QMdiSubWindow#
The QMdiSubWindow class provides a subwindow class for QMdiArea . More…
Synopsis#
Properties#
keyboardPageStep- Sets how far a widget should move or resize when using the keyboard page keyskeyboardSingleStep- Sets how far a widget should move or resize when using the keyboard arrow keys
Functions#
def
isShaded()def
keyboardPageStep()def
keyboardSingleStep()def
maximizedButtonsWidget()def
mdiArea()def
setKeyboardPageStep(step)def
setKeyboardSingleStep(step)def
setOption(option[, on=true])def
setSystemMenu(systemMenu)def
setWidget(widget)def
systemMenu()def
testOption(arg__1)def
widget()
Slots#
def
showShaded()def
showSystemMenu()
Signals#
def
aboutToActivate()def
windowStateChanged(oldState, newState)
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
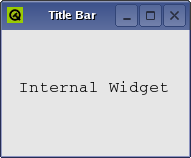
QMdiSubWindow represents a top-level window in a QMdiArea , and consists of a title bar with window decorations, an internal widget, and (depending on the current style) a window frame and a size grip. QMdiSubWindow has its own layout, which consists of the title bar and a center area for the internal widget.
The most common way to construct a QMdiSubWindow is to call addSubWindow() with the internal widget as the argument. You can also create a subwindow yourself, and set an internal widget by calling setWidget() .
You use the same API when programming with subwindows as with regular top-level windows (e.g., you can call functions such as show() , hide() , showMaximized() , and setWindowTitle() ).
Subwindow Handling#
QMdiSubWindow also supports behavior specific to subwindows in an MDI area.
By default, each QMdiSubWindow is visible inside the MDI area viewport when moved around, but it is also possible to specify transparent window movement and resizing behavior, where only the outline of a subwindow is updated during these operations. The setOption() function is used to enable this behavior.
The isShaded() function detects whether the subwindow is currently shaded (i.e., the window is collapsed so that only the title bar is visible). To enter shaded mode, call showShaded() . QMdiSubWindow emits the windowStateChanged() signal whenever the window state has changed (e.g., when the window becomes minimized, or is restored). It also emits aboutToActivate() before it is activated.
In keyboard-interactive mode, the windows are moved and resized with the keyboard. You can enter this mode through the system menu of the window. The keyboardSingleStep and keyboardPageStep properties control the distance the widget is moved or resized for each keypress event. When shift is pressed down page step is used; otherwise single step is used.
You can also change the active window with the keyboard. By pressing the control and tab keys at the same time, the next (using the current WindowOrder ) subwindow will be activated. By pressing control, shift, and tab, you will activate the previous window. This is equivalent to calling activateNextSubWindow() and activatePreviousSubWindow() . Note that these shortcuts overrides global shortcuts, but not the QMdiArea s shortcuts.
See also
- class PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow([parent=None[, flags=Qt.WindowFlags()]])#
- Parameters:
flags – Combination of
Qt.WindowTypeparent –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Constructs a new QMdiSubWindow widget. The parent and flags arguments are passed to QWidget ‘s constructor.
Instead of using addSubWindow(), it is also simply possible to use setParent() when you add the subwindow to a QMdiArea .
Note that only QMdiSubWindow s can be set as children of QMdiArea ; you cannot, for instance, write:
//bad code QMdiArea mdiArea; QTextEdit editor(&mdiArea); // invalid child widgetSee also
Note
Properties can be used directly when from __feature__ import true_property is used or via accessor functions otherwise.
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.keyboardPageStep: int#
This property holds sets how far a widget should move or resize when using the keyboard page keys..
When in keyboard-interactive mode, you can use the arrow and page keys to either move or resize the window. This property controls the page keys. The common way to enter keyboard interactive mode is to enter the subwindow menu, and select either “resize” or “move”.
The default keyboard page step value is 20 pixels.
See also
- Access functions:
setKeyboardPageStep(step)
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.keyboardSingleStep: int#
This property holds sets how far a widget should move or resize when using the keyboard arrow keys..
