Qt Quick Beispiele - Ansichten
Dies ist eine Sammlung von QML-Beispielen für Modelle und Ansichten.
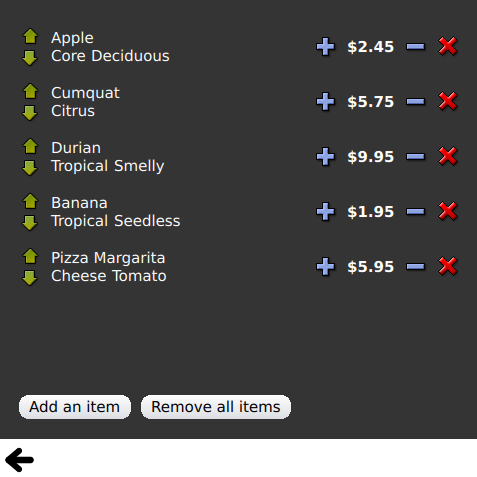
Views ist eine Sammlung von kleinen QML-Beispielen, die sich auf die Modell- und View-Funktionalität beziehen. Sie demonstrieren, wie man Daten aus einem Modell mit Hilfe der Qt Quick Ansichtstypen anzeigt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie auf der Seite Modelle und Ansichten in Qt Quick.
Ausführen des Beispiels
Zum Ausführen des Beispiels von Qt Creatorauszuführen, öffnen Sie den Modus Welcome und wählen Sie das Beispiel aus Examples. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Qt Creator: Tutorial: Erstellen und Ausführen.
GridView und PathView verwenden
GridView und PathView demonstrieren die Verwendung dieser Typen zur Anzeige von Ansichten.
GridView { anchors.fill: parent cellWidth: 100 cellHeight: 100 focus: true model: appModel highlight: Rectangle { width: 80 height: 80 color: "lightsteelblue" } delegate: Item { required property string icon required property string name required property int index width: 100 height: 100 Image { id: myIcon y: 20 anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter source: parent.icon } Text { anchors { top: myIcon.bottom horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter } text: parent.name } MouseArea { anchors.fill: parent onClicked: parent.GridView.view.currentIndex = parent.index } } }
Dynamische Liste verwenden
Dynamic List demonstriert die Animation von Hinzufügungen und Entfernungen zu einer ListView zur Laufzeit.
Der Signalhandler ListView.onAdd führt eine Animation aus, wenn neue Elemente zur Ansicht hinzugefügt werden, und der ListView.onRemove eine weitere, wenn sie entfernt werden.
Item { SequentialAnimation { id: addAnimation PropertyAction { target: delegateItem property: "height" value: 0 } NumberAnimation { target: delegateItem property: "height" to: 80 duration: 250 easing.type: Easing.InOutQuad } } ListView.onAdd: addAnimation.start() SequentialAnimation { id: removeAnimation PropertyAction { target: delegateItem property: "ListView.delayRemove" value: true } NumberAnimation { target: delegateItem property: "height" to: 0 duration: 250 easing.type: Easing.InOutQuad } // Make sure delayRemove is set back to false so that the item can be destroyed PropertyAction { target: delegateItem property: "ListView.delayRemove" value: false } } ListView.onRemove: removeAnimation.start() }
Erweiternde Delegierte
Expanding Delegates demonstriert Delegierte, die sich bei Aktivierung ausdehnen.
Es verfügt über einen komplexen Delegaten, dessen Größe und Aussehen sich ändern kann, wodurch andere Elemente in der Ansicht verschoben werden.
