QPainter#
The QPainter class performs low-level painting on widgets and other paint devices. More…
Inherited by: QStylePainter
Synopsis#
Functions#
def
__enter__()def
__exit__(arg__1, arg__2, arg__3)def
background()def
backgroundMode()def
begin(arg__1)def
beginNativePainting()def
boundingRect(rect, flags, text)def
boundingRect(rect, text[, o=QTextOption()])def
boundingRect(rect, flags, text)def
boundingRect(x, y, w, h, flags, text)def
brush()def
brushOrigin()def
clipBoundingRect()def
clipPath()def
clipRegion()def
combinedTransform()def
compositionMode()def
device()def
deviceTransform()def
drawArc(arg__1, a, alen)def
drawArc(rect, a, alen)def
drawArc(x, y, w, h, a, alen)def
drawChord(arg__1, a, alen)def
drawChord(rect, a, alen)def
drawChord(x, y, w, h, a, alen)def
drawConvexPolygon(arg__1)def
drawConvexPolygon(polygon)def
drawConvexPolygon(polygon)def
drawConvexPolygon(arg__1)def
drawEllipse(center, rx, ry)def
drawEllipse(r)def
drawEllipse(r)def
drawEllipse(x, y, w, h)def
drawEllipse(center, rx, ry)def
drawGlyphRun(position, glyphRun)def
drawImage(r, image)def
drawImage(x, y, image[, sx=0[, sy=0[, sw=-1[, sh=-1[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]]]]])def
drawImage(targetRect, image, sourceRect[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])def
drawImage(r, image)def
drawImage(targetRect, image, sourceRect[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])def
drawImage(p, image, sr[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])def
drawImage(p, image)def
drawImage(p, image, sr[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])def
drawImage(p, image)def
drawLine(line)def
drawLine(line)def
drawLine(p1, p2)def
drawLine(p1, p2)def
drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2)def
drawLines(pointPairs)def
drawLines(pointPairs)def
drawLines(lines, lineCount)def
drawLines(lines)def
drawLines(lines)def
drawPath(path)def
drawPicture(p, picture)def
drawPicture(p, picture)def
drawPicture(x, y, picture)def
drawPie(arg__1, a, alen)def
drawPie(rect, a, alen)def
drawPie(x, y, w, h, a, alen)def
drawPixmap(p, pm, sr)def
drawPixmap(x, y, w, h, pm, sx, sy, sw, sh)def
drawPixmap(x, y, w, h, pm)def
drawPixmap(x, y, pm, sx, sy, sw, sh)def
drawPixmap(x, y, pm)def
drawPixmap(targetRect, pixmap, sourceRect)def
drawPixmap(targetRect, pixmap, sourceRect)def
drawPixmap(r, pm)def
drawPixmap(p, pm)def
drawPixmap(p, pm, sr)def
drawPixmap(p, pm)def
drawPixmapFragments(fragments, fragmentCount, pixmap[, hints=QPainter.PixmapFragmentHints()])def
drawPoint(x, y)def
drawPoint(p)def
drawPoint(pt)def
drawPoints(arg__1)def
drawPoints(arg__1)def
drawPoints(points, pointCount)def
drawPoints(points)def
drawPoints(points)def
drawPointsNp(x, y)def
drawPolygon(arg__1, arg__2)def
drawPolygon(arg__1, arg__2)def
drawPolygon(polygon[, fillRule=Qt.OddEvenFill])def
drawPolygon(polygon[, fillRule=Qt.OddEvenFill])def
drawPolyline(arg__1)def
drawPolyline(polyline)def
drawPolyline(polygon)def
drawPolyline(arg__1)def
drawRect(rect)def
drawRect(rect)def
drawRect(x1, y1, w, h)def
drawRects(rectangles)def
drawRects(rectangles)def
drawRects(rects, rectCount)def
drawRoundedRect(rect, xRadius, yRadius[, mode=Qt.AbsoluteSize])def
drawRoundedRect(x, y, w, h, xRadius, yRadius[, mode=Qt.AbsoluteSize])def
drawRoundedRect(rect, xRadius, yRadius[, mode=Qt.AbsoluteSize])def
drawStaticText(topLeftPosition, staticText)def
drawStaticText(left, top, staticText)def
drawStaticText(topLeftPosition, staticText)def
drawText(p, s)def
drawText(p, s)def
drawText(r, flags, text)def
drawText(r, text[, o=QTextOption()])def
drawText(r, flags, text)def
drawText(x, y, s)def
drawText(x, y, w, h, flags, text)def
drawTextItem(p, ti)def
drawTextItem(p, ti)def
drawTextItem(x, y, ti)def
drawTiledPixmap(arg__1, arg__2[, pos=QPoint()])def
drawTiledPixmap(rect, pm[, offset=QPointF()])def
drawTiledPixmap(x, y, w, h, arg__5[, sx=0[, sy=0]])def
end()def
endNativePainting()def
eraseRect(arg__1)def
eraseRect(arg__1)def
eraseRect(x, y, w, h)def
fillPath(path, brush)def
fillRect(x, y, w, h, color)def
fillRect(x, y, w, h, arg__5)def
fillRect(r, preset)def
fillRect(x, y, w, h, c)def
fillRect(x, y, w, h, style)def
fillRect(x, y, w, h, preset)def
fillRect(r, c)def
fillRect(r, style)def
fillRect(arg__1, color)def
fillRect(arg__1, arg__2)def
fillRect(r, c)def
fillRect(r, style)def
fillRect(arg__1, color)def
fillRect(arg__1, arg__2)def
fillRect(r, preset)def
font()def
fontInfo()def
fontMetrics()def
hasClipping()def
isActive()def
layoutDirection()def
opacity()def
paintEngine()def
pen()def
renderHints()def
resetTransform()def
restore()def
rotate(a)def
save()def
scale(sx, sy)def
setBackground(bg)def
setBackgroundMode(mode)def
setBrush(style)def
setBrush(brush)def
setBrushOrigin(arg__1)def
setBrushOrigin(arg__1)def
setBrushOrigin(x, y)def
setClipPath(path[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])def
setClipRect(arg__1[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])def
setClipRect(x, y, w, h[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])def
setClipRect(arg__1[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])def
setClipRegion(arg__1[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])def
setClipping(enable)def
setCompositionMode(mode)def
setFont(f)def
setLayoutDirection(direction)def
setOpacity(opacity)def
setPen(pen)def
setPen(color)def
setPen(style)def
setRenderHint(hint[, on=true])def
setRenderHints(hints[, on=true])def
setTransform(transform[, combine=false])def
setViewTransformEnabled(enable)def
setViewport(viewport)def
setViewport(x, y, w, h)def
setWindow(window)def
setWindow(x, y, w, h)def
setWorldMatrixEnabled(enabled)def
setWorldTransform(matrix[, combine=false])def
shear(sh, sv)def
strokePath(path, pen)def
testRenderHint(hint)def
transform()def
translate(offset)def
translate(offset)def
translate(dx, dy)def
viewTransformEnabled()def
viewport()def
window()def
worldMatrixEnabled()def
worldTransform()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
QPainter provides highly optimized functions to do most of the drawing GUI programs require. It can draw everything from simple lines to complex shapes like pies and chords. It can also draw aligned text and pixmaps. Normally, it draws in a “natural” coordinate system, but it can also do view and world transformation. QPainter can operate on any object that inherits the QPaintDevice class.
