
Setter of property
optionsᅟ.Sets the standard color at
indexto the QColorcolorvalue.Note
This function does not apply to the Native Color Dialog on the macOS platform. If you still require this function, use the
DontUseNativeDialogoption.See also
Returns the standard color at the given
indexas a QColor value.See also
- testOption(option)¶
- Parameters:
option –
ColorDialogOption- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the givenoptionis enabled; otherwise, returns false.See also