Cockpit
Beispielanwendung zur Nachahmung eines Flugzeugcockpits unter Verwendung von Graphen.
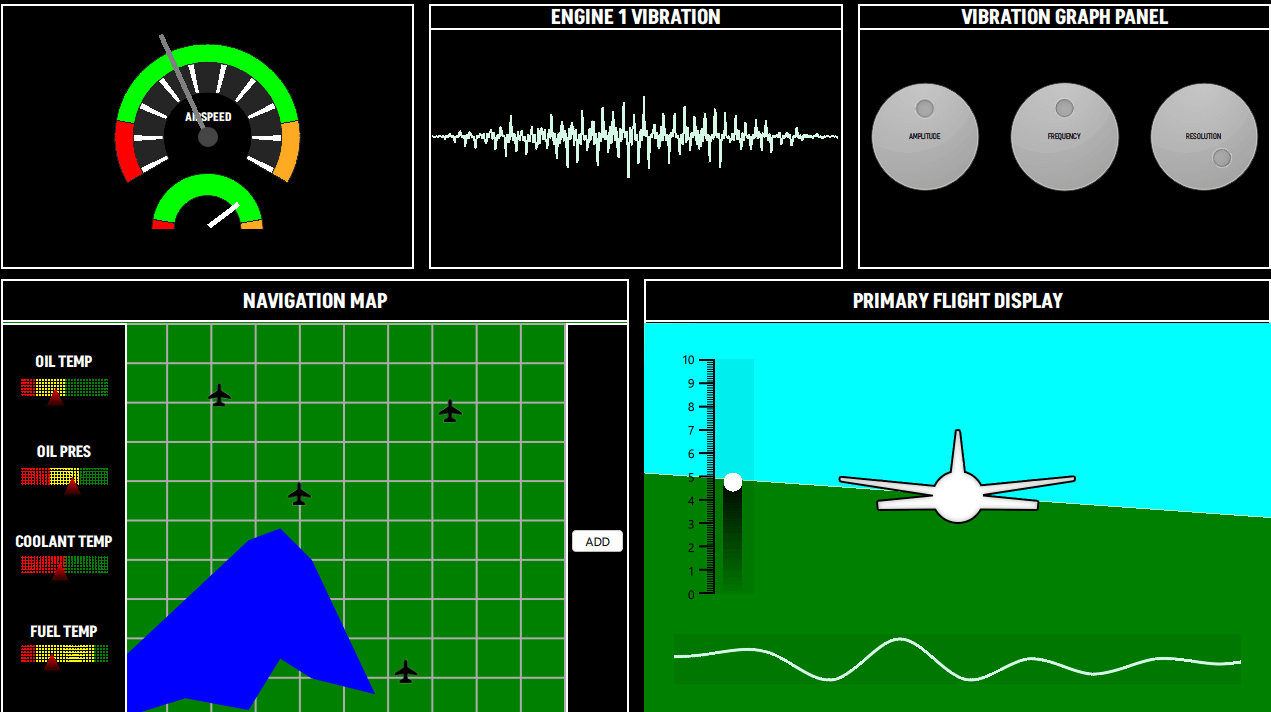
Das Cockpit-Beispiel enthält eine Reihe verschiedener Diagrammtypen, um fiktive Flugzeugsteuerungsbildschirme zu zeichnen. Die in diesem Beispiel verwendeten Graphen sind:
- PieSeries (Geschwindigkeitsmesser)
- LineSeries (Vibrationsanzeige, Navigationskarte)
- AreaSeries (Navigationskarte, Primäre Fluganzeige)
- BarSeries (Navigationskarte, Primäre Fluganzeige)
- ScatterSeries (Navigationskarte)
- SplineSeries (Primäre Fluganzeige)
Ausführen des Beispiels
Zum Ausführen des Beispiels von Qt Creatorzu starten, öffnen Sie den Modus Welcome und wählen Sie das Beispiel aus Examples. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Qt Creator: Tutorial: Erstellen und Ausführen.