The common use of QPainter is inside a widget’s paint event: Construct and customize (e.g. set the pen or the brush) the painter. Then draw. Remember to destroy the QPainter object after drawing. For example:
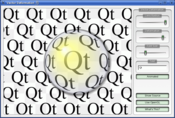
def paintEvent(self, arg__0): painter = QPainter(self) painter.setPen(Qt.blue) painter.setFont(QFont("Arial", 30)) painter.drawText(rect(), Qt.AlignCenter, "Qt")
The core functionality of QPainter is drawing, but the class also provide several functions that allows you to customize QPainter ‘s settings and its rendering quality, and others that enable clipping. In addition you can control how different shapes are merged together by specifying the painter’s composition mode.
The isActive() function indicates whether the painter is active. A painter is activated by the begin() function and the constructor that takes a QPaintDevice argument. The end() function, and the destructor, deactivates it.
Together with the QPaintDevice and QPaintEngine classes, QPainter form the basis for Qt’s paint system. QPainter is the class used to perform drawing operations. QPaintDevice represents a device that can be painted on using a QPainter . QPaintEngine provides the interface that the painter uses to draw onto different types of devices. If the painter is active, device() returns the paint device on which the painter paints, and paintEngine() returns the paint engine that the painter is currently operating on. For more information, see the Paint System .
Sometimes it is desirable to make someone else paint on an unusual QPaintDevice . QPainter supports a static function to do this, setRedirected().
Warning
When the paintdevice is a widget, QPainter can only be used inside a paintEvent() function or in a function called by paintEvent().
Settings#
There are several settings that you can customize to make QPainter draw according to your preferences:
font()is the font used for drawing text. If the painterisActive(), you can retrieve information about the currently set font, and its metrics, using thefontInfo()andfontMetrics()functions respectively.
brush()defines the color or pattern that is used for filling shapes.
pen()defines the color or stipple that is used for drawing lines or boundaries.
backgroundMode()defines whether there is abackground()or not, i.e it is eitherOpaqueModeorTransparentMode.
background()only applies whenbackgroundMode()isOpaqueModeandpen()is a stipple. In that case, it describes the color of the background pixels in the stipple.
brushOrigin()defines the origin of the tiled brushes, normally the origin of widget’s background.
viewport(),window(),worldTransform()make up the painter’s coordinate transformation system. For more information, see theCoordinate Transformationssection and the Coordinate System documentation.
hasClipping()tells whether the painter clips at all. (The paint device clips, too.) If the painter clips, it clips toclipRegion().
layoutDirection()defines the layout direction used by the painter when drawing text.
worldMatrixEnabled()tells whether world transformation is enabled.
viewTransformEnabled()tells whether view transformation is enabled.
Note that some of these settings mirror settings in some paint devices, e.g. font() . The begin() function (or equivalently the QPainter constructor) copies these attributes from the paint device.
You can at any time save the QPainter ‘s state by calling the save() function which saves all the available settings on an internal stack. The restore() function pops them back.
Drawing#
QPainter provides functions to draw most primitives: drawPoint() , drawPoints() , drawLine() , drawRect() , drawRoundedRect() , drawEllipse() , drawArc() , drawPie() , drawChord() , drawPolyline() , drawPolygon() , drawConvexPolygon() and drawCubicBezier(). The two convenience functions, drawRects() and drawLines() , draw the given number of rectangles or lines in the given array of QRects or QLines using the current pen and brush.
The QPainter class also provides the fillRect() function which fills the given QRect , with the given QBrush , and the eraseRect() function that erases the area inside the given rectangle.
All of these functions have both integer and floating point versions.
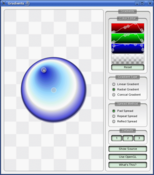
Basic Drawing Example
The Basic Drawing example shows how to display basic graphics primitives in a variety of styles using the
QPainterclass.
If you need to draw a complex shape, especially if you need to do so repeatedly, consider creating a QPainterPath and drawing it using drawPath() .
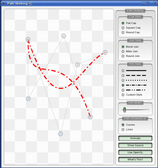
Painter Paths example
The
QPainterPathclass provides a container for painting operations, enabling graphical shapes to be constructed and reused.The Painter Paths example shows how painter paths can be used to build complex shapes for rendering.
QPainter also provides the fillPath() function which fills the given QPainterPath with the given QBrush , and the strokePath() function that draws the outline of the given path (i.e. strokes the path).
See also the Vector Deformation example which shows how to use advanced vector techniques to draw text using a QPainterPath , the Gradients example which shows the different types of gradients that are available in Qt, and the Path Stroking example which shows Qt’s built-in dash patterns and shows how custom patterns can be used to extend the range of available patterns.
Text drawing is done using drawText() . When you need fine-grained positioning, boundingRect() tells you where a given drawText() command will draw.
Drawing Pixmaps and Images#
There are functions to draw pixmaps/images, namely drawPixmap() , drawImage() and drawTiledPixmap() . Both drawPixmap() and drawImage() produce the same result, except that drawPixmap() is faster on-screen while drawImage() may be faster on a QPrinter or other devices.
There is a drawPicture() function that draws the contents of an entire QPicture . The drawPicture() function is the only function that disregards all the painter’s settings as QPicture has its own settings.
Drawing High Resolution Versions of Pixmaps and Images#
High resolution versions of pixmaps have a device pixel ratio value larger than 1 (see QImageReader , devicePixelRatio() ). Should it match the value of the underlying QPaintDevice , it is drawn directly onto the device with no additional transformation applied.
This is for example the case when drawing a QPixmap of 64x64 pixels size with a device pixel ratio of 2 onto a high DPI screen which also has a device pixel ratio of 2. Note that the pixmap is then effectively 32x32 pixels in user space. Code paths in Qt that calculate layout geometry based on the pixmap size will use this size. The net effect of this is that the pixmap is displayed as high DPI pixmap rather than a large pixmap.
Rendering Quality#
To get the optimal rendering result using QPainter , you should use the platform independent QImage as paint device; i.e. using QImage will ensure that the result has an identical pixel representation on any platform.
The QPainter class also provides a means of controlling the rendering quality through its RenderHint enum and the support for floating point precision: All the functions for drawing primitives has a floating point version. These are often used in combination with the Antialiasing render hint.
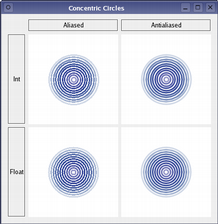
Concentric Circles Example
The Concentric Circles example shows the improved rendering quality that can be obtained using floating point precision and anti-aliasing when drawing custom widgets.
