PySide6.QtWidgets.QGraphicsEffect¶
- class QGraphicsEffect¶
The
QGraphicsEffectclass is the base class for all graphics effects.Details
Effects alter the appearance of elements by hooking into the rendering pipeline and operating between the source (e.g., a
QGraphicsPixmapItem) and the destination device (e.g.,QGraphicsView‘s viewport). Effects can be disabled by callingsetEnabled(false). If effects are disabled, the source is rendered directly.To add a visual effect to a
QGraphicsItem, for example, you can use one of the standard effects, or alternately, create your own effect by creating a subclass ofQGraphicsEffect. The effect can then be installed on the item usingsetGraphicsEffect().Qt provides the following standard effects:
QGraphicsBlurEffect- blurs the item by a given radiusQGraphicsDropShadowEffect- renders a dropshadow behind the itemQGraphicsColorizeEffect- renders the item in shades of any given colorQGraphicsOpacityEffect- renders the item with an opacity

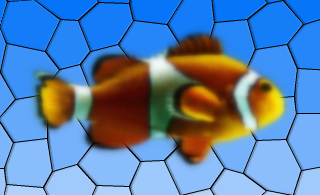
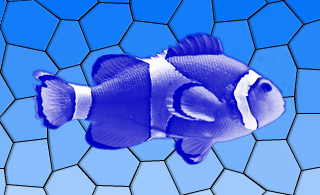


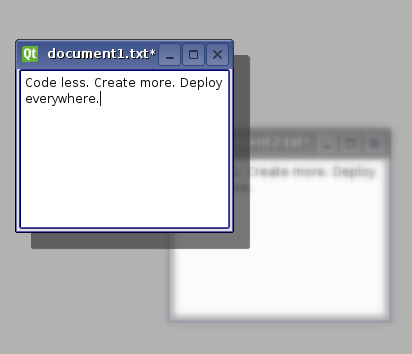
For more information on how to use each effect, refer to the specific effect’s documentation.
To create your own custom effect, create a subclass of
QGraphicsEffect(or any other existing effects) and reimplement the virtual functiondraw(). This function is called whenever the effect needs to redraw. Thedraw()function takes the painter with which to draw as an argument. For more information, refer to the documentation fordraw(). In thedraw()function you can callsourcePixmap()to get a pixmap of the graphics effect source which you can then process.If your effect changes, use
update()to request for a redraw. If your custom effect changes the bounding rectangle of the source, e.g., a radial glow effect may need to apply an extra margin, you can reimplement the virtualboundingRectFor()function, and callupdateBoundingRect()to notify the framework whenever this rectangle changes. The virtualsourceChanged()function is called to notify the effects that the source has changed in some way - e.g., if the source is aQGraphicsRectItemand its rectangle parameters have changed.See also
Inherited by:
QGraphicsOpacityEffect,QGraphicsDropShadowEffect,QGraphicsColorizeEffect,QGraphicsBlurEffectSynopsis¶
Properties¶
enabledᅟ- Whether the effect is enabled or not
Methods¶
def
__init__()def
boundingRect()def
drawSource()def
isEnabled()def
sourceIsPixmap()def
sourcePixmap()
Virtual methods¶
def
draw()def
sourceChanged()
Slots¶
def
setEnabled()def
update()
Signals¶
def
enabledChanged()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
- class ChangeFlag¶
(inherits
enum.Flag) This enum describes what has changed in QGraphicsEffectSource.Constant
Description
QGraphicsEffect.ChangeFlag.SourceAttached
The effect is installed on a source.
QGraphicsEffect.ChangeFlag.SourceDetached
The effect is uninstalled on a source.
QGraphicsEffect.ChangeFlag.SourceBoundingRectChanged
The bounding rect of the source has changed.
QGraphicsEffect.ChangeFlag.SourceInvalidated
The visual appearance of the source has changed.
- class PixmapPadMode¶
This enum describes how the pixmap returned from
sourcePixmapshould be padded.Constant
Description
QGraphicsEffect.PixmapPadMode.NoPad
The pixmap should not receive any additional padding.
QGraphicsEffect.PixmapPadMode.PadToTransparentBorder
The pixmap should be padded to ensure it has a completely transparent border.
QGraphicsEffect.PixmapPadMode.PadToEffectiveBoundingRect
The pixmap should be padded to match the effective bounding rectangle of the effect.