Item { id: recipe required property string title required property string picture required property string ingredients required property string method // Create a property to contain the visibility of the details. // We can bind multiple element's opacity to this one property, // rather than having a "PropertyChanges" line for each element we // want to fade. property real detailsOpacity : 0 MouseArea { anchors.fill: parent onClicked: recipe.state = 'Details'; } // Lay out the page: picture, title and ingredients at the top, and method at the // bottom. Note that elements that should not be visible in the list // mode have their opacity set to recipe.detailsOpacity. Row { id: topLayout x: 10 y: 10 height: recipeImage.height width: parent.width spacing: 10 Image { id: recipeImage width: 50 height: 50 source: recipe.picture } Item { id: details x: 10 width: parent.width - 20 anchors { top: topLayout.bottom topMargin: 10 bottom: parent.bottom bottomMargin: 10 } opacity: recipe.detailsOpacity } // A button to close the detailed view, i.e. set the state back to default (''). TextButton { y: 10 anchors { right: background.right rightMargin: 10 } opacity: recipe.detailsOpacity text: qsTr("Close") onClicked: recipe.state = ''; } states: State { name: "Details" PropertyChanges { background.color: "white" recipeImage { // Make picture bigger width: 130 height: 130 } recipe { // Make details visible detailsOpacity: 1 x: 0 // Fill the entire list area with the detailed view height: listView.height } } // Move the list so that this item is at the top. PropertyChanges { recipe.ListView.view.contentY: recipe.y explicit: true; } // Disallow flicking while we're in detailed view PropertyChanges { recipe.ListView.view.interactive: false } } transitions: Transition { // Make the state changes smooth ParallelAnimation { ColorAnimation { property: "color" duration: 500 } NumberAnimation { duration: 300 properties: "detailsOpacity,x,contentY,height,width" } } } }
Hervorhebung verwenden
Highlight demonstriert das Hinzufügen einer benutzerdefinierten Hervorhebung zu einer ListView.
// Define a highlight with customized movement between items. component HighlightBar : Rectangle { width: 200 height: 50 color: "#FFFF88" y: ListView.view.currentItem.y Behavior on y { SpringAnimation { spring: 2 damping: 0.1 } } } ListView { id: listView width: 200 height: parent.height x: 30 model: PetsModel { } delegate: PetDelegate { } focus: true // Set the highlight delegate. Note we must also set highlightFollowsCurrentItem // to false so the highlight delegate can control how the highlight is moved. highlight: HighlightBar { } highlightFollowsCurrentItem: false }
Hervorhebungsbereiche verwenden
Hervorhebungsbereiche zeigt die drei verschiedenen Hervorhebungsbereichsmodi von ListView.
Rectangle { id: root property int current: 0 property bool increasing: true // Example index automation for convenience, disabled on click or tap SequentialAnimation { id: anim loops: -1 running: true ScriptAction { script: if (root.increasing) { root.current++; if (root.current >= aModel.count -1) { root.current = aModel.count - 1; root.increasing = !root.increasing; } } else { root.current--; if (root.current <= 0) { root.current = 0; root.increasing = !root.increasing; } } } PauseAnimation { duration: 500 } } ListView { id: list1 height: 50 width: parent.width model: PetsModel { id: aModel } delegate: petDelegate orientation: ListView.Horizontal highlight: Rectangle { color: "lightsteelblue" } currentIndex: root.current onCurrentIndexChanged: root.current = currentIndex focus: true } ListView { id: list2 y: 160 height: 50 width: parent.width model: PetsModel { } delegate: petDelegate orientation: ListView.Horizontal highlight: Rectangle { color: "yellow" } currentIndex: root.current preferredHighlightBegin: 80 preferredHighlightEnd: 220 highlightRangeMode: ListView.ApplyRange } ListView { id: list3 y: 320 height: 50 width: parent.width model: PetsModel {} delegate: petDelegate orientation: ListView.Horizontal highlight: Rectangle { color: "yellow" } currentIndex: root.current onCurrentIndexChanged: root.current = currentIndex preferredHighlightBegin: 125 preferredHighlightEnd: 125 highlightRangeMode: ListView.StrictlyEnforceRange } }
Abschnitte verwenden
Abschnitte demonstriert die verschiedenen Kopf- und Fußzeilen, die ListView zur Verfügung stehen.