The application’s main window displays several widgets which are drawn using the various combinations of precision and anti-aliasing.
The RenderHint enum specifies flags to QPainter that may or may not be respected by any given engine. Antialiasing indicates that the engine should antialias edges of primitives if possible, TextAntialiasing indicates that the engine should antialias text if possible, and the SmoothPixmapTransform indicates that the engine should use a smooth pixmap transformation algorithm.
The renderHints() function returns a flag that specifies the rendering hints that are set for this painter. Use the setRenderHint() function to set or clear the currently set RenderHints .
Coordinate Transformations#
Normally, the QPainter operates on the device’s own coordinate system (usually pixels), but QPainter has good support for coordinate transformations.
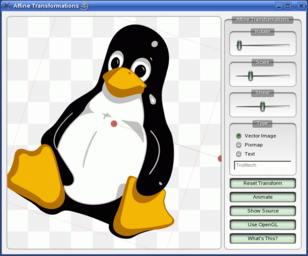
The most commonly used transformations are scaling, rotation, translation and shearing. Use the scale() function to scale the coordinate system by a given offset, the rotate() function to rotate it clockwise and translate() to translate it (i.e. adding a given offset to the points). You can also twist the coordinate system around the origin using the shear() function. See the Affine Transformations example for a visualization of a sheared coordinate system.
See also the Transformations example which shows how transformations influence the way that QPainter renders graphics primitives. In particular it shows how the order of transformations affects the result.
Affine Transformations Example
The Affine Transformations example shows Qt’s ability to perform affine transformations on painting operations. The demo also allows the user to experiment with the transformation operations and see the results immediately.
All the transformation operations operate on the transformation worldTransform() . A matrix transforms a point in the plane to another point. For more information about the transformation matrix, see the Coordinate System and QTransform documentation.
The setWorldTransform() function can replace or add to the currently set worldTransform() . The resetTransform() function resets any transformations that were made using translate() , scale() , shear() , rotate() , setWorldTransform() , setViewport() and setWindow() functions. The deviceTransform() returns the matrix that transforms from logical coordinates to device coordinates of the platform dependent paint device. The latter function is only needed when using platform painting commands on the platform dependent handle, and the platform does not do transformations nativly.
When drawing with QPainter , we specify points using logical coordinates which then are converted into the physical coordinates of the paint device. The mapping of the logical coordinates to the physical coordinates are handled by QPainter ‘s combinedTransform() , a combination of viewport() and window() and worldTransform() . The viewport() represents the physical coordinates specifying an arbitrary rectangle, the window() describes the same rectangle in logical coordinates, and the worldTransform() is identical with the transformation matrix.
See also Coordinate System
Clipping#
QPainter can clip any drawing operation to a rectangle, a region, or a vector path. The current clip is available using the functions clipRegion() and clipPath() . Whether paths or regions are preferred (faster) depends on the underlying paintEngine() . For example, the QImage paint engine prefers paths while the X11 paint engine prefers regions. Setting a clip is done in the painters logical coordinates.
After QPainter ‘s clipping, the paint device may also clip. For example, most widgets clip away the pixels used by child widgets, and most printers clip away an area near the edges of the paper. This additional clipping is not reflected by the return value of clipRegion() or hasClipping() .
Composition Modes#
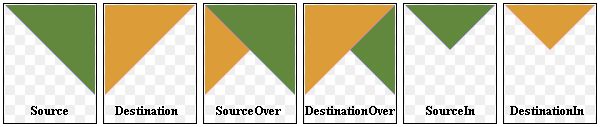
QPainter provides the CompositionMode enum which defines the Porter-Duff rules for digital image compositing; it describes a model for combining the pixels in one image, the source, with the pixels in another image, the destination.
The two most common forms of composition are Source and SourceOver . Source is used to draw opaque objects onto a paint device. In this mode, each pixel in the source replaces the corresponding pixel in the destination. In SourceOver composition mode, the source object is transparent and is drawn on top of the destination.
Note that composition transformation operates pixelwise. For that reason, there is a difference between using the graphic primitive itself and its bounding rectangle: The bounding rect contains pixels with alpha == 0 (i.e the pixels surrounding the primitive). These pixels will overwrite the other image’s pixels, effectively clearing those, while the primitive only overwrites its own area.
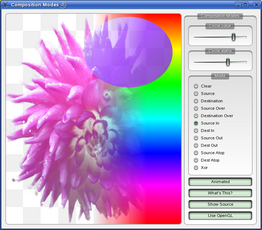
Composition Modes Example
The Composition Modes example, available in Qt’s examples directory, allows you to experiment with the various composition modes and see the results immediately.
Limitations#
If you are using coordinates with Qt’s raster-based paint engine, it is important to note that, while coordinates greater than +/- 2 15 can be used, any painting performed with coordinates outside this range is not guaranteed to be shown; the drawing may be clipped. This is due to the use of short int in the implementation.
The outlines generated by Qt’s stroker are only an approximation when dealing with curved shapes. It is in most cases impossible to represent the outline of a bezier curve segment using another bezier curve segment, and so Qt approximates the curve outlines by using several smaller curves. For performance reasons there is a limit to how many curves Qt uses for these outlines, and thus when using large pen widths or scales the outline error increases. To generate outlines with smaller errors it is possible to use the QPainterPathStroker class, which has the setCurveThreshold member function which let’s the user specify the error tolerance. Another workaround is to convert the paths to polygons first and then draw the polygons instead.
Performance#
QPainter is a rich framework that allows developers to do a great variety of graphical operations, such as gradients, composition modes and vector graphics. And QPainter can do this across a variety of different hardware and software stacks. Naturally the underlying combination of hardware and software has some implications for performance, and ensuring that every single operation is fast in combination with all the various combinations of composition modes, brushes, clipping, transformation, etc, is close to an impossible task because of the number of permutations. As a compromise we have selected a subset of the QPainter API and backends, where performance is guaranteed to be as good as we can sensibly get it for the given combination of hardware and software.
The backends we focus on as high-performance engines are:
Raster - This backend implements all rendering in pure software and is always used to render into QImages. For optimal performance only use the format types
Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied,Format_RGB32orFormat_RGB16. Any other format, includingFormat_ARGB32, has significantly worse performance. This engine is used by default forQWidgetandQPixmap.OpenGL 2.0 (ES) - This backend is the primary backend for hardware accelerated graphics. It can be run on desktop machines and embedded devices supporting the OpenGL 2.0 or OpenGL/ES 2.0 specification. This includes most graphics chips produced in the last couple of years. The engine can be enabled by using
QPainteronto aQOpenGLWidget.
These operations are:
Simple transformations, meaning translation and scaling, pluss 0, 90, 180, 270 degree rotations.
drawPixmap()in combination with simple transformations and opacity with non-smooth transformation mode (QPainter::SmoothPixmapTransformnot enabled as a render hint).Rectangle fills with solid color, two-color linear gradients and simple transforms.
Rectangular clipping with simple transformations and intersect clip.