Geschwindigkeitsmesser
Die Tachometer-Ansicht besteht aus 3 PieSeries in einem einzigen GraphsView mit QML-Rechtecken als Nadeln für beide Tachometer.
Die Eigenschaft backgroundVisible für die GraphsTheme ist auf false eingestellt. Alle PieSlices haben ihre eigenen benutzerdefinierten Farben. Um eine Kreisskala mit einem hohlen Zentrum anzuzeigen, verwendet das Beispiel PieSeries mit unterschiedlicher holeSize.
GraphsView { id: chart anchors.fill: parent anchors.margins: 20 theme: GraphsTheme { backgroundVisible: false borderColors: ["#252525"] } PieSeries { id: pieOuter pieSize: 1 holeSize: 0.8 startAngle: -120 endAngle: 120 PieSlice { label: "Stall"; value: 1; color: "#ff0000"; labelVisible: false } PieSlice { label: "Optimal"; value: 4; color: "#00ff00"; labelVisible: false } PieSlice { label: "Overspeed"; value: 1; color: "#ffaa22"; labelVisible: false } } PieSeries { pieSize: 0.8 holeSize: 0.6 startAngle: -120 endAngle: 120 PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } PieSlice { value: 4; color: "#252525"; } PieSlice { value: 1; color: "#ffffff"; } } PieSeries { pieSize: 0.6 holeSize: 1.0 startAngle: -120 endAngle: 120 verticalPosition: 1 PieSlice { label: "Stall"; value: 1; color: "#ff0000"; labelVisible: false } PieSlice { label: "Optimal"; value: 4; color: "#00ff00"; labelVisible: false } PieSlice { label: "Overspeed"; value: 1; color: "#ffaa22"; labelVisible: false } } }
Vibrationstafel
Das Vibration Panel enthält eine LineSeries, die zur Laufzeit dynamisch aktualisiert wird. Nach dem Start wird mit der in QML aufgerufenen Funktion append eine Reihe von Punkten zu der Serie hinzugefügt. Bei jedem Frame werden die Werte dann mit der Funktion replace durch berechnete Werte ersetzt. Der Benutzer kann diese Werte über das Vibration Graph Panel ändern.
LineSeries { id: line property int divisions: 500 property real amplitude: 0.5 property real resolution: 0.5 FrameAnimation { running: true onTriggered: { for (let i = 0; i < line.divisions; ++i) { let y = Math.sin(line.resolution*i) y *= Math.cos(i) y *= Math.sin(i / line.divisions * 3.2) * 3 * line.amplitude * Math.random() line.replace(i, (i/line.divisions) * 8.0, y + 4) } } } Component.onCompleted: { for (let i = 1; i <= divisions; ++i) { append((i/divisions) * 8.0, 4.0) } } function change(newDivs) { let delta = newDivs - divisions if (delta < 0) { delta = Math.abs(delta) removeMultiple(count - 1 - delta, delta) } else { for (let i = 0; i < delta; ++i) { append(((count + i)/divisions) * 8.0, 4.0) } } divisions = newDivs } }
Schwingungsdiagramm-Panel
Dieses Feld enthält Steuerknöpfe zur Einstellung von Werten, die sich auf die Visualisierung im Schwingungsfeld auswirken.
Navigationskarte
Die Navigationskarte besteht aus zwei Hauptbereichen:
- Der linke Bereich enthält eine Reihe von BarSeries mit einem benutzerdefinierten Shader, der die BarSets Farbe zum Schattieren der einzelnen Balken verwendet.