When in keyboard-interactive mode, you can use the arrow and page keys to either move or resize the window. This property controls the arrow keys. The common way to enter keyboard interactive mode is to enter the subwindow menu, and select either “resize” or “move”.
The default keyboard single step value is 5 pixels.
See also
- Access functions:
setKeyboardSingleStep(step)
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.SubWindowOption#
(inherits enum.Flag) This enum describes options that customize the behavior of QMdiSubWindow .
Constant
Description
QMdiSubWindow.RubberBandResize
If you enable this option, a rubber band control is used to represent the subwindow’s outline, and the user resizes this instead of the subwindow itself. As a result, the subwindow maintains its original position and size until the resize operation has been completed, at which time it will receive a single QResizeEvent. By default, this option is disabled.
QMdiSubWindow.RubberBandMove
If you enable this option, a rubber band control is used to represent the subwindow’s outline, and the user moves this instead of the subwindow itself. As a result, the subwindow remains in its original position until the move operation has completed, at which time a QMoveEvent is sent to the window. By default, this option is disabled.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.aboutToActivate()#
QMdiSubWindow emits this signal immediately before it is activated. After the subwindow has been activated, the QMdiArea that manages the subwindow will also emit the subWindowActivated() signal.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.isShaded()#
- Return type:
bool
Returns true if this window is shaded; otherwise returns false.
A window is shaded if it is collapsed so that only the title bar is visible.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.keyboardPageStep()#
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property keyboardPageStep .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.keyboardSingleStep()#
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property keyboardSingleStep .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.maximizedButtonsWidget()#
- Return type:
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.maximizedSystemMenuIconWidget()#
- Return type:
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.mdiArea()#
- Return type:
Returns the area containing this sub-window, or None if there is none.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.setKeyboardPageStep(step)#
- Parameters:
step – int
See also
Setter of property keyboardPageStep .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.setKeyboardSingleStep(step)#
- Parameters:
step – int
See also
Setter of property keyboardSingleStep .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.setOption(option[, on=true])#
- Parameters:
option –
SubWindowOptionon – bool
If on is true, option is enabled on the subwindow; otherwise it is disabled. See SubWindowOption for the effect of each option.
See also
SubWindowOptiontestOption()
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.setSystemMenu(systemMenu)#
- Parameters:
systemMenu –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QMenu
Sets systemMenu as the current system menu for this subwindow.
By default, each QMdiSubWindow has a standard system menu.
QActions for the system menu created by QMdiSubWindow will automatically be updated depending on the current window state; e.g., the minimize action will be disabled after the window is minimized.
QActions added by the user are not updated by QMdiSubWindow .
QMdiSubWindow takes ownership of systemMenu; you do not have to delete it. Any existing menus will be deleted.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.setWidget(widget)#
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Sets widget as the internal widget of this subwindow. The internal widget is displayed in the center of the subwindow beneath the title bar.
QMdiSubWindow takes temporary ownership of widget; you do not have to delete it. Any existing internal widget will be removed and reparented to the root window.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.showShaded()#
Calling this function makes the subwindow enter the shaded mode. When the subwindow is shaded, only the title bar is visible.
Although shading is not supported by all styles, this function will still show the subwindow as shaded, regardless of whether support for shading is available. However, when used with styles without shading support, the user will be unable to return from shaded mode through the user interface (e.g., through a shade button in the title bar).
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.showSystemMenu()#
Shows the system menu below the system menu icon in the title bar.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.systemMenu()#
- Return type:
Returns a pointer to the current system menu, or zero if no system menu is set. QMdiSubWindow provides a default system menu, but you can also set the menu with setSystemMenu() .
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.testOption(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
SubWindowOption- Return type:
bool
Returns true if option is enabled; otherwise returns false.
See also
SubWindowOptionsetOption()
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.widget()#
- Return type:
Returns the current internal widget.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QMdiSubWindow.windowStateChanged(oldState, newState)#
- Parameters:
oldState – Combination of
Qt.WindowStatenewState – Combination of
Qt.WindowState
QMdiSubWindow emits this signal after the window state changes. oldState is the window state before it changed, and newState is the new, current state.