Composition Modes
QPainter::CompositionMode_SourceandCompositionMode_SourceOver.Rounded rectangle filling using solid color and two-color linear gradients fills.
3x3 patched pixmaps, via
qDrawBorderPixmap.
This list gives an indication of which features to safely use in an application where performance is critical. For certain setups, other operations may be fast too, but before making extensive use of them, it is recommended to benchmark and verify them on the system where the software will run in the end. There are also cases where expensive operations are ok to use, for instance when the result is cached in a QPixmap .
See also
QPaintDeviceQPaintEngineQt SVG Basic Drawing Example Drawing Utility Functions
- class PySide6.QtGui.QPainter#
PySide6.QtGui.QPainter(arg__1)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtGui.QPaintDevice
Constructs a painter.
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Constructs a painter that begins painting the paint device immediately.
This constructor is convenient for short-lived painters, e.g. in a paintEvent() and should be used only once. The constructor calls begin() for you and the QPainter destructor automatically calls end() .
Here’s an example using begin() and end() :
def paintEvent(self, arg__0): p = QPainter() p.begin(self) p.drawLine(drawingCode) # drawing code p.end()
The same example using this constructor:
def paintEvent(self, arg__0): p = QPainter(self) p.drawLine(drawingCode) # drawing code
Since the constructor cannot provide feedback when the initialization of the painter failed you should rather use begin() and end() to paint on external devices, e.g. printers.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.RenderHint#
(inherits enum.Flag) Renderhints are used to specify flags to QPainter that may or may not be respected by any given engine.
Constant
Description
QPainter.Antialiasing
Indicates that the engine should antialias edges of primitives if possible.
QPainter.TextAntialiasing
Indicates that the engine should antialias text if possible. To forcibly disable antialiasing for text, do not use this hint. Instead, set
NoAntialiason your font’s style strategy.QPainter.SmoothPixmapTransform
Indicates that the engine should use a smooth pixmap transformation algorithm (such as bilinear) rather than nearest neighbor.
QPainter.VerticalSubpixelPositioning
Allow text to be positioned at fractions of pixels vertically as well as horizontally, if this is supported by the font engine. This is currently supported by Freetype on all platforms when the hinting preference is
PreferNoHinting, and also on macOS. For most use cases this will not improve visual quality, but may increase memory consumption and some reduction in text rendering performance. Therefore, enabling this is not recommended unless the use case requires it. One such use case could be aligning glyphs with other visual primitives. This value was added in Qt 6.1.QPainter.LosslessImageRendering
Use a lossless image rendering, whenever possible. Currently, this hint is only used when
QPainteris employed to output a PDF file throughQPrinterorQPdfWriter, wheredrawImage()/drawPixmap()calls will encode images using a lossless compression algorithm instead of lossy JPEG compression. This value was added in Qt 5.13.QPainter.NonCosmeticBrushPatterns
When painting with a brush with one of the predefined pattern styles, transform the pattern too, along with the object being painted. The default is to treat the pattern as cosmetic, so that the pattern pixels will map directly to device pixels, independently of any active transformations. This value was added in Qt 6.4.
See also
renderHints()setRenderHint()Rendering QualityConcentric Circles Example
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.PixmapFragmentHint#
Constant
Description
QPainter.OpaqueHint
(inherits
enum.Flag) Indicates that the pixmap fragments to be drawn are opaque. Opaque fragments are potentially faster to draw.See also
drawPixmapFragments()PixmapFragment
New in version 4.7.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.CompositionMode#
Defines the modes supported for digital image compositing. Composition modes are used to specify how the pixels in one image, the source, are merged with the pixel in another image, the destination.
Please note that the bitwise raster operation modes, denoted with a RasterOp prefix, are only natively supported in the X11 and raster paint engines. This means that the only way to utilize these modes on the Mac is via a QImage . The RasterOp denoted blend modes are not supported for pens and brushes with alpha components. Also, turning on the Antialiasing render hint will effectively disable the RasterOp modes.
The most common type is SourceOver (often referred to as just alpha blending) where the source pixel is blended on top of the destination pixel in such a way that the alpha component of the source defines the translucency of the pixel.
Several composition modes require an alpha channel in the source or target images to have an effect. For optimal performance the image format Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied is preferred.
When a composition mode is set it applies to all painting operator, pens, brushes, gradients and pixmap/image drawing.
Constant
Description
QPainter.CompositionMode_SourceOver
This is the default mode. The alpha of the source is used to blend the pixel on top of the destination.
QPainter.CompositionMode_DestinationOver
The alpha of the destination is used to blend it on top of the source pixels. This mode is the inverse of CompositionMode_SourceOver.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Clear
The pixels in the destination are cleared (set to fully transparent) independent of the source.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Source
The output is the source pixel. (This means a basic copy operation and is identical to SourceOver when the source pixel is opaque).
QPainter.CompositionMode_Destination
The output is the destination pixel. This means that the blending has no effect. This mode is the inverse of CompositionMode_Source.
QPainter.CompositionMode_SourceIn
The output is the source, where the alpha is reduced by that of the destination.
QPainter.CompositionMode_DestinationIn
The output is the destination, where the alpha is reduced by that of the source. This mode is the inverse of CompositionMode_SourceIn.
QPainter.CompositionMode_SourceOut
The output is the source, where the alpha is reduced by the inverse of destination.
QPainter.CompositionMode_DestinationOut
The output is the destination, where the alpha is reduced by the inverse of the source. This mode is the inverse of CompositionMode_SourceOut.
QPainter.CompositionMode_SourceAtop
The source pixel is blended on top of the destination, with the alpha of the source pixel reduced by the alpha of the destination pixel.
QPainter.CompositionMode_DestinationAtop
The destination pixel is blended on top of the source, with the alpha of the destination pixel is reduced by the alpha of the destination pixel. This mode is the inverse of CompositionMode_SourceAtop.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Xor
The source, whose alpha is reduced with the inverse of the destination alpha, is merged with the destination, whose alpha is reduced by the inverse of the source alpha. CompositionMode_Xor is not the same as the bitwise Xor.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Plus
Both the alpha and color of the source and destination pixels are added together.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Multiply
The output is the source color multiplied by the destination. Multiplying a color with white leaves the color unchanged, while multiplying a color with black produces black.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Screen
The source and destination colors are inverted and then multiplied. Screening a color with white produces white, whereas screening a color with black leaves the color unchanged.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Overlay
Multiplies or screens the colors depending on the destination color. The destination color is mixed with the source color to reflect the lightness or darkness of the destination.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Darken
The darker of the source and destination colors is selected.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Lighten
The lighter of the source and destination colors is selected.
QPainter.CompositionMode_ColorDodge
The destination color is brightened to reflect the source color. A black source color leaves the destination color unchanged.
QPainter.CompositionMode_ColorBurn
The destination color is darkened to reflect the source color. A white source color leaves the destination color unchanged.
QPainter.CompositionMode_HardLight
Multiplies or screens the colors depending on the source color. A light source color will lighten the destination color, whereas a dark source color will darken the destination color.