BarSeries { property real barOpacity: 0. id: barSeries barsType: BarSeries.BarsType.Stacked barWidth: 0.2 barDelegate: Item { id: delegate antialiasing: true property real barOpacity: 0.5 property color barColor property string barLabel FrameAnimation { running: true onTriggered: { delegate.barOpacity = Math.abs(Math.sin(elapsedTime)) } } ShaderEffect { id: effect readonly property alias iTime: delegate.barOpacity readonly property alias iColor: delegate.barColor readonly property vector3d iResolution: Qt.vector3d(width, height, 1.0) blending: true fragmentShader: 'bar.frag.qsb' anchors.fill: parent } } BarSet { id: set1; label: "Low"; values: [1, 2, 3, 1]; color: "red" } BarSet { id: set2; label: "Medium"; values: [2, 2, 0, 4]; color: "yellow"} BarSet { id: set3; label: "High"; values: [3, 2, 3, 1]; color: "green"} }
- Der rechte Bereich enthält:
- Ein AreaSeries mit zwei LineSeries visualisiert einen fiktiven See.
- Ein ScatterSeries zeigt darüber hinaus benutzerdefinierte Symbole, z. B. Flughäfen, auf einer Karte an.
- Die Schaltfläche ADD fügt eine LineSeries hinzu, deren Punkte verschoben werden können, um einen Pfad zu erstellen. Dieses LineSeries verwendet einen benutzerdefinierten Shader für das pointDelegate und das ScatterSeries verwendet ein Bild.
AreaSeries { property double x: 0 property double y: 0 id: lake1 color: "blue" upperSeries: LineSeries { id: s1 XYPoint { x: 0.0; y: -3.5 } XYPoint { x: 1.0; y: -5.0 } XYPoint { x: 2.0; y: -2.5 } XYPoint { x: 2.5; y: -4.0 } XYPoint { x: 3.0; y: -4.2 } } lowerSeries: LineSeries { id: s2 XYPoint { x: 0.0; y: -7.2 } XYPoint { x: 1.0; y: -7.0 } XYPoint { x: 2.0; y: -8.5 } XYPoint { x: 2.5; y: -8.0 } XYPoint { x: 3.0; y: -9.0 } XYPoint { x: 4.0; y: -6.5 } } } AreaSeries { property double x: 0 property double y: 0 id: lake2 color: "blue" upperSeries: LineSeries { id: s3 XYPoint { x: 0.0; y: 1.5 } XYPoint { x: 1.0; y: 3.0 } XYPoint { x: 2.0; y: 4.5 } XYPoint { x: 2.5; y: 4.8 } XYPoint { x: 3.0; y: 4.0 } } lowerSeries: LineSeries { id: s4 XYPoint { x: 0.0; y: 0.0 } XYPoint { x: 1.0; y: 0.5 } XYPoint { x: 2.0; y: 0.2 } XYPoint { x: 2.5; y: 1.5 } XYPoint { x: 3.0; y: 1.0 } XYPoint { x: 4.0; y: 0.6 } } } // POI ScatterSeries { name: "Airport" pointDelegate: Image { source: "airplane-ico.png" mipmap: true width: 30 height: 30 } XYPoint{x: 4.0; y: 5.7} XYPoint{x: 2.2; y: 8.2} XYPoint{x: 6.4; y: 1.2} XYPoint{x: 7.4; y: 7.8} } LineSeries { id: linePath selectable: true draggable: true color: "white" pointDelegate: Item { width: 50 height: 50 property real pointValueX property real pointValueY FrameAnimation { id: scatterAnim running: true } ShaderEffect { readonly property vector3d iResolution: Qt.vector3d(width, height, 1.0) readonly property alias iTime: scatterAnim.elapsedTime blending: true fragmentShader: 'circleMarker.frag.qsb' anchors.fill: parent } Text { color: "white" font.pointSize: 4 text: "LAT: " + pointValueX.toFixed(1) + ", " + "LON: " + pointValueY.toFixed(1) } } }
Primäre Fluganzeige
Die primäre Fluganzeige bietet eine Nachahmung der "3D"-Ansicht des Geländes. Es ist mit zwei AreaSeries implementiert, um den Boden und den Himmel mit jeweils eigenen Farben darzustellen. Eine FrameAnimation aktualisiert die Werte dieser Reihen.