// The delegate for each section header Component { id: sectionHeading Rectangle { width: ListView.view.width height: childrenRect.height color: "lightsteelblue" required property string section Text { text: parent.section font.bold: true font.pixelSize: 20 } } } ListView { id: view anchors.top: parent.top anchors.bottom: buttonBar.top width: parent.width model: animalsModel delegate: Text { required property string name text: name font.pixelSize: 18 } section.property: "size" section.criteria: ViewSection.FullString section.delegate: sectionHeading }
Pakete verwenden
Packages verwendet den Typ Package für den Übergang von Delegierten zwischen zwei Ansichten.
Es hat ein Package-Objekt, das Delegate-Elemente für jede Ansicht und ein Element definiert, das zwischen Delegates übertragen werden kann.
Package { id: delegate required property int upTo required property int index required property string display Text { id: listDelegate width: parent.width height: 25 text: 'Empty' Package.name: 'list' } Text { id: gridDelegate width: parent.width / 2 height: 50 text: 'Empty' Package.name: 'grid' } Rectangle { id: wrapper width: parent?.width ?? 0 height: 25 color: 'lightsteelblue' Text { text: delegate.display anchors.centerIn: parent } state: delegate.upTo > delegate.index ? 'inGrid' : 'inList' states: [ State { name: 'inList' ParentChange { target: wrapper parent: listDelegate } }, State { name: 'inGrid' ParentChange { target: wrapper parent: gridDelegate x: 0 y: 0 width: gridDelegate.width height: gridDelegate.height } } ] transitions: [ Transition { ParentAnimation { NumberAnimation { properties: 'x,y,width,height' duration: 300 } } } ] } }
Eine DelegateModel ermöglicht den einzelnen Ansichten den Zugriff auf ihre spezifischen Elemente über den gemeinsamen Paketdelegierten.
DelegateModel { id: visualModel delegate: Delegate { upTo: root.upTo } model: myModel } ListView { id: lv height: parent.height / 2 width: parent.width model: visualModel.parts.list } GridView { y: parent.height / 2 height: parent.height / 2 width: parent.width cellWidth: width / 2 cellHeight: 50 model: visualModel.parts.grid }
Draggable Selections demonstriert die Verwendung von Package, um mehrere ausgewählte Delegaten für Drag-and-Drop innerhalb einer Elementansicht zu gruppieren.
Package { id: packageRoot required property var modelData MouseArea { id: visibleContainer Package.name: "visible" width: 64 height: 64 enabled: packageRoot.DelegateModel.inSelected drag.target: draggable Item { id: draggable Drag.active: visibleContainer.drag.active
Verwendung von ObjectModel
ObjectModel verwendet ein ObjectModel für das Modell anstelle eines ListModel.
ObjectModel { id: itemModel Rectangle { width: view.width height: view.height color: "#FFFEF0" Text { anchors.centerIn: parent text: qsTr("Page 1") font.bold: true } Component.onDestruction: if (root.printDestruction) print("destroyed 1") } Rectangle { width: view.width height: view.height color: "#F0FFF7" Text { anchors.centerIn: parent text: qsTr("Page 2") font.bold: true } Component.onDestruction: if (root.printDestruction) print("destroyed 2") } Rectangle { width: view.width height: view.height color: "#F4F0FF" Text { anchors.centerIn: parent text: qsTr("Page 3") font.bold: true } Component.onDestruction: if (root.printDestruction) print("destroyed 3") } } ListView { id: view anchors { fill: parent bottomMargin: 30 } model: itemModel preferredHighlightBegin: 0 preferredHighlightEnd: 0 highlightRangeMode: ListView.StrictlyEnforceRange orientation: ListView.Horizontal snapMode: ListView.SnapOneItem flickDeceleration: 2000 cacheBuffer: 200 }
Verwendung von Display Margins
Display Margins verwendet Delegates zur Anzeige von Elementen und implementiert eine einfache Kopf- und Fußzeilenkomponente.
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