QPainter.CompositionMode_SoftLight
Darkens or lightens the colors depending on the source color. Similar to CompositionMode_HardLight.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Difference
Subtracts the darker of the colors from the lighter. Painting with white inverts the destination color, whereas painting with black leaves the destination color unchanged.
QPainter.CompositionMode_Exclusion
Similar to CompositionMode_Difference, but with a lower contrast. Painting with white inverts the destination color, whereas painting with black leaves the destination color unchanged.
QPainter.RasterOp_SourceOrDestination
Does a bitwise OR operation on the source and destination pixels (src OR dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_SourceAndDestination
Does a bitwise AND operation on the source and destination pixels (src AND dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_SourceXorDestination
Does a bitwise XOR operation on the source and destination pixels (src XOR dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_NotSourceAndNotDestination
Does a bitwise NOR operation on the source and destination pixels ((NOT src) AND (NOT dst)).
QPainter.RasterOp_NotSourceOrNotDestination
Does a bitwise NAND operation on the source and destination pixels ((NOT src) OR (NOT dst)).
QPainter.RasterOp_NotSourceXorDestination
Does a bitwise operation where the source pixels are inverted and then XOR’ed with the destination ((NOT src) XOR dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_NotSource
Does a bitwise operation where the source pixels are inverted (NOT src).
QPainter.RasterOp_NotSourceAndDestination
Does a bitwise operation where the source is inverted and then AND’ed with the destination ((NOT src) AND dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_SourceAndNotDestination
Does a bitwise operation where the source is AND’ed with the inverted destination pixels (src AND (NOT dst)).
QPainter.RasterOp_NotSourceOrDestination
Does a bitwise operation where the source is inverted and then OR’ed with the destination ((NOT src) OR dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_ClearDestination
The pixels in the destination are cleared (set to 0) independent of the source.
QPainter.RasterOp_SetDestination
The pixels in the destination are set (set to 1) independent of the source.
QPainter.RasterOp_NotDestination
Does a bitwise operation where the destination pixels are inverted (NOT dst).
QPainter.RasterOp_SourceOrNotDestination
Does a bitwise operation where the source is OR’ed with the inverted destination pixels (src OR (NOT dst)).
See also
compositionMode()setCompositionMode()Composition ModesImage Composition Example
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.__enter__()#
- Return type:
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.__exit__(arg__1, arg__2, arg__3)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 – object
arg__2 – object
arg__3 – object
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.background()#
- Return type:
Returns the current background brush.
See also
setBackground()Settings
Returns the current background mode.
See also
setBackgroundMode()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.begin(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtGui.QPaintDevice- Return type:
bool
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Begins painting the paint device and returns true if successful; otherwise returns false.
Notice that all painter settings ( setPen() , setBrush() etc.) are reset to default values when begin() is called.
The errors that can occur are serious problems, such as these:
painter.begin(0) # impossible - paint device cannot be 0 image = QPixmap(0, 0) painter.begin(image) # impossible - image.isNull() == true painter.begin(myWidget) painter2.begin(myWidget) # impossible - only one painter at a time
Note that most of the time, you can use one of the constructors instead of begin(), and that end() is automatically done at destruction.
Warning
A paint device can only be painted by one painter at a time.
Warning
Painting on a QImage with the format Format_Indexed8 is not supported.
See also
end() QPainter()
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.beginNativePainting()#
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Flushes the painting pipeline and prepares for the user issuing commands directly to the underlying graphics context. Must be followed by a call to endNativePainting() .
Note that only the states the underlying paint engine changes will be reset to their respective default states. The states we reset may change from release to release. The following states are currently reset in the OpenGL 2 engine:
blending is disabled
the depth, stencil and scissor tests are disabled
the active texture unit is reset to 0
the depth mask, depth function and the clear depth are reset to their default values
the stencil mask, stencil operation and stencil function are reset to their default values
the current color is reset to solid white
If, for example, the OpenGL polygon mode is changed by the user inside a beginNativePaint()/ endNativePainting() block, it will not be reset to the default state by endNativePainting() . Here is an example that shows intermixing of painter commands and raw OpenGL commands:
painter = QPainter(self) painter.fillRect(0, 0, 128, 128, Qt.green) painter.beginNativePainting() glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST) glScissor(0, 0, 64, 64) glClearColor(1, 0, 0, 1) glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT) glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST) painter.endNativePainting()See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.boundingRect(rect, flags, text)#
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectflags – int
text – str
- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Returns the bounding rectangle of the text as it will appear when drawn inside the given rectangle with the specified flags using the currently set font() .
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.boundingRect(rect, text[, o=QTextOption()])
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFtext – str
- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Instead of specifying flags as a bitwise OR of the AlignmentFlag and TextFlag , this overloaded function takes an option argument. The QTextOption class provides a description of general rich text properties.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.boundingRect(rect, flags, text)
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFflags – int
text – str
- Return type:
Returns the bounding rectangle of the text as it will appear when drawn inside the given rectangle with the specified flags using the currently set font() ; i.e the function tells you where the drawText() function will draw when given the same arguments.
If the text does not fit within the given rectangle using the specified flags, the function returns the required rectangle.
The flags argument is a bitwise OR of the following flags:
AlignLeft
AlignRight
AlignHCenter
AlignTop
AlignBottom
AlignVCenter
AlignCenter
TextSingleLine
TextExpandTabs
TextShowMnemonic
TextWordWrap
TextIncludeTrailingSpaces
If several of the horizontal or several of the vertical alignment flags are set, the resulting alignment is undefined.
See also
drawText()AlignmentTextFlag
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.boundingRect(x, y, w, h, flags, text)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
flags – int
text – str
- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Returns the bounding rectangle of the given text as it will appear when drawn inside the rectangle beginning at the point (x, y) with width w and height h.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.brush()#
- Return type:
Returns the painter’s current brush.
See also
setBrush()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.brushOrigin()#
- Return type:
Returns the currently set brush origin.
See also
setBrushOrigin()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.clipBoundingRect()#
- Return type:
Returns the bounding rectangle of the current clip if there is a clip; otherwise returns an empty rectangle. Note that the clip region is given in logical coordinates.
The bounding rectangle is not guaranteed to be tight.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.clipPath()#
- Return type:
Returns the current clip path in logical coordinates.
Warning
QPainter does not store the combined clip explicitly as this is handled by the underlying QPaintEngine , so the path is recreated on demand and transformed to the current logical coordinate system. This is potentially an expensive operation.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.clipRegion()#
- Return type:
Returns the currently set clip region. Note that the clip region is given in logical coordinates.
Warning
QPainter does not store the combined clip explicitly as this is handled by the underlying QPaintEngine , so the path is recreated on demand and transformed to the current logical coordinate system. This is potentially an expensive operation.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.combinedTransform()#
- Return type:
Returns the transformation matrix combining the current window/viewport and world transformation.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.compositionMode()#
- Return type:
Returns the current composition mode.