Note
Properties can be used directly when
from __feature__ import true_propertyis used or via accessor functions otherwise.- property enabledᅟ: bool¶
This property holds whether the effect is enabled or not..
If an effect is disabled, the source will be rendered with as normal, with no interference from the effect. If the effect is enabled, the source will be rendered with the effect applied.
This property is enabled by default.
Using this property, you can disable certain effects on slow platforms, in order to ensure that the user interface is responsive.
- Access functions:
Constructs a new
QGraphicsEffectinstance having the specifiedparent.Returns the effective bounding rectangle for this effect, i.e., the bounding rectangle of the source in device coordinates, adjusted by any margins applied by the effect itself.
See also
Returns the effective bounding rectangle for this effect, given the provided
rectin the device coordinates. When writing you own custom effect, you must callupdateBoundingRect()whenever any parameters are changed that may cause this this function to return a different value.See also
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This pure virtual function draws the effect and is called whenever the source needs to be drawn.
Reimplement this function in a
QGraphicsEffectsubclass to provide the effect’s drawing implementation, usingpainter.For example:
MyGraphicsEffect::draw(QPainter painter) ... offset = QPoint() if sourceIsPixmap(): # No point in drawing in device coordinates (pixmap will be scaled anyways). pixmap = sourcePixmap(Qt.LogicalCoordinates, offset) ... painter.drawPixmap(offset, pixmap) else: # Draw pixmap in device coordinates to avoid pixmap scaling pixmap = sourcePixmap(Qt.DeviceCoordinates, offset) painter.setWorldTransform(QTransform()) ... painter.drawPixmap(offset, pixmap) ...
This function should not be called explicitly by the user, since it is meant for reimplementation purposes only.
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the source directly using the given
painter.This function should only be called from
draw().For example:
MyGraphicsOpacityEffect::draw(QPainter painter) # Fully opaque; draw directly without going through a pixmap. if qFuzzyCompare(m_opacity, 1): drawSource(painter) return ...
See also
- enabledChanged(enabled)¶
- Parameters:
enabled – bool
This signal is emitted whenever the effect is enabled or disabled. The
enabledparameter holds the effects’s new enabled state.See also
Notification signal of property
enabledᅟ.- isEnabled()¶
- Return type:
bool
Getter of property
enabledᅟ.- setEnabled(enable)¶
- Parameters:
enable – bool
See also
Setter of property
enabledᅟ.- sourceBoundingRect([system=Qt.LogicalCoordinates])¶
- Parameters:
system –
CoordinateSystem- Return type:
Returns the bounding rectangle of the source mapped to the given
system.Calling this function with Qt::DeviceCoordinates outside of
draw()will give undefined results, as there is no device context available.See also
- sourceChanged(flags)¶
- Parameters:
flags – Combination of
ChangeFlag
This virtual function is called by
QGraphicsEffectto notify the effect that the source has changed. If the effect applies any cache, then this cache must be purged in order to reflect the new appearance of the source.The
flagsdescribes what has changed.- sourceIsPixmap()¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the source effectively is a pixmap, e.g., aQGraphicsPixmapItem.This function is useful for optimization purposes. For instance, there’s no point in drawing the source in device coordinates to avoid pixmap scaling if this function returns
true- the source pixmap will be scaled anyways.- sourcePixmap([system=Qt.LogicalCoordinates[, offset=None[, mode=QGraphicsEffect.PixmapPadMode.PadToEffectiveBoundingRect]]])¶
- Parameters:
system –
CoordinateSystemoffset –
QPointmode –
PixmapPadMode
- Return type:
Returns a pixmap with the source painted into it.
The
systemspecifies which coordinate system to be used for the source. The optionaloffsetparameter returns the offset where the pixmap should be painted at using the current painter. For control on how the pixmap is padded use themodeparameter.The returned pixmap is clipped to the current painter’s device rectangle when
systemis Qt::DeviceCoordinates.Calling this function with Qt::DeviceCoordinates outside of
draw()will give undefined results, as there is no device context available.See also
- update()¶
Schedules a redraw of the effect. Call this function whenever the effect needs to be redrawn. This function does not trigger a redraw of the source.
See also
- updateBoundingRect()¶
This function notifies the effect framework when the effect’s bounding rectangle has changed. As a custom effect author, you must call this function whenever you change any parameters that will cause the virtual
boundingRectFor()function to return a different value.This function will call
update()if this is necessary.