AreaSeries { id: upperArea color: "cyan" upperSeries: LineSeries { XYPoint {x: 0; y: 10} XYPoint {x: 10; y: 10} } lowerSeries: LineSeries { id: upperLine XYPoint {x: 0; y: 3} XYPoint {x: 10; y: 4} } } FrameAnimation { running: true onTriggered: { upperLine.replace(0, upperLine.at(0).x, Math.sin(elapsedTime) + 6) upperLine.replace(1, upperLine.at(1).x, Math.cos(elapsedTime) + 6) lowerLine.replace(0, lowerLine.at(0).x, Math.sin(elapsedTime) + 6) lowerLine.replace(1, lowerLine.at(1).x, Math.cos(elapsedTime) + 6) barSet.values = [Math.sin(elapsedTime) + 5] } }
Auf der linken Seite zeigt ein thematisches BarSeries die Beschriftung der y-Achse an. Dieses BarSeries verwendet auch einen benutzerdefinierten Shader für den Balken.
BarSeries { id: barSeries selectable: true barDelegate: Item { id: delegate antialiasing: true property real barOpacity: 0.5 property color barColor property string barLabel ShaderEffect { id: effect readonly property vector3d iResolution: Qt.vector3d(width, height, 1.0) blending: true fragmentShader: 'pitchbar.frag.qsb' anchors.fill: parent } } BarSet { id: barSet; values: []; selectedColor: "red" } }
Am unteren Rand der Ansicht visualisiert ein SplineSeries die Geländehöhe unter dem Flugzeug. Die SplineSeries wird bei jedem Frame aktualisiert. Der Code, der die Serie aktualisiert, fügt hinten eine kontinuierliche Serie von Punkten hinzu und entfernt sie vorne. Wenn der Mauszeiger über der SplineSeries schwebt, wird ein Tooltip angezeigt, der den Wert der y-Achse (Höhe) anzeigt.
GraphsView { anchors.fill: parent anchors.leftMargin: -90 anchors.rightMargin: -80 anchors.bottomMargin: -30 theme: GraphsTheme { backgroundVisible: false plotAreaBackgroundColor: "#11000000" } axisX: ValueAxis { max: 10 subTickCount: 9 lineVisible: false gridVisible: false subGridVisible: false labelsVisible: false visible: false } axisY: ValueAxis { max: 10 subTickCount: 9 lineVisible: false gridVisible: false subGridVisible: false labelsVisible: false visible: false } ToolTip { id: tooltip } onHoverEnter: { tooltip.visible = true; } onHoverExit: { tooltip.visible = false; } onHover: (seriesName, position, value) => { tooltip.x = position.x + 1; tooltip.y = position.y + 1; tooltip.text = "Altitude: " + (value.y * 1000).toFixed(1) + "m"; } FrameAnimation { property var points: [] Component.onCompleted: { for (let i = 0; i < altitudeLine.count; ++i) { points[i] = altitudeLine.at(i) } } running: true onTriggered: { for (let i = 0; i < points.length; ++i) { points[i].x -= frameTime if (points[1].x <= -2) { let p = points[0] p.x = points[points.length - 1].x + 1 altitudeLine.append(p) altitudeLine.remove(0) points.length = 0 for (let i = 0; i < altitudeLine.count; ++i) { points[i] = altitudeLine.at(i) } } } altitudeLine.replace(points) altitudeLine.update() } } SplineSeries { id: altitudeLine hoverable: true width: 3 XYPoint {x: 0; y: 5} XYPoint {x: 1; y: 2} XYPoint {x: 2; y: 5} XYPoint {x: 3; y: 4} XYPoint {x: 4; y: 6} XYPoint {x: 5; y: 7} XYPoint {x: 6; y: 9} XYPoint {x: 7; y: 8} XYPoint {x: 8; y: 9} XYPoint {x: 9; y: 6} XYPoint {x: 10; y: 6} XYPoint {x: 11; y: 6} XYPoint {x: 12; y: 1} XYPoint {x: 13; y: 9} XYPoint {x: 14; y: 1} } }
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