See also
CompositionModesetCompositionMode()
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.device()#
- Return type:
Returns the paint device on which this painter is currently painting, or None if the painter is not active.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.deviceTransform()#
- Return type:
Returns the matrix that transforms from logical coordinates to device coordinates of the platform dependent paint device.
This function is only needed when using platform painting commands on the platform dependent handle ( HANDLE ), and the platform does not do transformations nativly.
The PaintEngineFeature enum can be queried to determine whether the platform performs the transformations or not.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawArc(arg__1, a, alen)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRecta – int
alen – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the arc defined by the given rectangle, startAngle and spanAngle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawArc(rect, a, alen)
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFa – int
alen – int
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the arc defined by the given rectangle, startAngle and spanAngle.
The startAngle and spanAngle must be specified in 1/16th of a degree, i.e. a full circle equals 5760 (16 * 360). Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawArc(x, y, w, h, a, alen)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
a – int
alen – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the arc defined by the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the specified width and height, and the given startAngle and spanAngle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawChord(arg__1, a, alen)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRecta – int
alen – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the chord defined by the given rectangle, startAngle and spanAngle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawChord(rect, a, alen)
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFa – int
alen – int
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the chord defined by the given rectangle, startAngle and spanAngle. The chord is filled with the current brush() .
The startAngle and spanAngle must be specified in 1/16th of a degree, i.e. a full circle equals 5760 (16 * 360). Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawChord(x, y, w, h, a, alen)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
a – int
alen – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the chord defined by the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the specified width and height, and the given startAngle and spanAngle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawConvexPolygon(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawConvexPolygon(polygon)
- Parameters:
polygon –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygonF
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the convex polygon defined by polygon using the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawConvexPolygon(polygon)
- Parameters:
polygon –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygon
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the convex polygon defined by polygon using the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawConvexPolygon(arg__1)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawEllipse(center, rx, ry)#
- Parameters:
center –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointFrx – float
ry – float
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the ellipse positioned at center with radii rx and ry.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawEllipse(r)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the ellipse defined by the given rectangle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawEllipse(r)
- Parameters:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the ellipse defined by the given rectangle.
A filled ellipse has a size of rectangle. size() . A stroked ellipse has a size of rectangle. size() plus the pen width.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawEllipse(x, y, w, h)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the ellipse defined by the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawEllipse(center, rx, ry)
- Parameters:
center –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointrx – int
ry – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the ellipse positioned at center with radii rx and ry.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawGlyphRun(position, glyphRun)#
- Parameters:
position –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointFglyphRun –
PySide6.QtGui.QGlyphRun
Draws the glyphs represented by glyphs at position. The position gives the edge of the baseline for the string of glyphs. The glyphs will be retrieved from the font selected on glyphs and at offsets given by the positions in glyphs.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(r, image)#
- Parameters:
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImage
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given image into the given rectangle.
Note
The image is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the image and rectangle size disagree.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(x, y, image[, sx=0[, sy=0[, sw=-1[, sh=-1[, flags=Qt.AutoColor]]]]])
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImagesx – int
sy – int
sw – int
sh – int
flags –
ImageConversionFlags
This is an overloaded function.
Draws an image at (x, y) by copying a part of image into the paint device.
(x, y) specifies the top-left point in the paint device that is to be drawn onto. (sx, sy) specifies the top-left point in image that is to be drawn. The default is (0, 0).
(sw, sh) specifies the size of the image that is to be drawn. The default, (0, 0) (and negative) means all the way to the bottom-right of the image.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(targetRect, image, sourceRect[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- Parameters:
targetRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFimage –
PySide6.QtGui.QImagesourceRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFflags –
ImageConversionFlags
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given image into the target rectangle in the paint device.
Note
The image is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the image and rectangle size disagree.
Note
See Drawing High Resolution Versions of Pixmaps and Images on how this is affected by QImage::devicePixelRatio().
If the image needs to be modified to fit in a lower-resolution result (e.g. converting from 32-bit to 8-bit), use the flags to specify how you would prefer this to happen.
See also
drawPixmap()devicePixelRatio()
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(r, image)
- Parameters:
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImage
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given image into the given rectangle.
Note
The image is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the image and rectangle size disagree.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(targetRect, image, sourceRect[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- Parameters:
targetRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectimage –
PySide6.QtGui.QImagesourceRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectflags –
ImageConversionFlags
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given image into the target rectangle in the paint device.
Note
The image is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the image and rectangle size disagree.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(p, image, sr[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- Parameters:
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImageflags –
ImageConversionFlags
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given image with its origin at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(p, image)
- Parameters:
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImage
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given image at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(p, image, sr[, flags=Qt.AutoColor])
- Parameters:
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImagesr –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectflags –
ImageConversionFlags
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given image with its origin at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawImage(p, image)
- Parameters:
image –
PySide6.QtGui.QImage
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given image at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLine(line)#
- Parameters:
line –
PySide6.QtCore.QLine
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a line defined by line.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLine(line)
- Parameters:
line –
PySide6.QtCore.QLineF
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws a line defined by line.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLine(p1, p2)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a line from p1 to p2.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLine(p1, p2)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a line from p1 to p2.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2)
- Parameters:
x1 – int
y1 – int
x2 – int
y2 – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a line from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLines(pointPairs)#
- Parameters:
pointPairs –
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a line for each pair of points in the vector pointPairs using the current pen.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLines(pointPairs)
- Parameters:
pointPairs –
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a line for each pair of points in the vector pointPairs using the current pen. If there is an odd number of points in the array, the last point will be ignored.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLines(lines, lineCount)
- Parameters:
lines –
PySide6.QtCore.QLineFlineCount – int
Draws the first lineCount lines in the array lines using the current pen.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLines(lines)
- Parameters:
lines –
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the set of lines defined by the list lines using the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawLines(lines)
- Parameters:
lines –
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the set of lines defined by the list lines using the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPath(path)#
- Parameters:
path –
PySide6.QtGui.QPainterPath
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the given painter path using the current pen for outline and the current brush for filling.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPicture(p, picture)#
- Parameters:
picture –
PySide6.QtGui.QPicture
This is an overloaded function.
Replays the given picture at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPicture(p, picture)
- Parameters:
picture –
PySide6.QtGui.QPicture
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Replays the given picture at the given point.
The QPicture class is a paint device that records and replays QPainter commands. A picture serializes the painter commands to an IO device in a platform-independent format. Everything that can be painted on a widget or pixmap can also be stored in a picture.
This function does exactly the same as play() when called with point = QPointF (0, 0).
Note
The state of the painter is preserved by this function.
picture = QPicture()
point = QPointF(10.0, 20.0)
picture.load("drawing.pic")
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.drawPicture(0, 0, picture)
|
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPicture(x, y, picture)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
picture –
PySide6.QtGui.QPicture
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given picture at point (x, y).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPie(arg__1, a, alen)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRecta – int
alen – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a pie defined by the given rectangle, startAngle and and spanAngle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPie(rect, a, alen)
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFa – int
alen – int
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws a pie defined by the given rectangle, startAngle and spanAngle.
The pie is filled with the current brush() .
The startAngle and spanAngle must be specified in 1/16th of a degree, i.e. a full circle equals 5760 (16 * 360). Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o’clock position.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPie(x, y, w, h, a, alen)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
a – int
alen – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the pie defined by the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the specified width and height, and the given startAngle and spanAngle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(p, pm, sr)#
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given pixmap with its origin at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(x, y, w, h, pm, sx, sy, sw, sh)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
sx – int
sy – int
sw – int
sh – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion with the origin (sx, sy), width sw and height sh, of the given pixmap , at the point (x, y), with a width of w and a height of h. If sw or sh are equal to zero the width/height of the pixmap is used and adjusted by the offset sx/sy;
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(x, y, w, h, pm)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the pixmap into the rectangle at position (x, y) with the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(x, y, pm, sx, sy, sw, sh)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
sx – int
sy – int
sw – int
sh – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a pixmap at (x, y) by copying a part of the given pixmap into the paint device.
(x, y) specifies the top-left point in the paint device that is to be drawn onto. (sx, sy) specifies the top-left point in pixmap that is to be drawn. The default is (0, 0).
(sw, sh) specifies the size of the pixmap that is to be drawn. The default, (0, 0) (and negative) means all the way to the bottom-right of the pixmap.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(x, y, pm)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given pixmap at position (x, y).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(targetRect, pixmap, sourceRect)
- Parameters:
targetRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFpixmap –
PySide6.QtGui.QPixmapsourceRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectF
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given pixmap into the given target in the paint device.
Note
The pixmap is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the pixmap and rectangle size disagree.
Note
See Drawing High Resolution Versions of Pixmaps and Images on how this is affected by devicePixelRatio() .
target = QRectF(10.0, 20.0, 80.0, 60.0)
source = QRectF(0.0, 0.0, 70.0, 40.0)
pixmap = QPixmap(":myPixmap.png")
QPainter(self)
painter.drawPixmap(target, pixmap, source)
|
If pixmap is a QBitmap it is drawn with the bits that are “set” using the pens color. If backgroundMode is OpaqueMode , the “unset” bits are drawn using the color of the background brush; if backgroundMode is TransparentMode , the “unset” bits are transparent. Drawing bitmaps with gradient or texture colors is not supported.
See also
drawImage()devicePixelRatio()
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(targetRect, pixmap, sourceRect)
- Parameters:
targetRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectpixmap –
PySide6.QtGui.QPixmapsourceRect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRect
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given pixmap into the given target in the paint device.
Note
The pixmap is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the pixmap and rectangle size disagree.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(r, pm)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given pixmap into the given rectangle.
Note
The pixmap is scaled to fit the rectangle, if both the pixmap and rectangle size disagree.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(p, pm)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given pixmap with its origin at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(p, pm, sr)
- Parameters:
sr –
PySide6.QtCore.QRect
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the rectangular portion source of the given pixmap with its origin at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmap(p, pm)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given pixmap with its origin at the given point.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPixmapFragments(fragments, fragmentCount, pixmap[, hints=QPainter.PixmapFragmentHints()])#
- Parameters:
fragments –
PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.PixmapFragmentfragmentCount – int
pixmap –
PySide6.QtGui.QPixmaphints –
PixmapFragmentHints
This function is used to draw pixmap, or a sub-rectangle of pixmap, at multiple positions with different scale, rotation and opacity. fragments is an array of fragmentCount elements specifying the parameters used to draw each pixmap fragment. The hints parameter can be used to pass in drawing hints.
This function is potentially faster than multiple calls to drawPixmap() , since the backend can optimize state changes.
See also
PixmapFragmentPixmapFragmentHint
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoint(x, y)#
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a single point at position (x, y).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoint(p)
- Parameters:
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a single point at the given position using the current pen’s color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoint(pt)
- Parameters:
Draws a single point at the given position using the current pen’s color.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoints(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoints(arg__1)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoints(points, pointCount)
- Parameters:
points –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointFpointCount – int
Draws the first pointCount points in the array points using the current pen’s color.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoints(points)
- Parameters:
points –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygon
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the points in the vector points.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPoints(points)
- Parameters:
points –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygonF
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the points in the vector points.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPointsNp(x, y)#
- Parameters:
x –
PyArrayObjecty –
PyArrayObject
Draws the points specified by two one-dimensional, equally sized numpy arrays representing the x, y values, respectively.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolygon(arg__1, arg__2)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
arg__2 –
FillRule
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolygon(polygon[, fillRule=Qt.OddEvenFill])
- Parameters:
polygon –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygonfillRule –
FillRule
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the polygon defined by the given points using the fill rule fillRule.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolygon(polygon[, fillRule=Qt.OddEvenFill])
- Parameters:
polygon –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygonFfillRule –
FillRule
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the polygon defined by the given points using the fill rule fillRule.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolyline(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolyline(polyline)
- Parameters:
polyline –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygonF
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the polyline defined by the given points using the current pen.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolyline(polygon)
- Parameters:
polygon –
PySide6.QtGui.QPolygon
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the polyline defined by the given points using the current pen.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawPolyline(arg__1)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRect(rect)#
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRect
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the current rectangle with the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRect(rect)
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectF
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the current rectangle with the current pen and brush.
A filled rectangle has a size of rectangle. size() . A stroked rectangle has a size of rectangle. size() plus the pen width.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRect(x1, y1, w, h)
- Parameters:
x1 – int
y1 – int
w – int
h – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a rectangle with upper left corner at (x, y) and with the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRects(rectangles)#
- Parameters:
rectangles –
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given rectangles using the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRects(rectangles)
- Parameters:
rectangles –
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given rectangles using the current pen and brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRects(rects, rectCount)
- Parameters:
rects –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFrectCount – int
Draws the first rectCount of the given rectangles using the current pen and brush.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRoundedRect(rect, xRadius, yRadius[, mode=Qt.AbsoluteSize])#
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectxRadius – float
yRadius – float
mode –
SizeMode
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given rectangle rect with rounded corners.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRoundedRect(x, y, w, h, xRadius, yRadius[, mode=Qt.AbsoluteSize])
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
xRadius – float
yRadius – float
mode –
SizeMode
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given rectangle x, y, w, h with rounded corners.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawRoundedRect(rect, xRadius, yRadius[, mode=Qt.AbsoluteSize])
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFxRadius – float
yRadius – float
mode –
SizeMode
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Draws the given rectangle rect with rounded corners.
The xRadius and yRadius arguments specify the radii of the ellipses defining the corners of the rounded rectangle. When mode is RelativeSize , xRadius and yRadius are specified in percentage of half the rectangle’s width and height respectively, and should be in the range 0.0 to 100.0.
A filled rectangle has a size of rect. size() . A stroked rectangle has a size of rect. size() plus the pen width.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawStaticText(topLeftPosition, staticText)#
- Parameters:
topLeftPosition –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointstaticText –
PySide6.QtGui.QStaticText
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the staticText at the topLeftPosition.
Note
The y-position is used as the top of the font.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawStaticText(left, top, staticText)
- Parameters:
left – int
top – int
staticText –
PySide6.QtGui.QStaticText
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the staticText at coordinates left and top.
Note
The y-position is used as the top of the font.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawStaticText(topLeftPosition, staticText)
- Parameters:
topLeftPosition –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointFstaticText –
PySide6.QtGui.QStaticText
Draws the given staticText at the given topLeftPosition.
The text will be drawn using the font and the transformation set on the painter. If the font and/or transformation set on the painter are different from the ones used to initialize the layout of the QStaticText , then the layout will have to be recalculated. Use prepare() to initialize staticText with the font and transformation with which it will later be drawn.
If topLeftPosition is not the same as when staticText was initialized, or when it was last drawn, then there will be a slight overhead when translating the text to its new position.
Note
If the painter’s transformation is not affine, then staticText will be drawn using regular calls to drawText() , losing any potential for performance improvement.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(p, s)#
- Parameters:
s – str
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given text with the currently defined text direction, beginning at the given position.
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(p, s)
- Parameters:
s – str
Draws the given text with the currently defined text direction, beginning at the given position.
This function does not handle the newline character (\n), as it cannot break text into multiple lines, and it cannot display the newline character. Use the QPainter::drawText() overload that takes a rectangle instead if you want to draw multiple lines of text with the newline character, or if you want the text to be wrapped.
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(r, flags, text)
- Parameters:
flags – int
text – str
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given text within the provided rectangle according to the specified flags.
The boundingRect (if not null) is set to the what the bounding rectangle should be in order to enclose the whole text. For example, in the following image, the dotted line represents boundingRect as calculated by the function, and the dashed line represents rectangle:
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(r, text[, o=QTextOption()])
- Parameters:
text – str
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given text in the rectangle specified using the option to control its positioning, direction, and orientation. The options given in option override those set on the QPainter object itself.
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(r, flags, text)
- Parameters:
flags – int
text – str
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given text within the provided rectangle. The rectangle along with alignment flags defines the anchors for the text.
The boundingRect (if not null) is set to what the bounding rectangle should be in order to enclose the whole text. For example, in the following image, the dotted line represents boundingRect as calculated by the function, and the dashed line represents rectangle:
The flags argument is a bitwise OR of the following flags:
AlignLeft
AlignRight
AlignHCenter
AlignJustify
AlignTop
AlignBottom
AlignVCenter
AlignCenter
TextDontClip
TextSingleLine
TextExpandTabs
TextShowMnemonic
TextWordWrap
TextIncludeTrailingSpaces
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
Note
The y-coordinate of rectangle is used as the top of the font.
See also
AlignmentFlag TextFlag boundingRect() layoutDirection()
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(x, y, s)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
s – str
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given text at position (x, y), using the painter’s currently defined text direction.
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawText(x, y, w, h, flags, text)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
flags – int
text – str
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Draws the given text within the rectangle with origin (x, y), width and height.
The boundingRect (if not null) is set to the what the bounding rectangle should be in order to enclose the whole text. For example, in the following image, the dotted line represents boundingRect as calculated by the function, and the dashed line represents the rectangle defined by x, y, width and height:
The flags argument is a bitwise OR of the following flags:
AlignLeft
AlignRight
AlignHCenter
AlignJustify
AlignTop
AlignBottom
AlignVCenter
AlignCenter
TextSingleLine
TextExpandTabs
TextShowMnemonic
TextWordWrap
By default, QPainter draws text anti-aliased.
Note
The y-position is used as the top of the font.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawTextItem(p, ti)#
- Parameters:
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawTextItem(p, ti)
- Parameters:
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawTextItem(x, y, ti)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawTiledPixmap(arg__1, arg__2[, pos=QPoint()])#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectarg__2 –
PySide6.QtGui.QPixmappos –
PySide6.QtCore.QPoint
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a tiled pixmap, inside the given rectangle with its origin at the given position.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawTiledPixmap(rect, pm[, offset=QPointF()])
- Parameters:
rect –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFoffset –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointF
Draws a tiled pixmap, inside the given rectangle with its origin at the given position.
Calling drawTiledPixmap() is similar to calling drawPixmap() several times to fill (tile) an area with a pixmap, but is potentially much more efficient depending on the underlying window system.
drawTiledPixmap() will produce the same visual tiling pattern on high-dpi displays (with devicePixelRatio > 1), compared to normal- dpi displays. Set the devicePixelRatio on the pixmap to control the tile size. For example, setting it to 2 halves the tile width and height (on both 1x and 2x displays), and produces high-resolution output on 2x displays.
The position offset is always in the painter coordinate system, indepentent of display devicePixelRatio.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.drawTiledPixmap(x, y, w, h, arg__5[, sx=0[, sy=0]])
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
arg__5 –
PySide6.QtGui.QPixmapsx – int
sy – int
This is an overloaded function.
Draws a tiled pixmap in the specified rectangle.
(x, y) specifies the top-left point in the paint device that is to be drawn onto; with the given width and height. (sx, sy) specifies the top-left point in the pixmap that is to be drawn; this defaults to (0, 0).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.end()#
- Return type:
bool
Ends painting. Any resources used while painting are released. You don’t normally need to call this since it is called by the destructor.
Returns true if the painter is no longer active; otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.endNativePainting()#
Restores the painter after manually issuing native painting commands. Lets the painter restore any native state that it relies on before calling any other painter commands.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.eraseRect(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRect
This is an overloaded function.
Erases the area inside the given rectangle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.eraseRect(arg__1)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectF
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Erases the area inside the given rectangle. Equivalent to calling
fillRect(rectangle, background())See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.eraseRect(x, y, w, h)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
This is an overloaded function.
Erases the area inside the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillPath(path, brush)#
- Parameters:
path –
PySide6.QtGui.QPainterPathbrush –
PySide6.QtGui.QBrush
Fills the given path using the given brush. The outline is not drawn.
Alternatively, you can specify a QColor instead of a QBrush ; the QBrush constructor (taking a QColor argument) will automatically create a solid pattern brush.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(x, y, w, h, color)#
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
color –
PySide6.QtGui.QColor
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height, using the given color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(x, y, w, h, arg__5)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
arg__5 –
PySide6.QtGui.QBrush
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height, using the given brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(r, preset)
- Parameters:
preset –
Preset
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the specified gradient preset.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(x, y, w, h, c)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
c –
GlobalColor
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height, using the given color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(x, y, w, h, style)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
style –
BrushStyle
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height, using the brush style specified.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(x, y, w, h, preset)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
preset –
Preset
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height, using the given gradient preset.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(r, c)
- Parameters:
c –
GlobalColor
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the specified color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(r, style)
- Parameters:
style –
BrushStyle
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the brush style specified.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(arg__1, color)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFcolor –
PySide6.QtGui.QColor
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the color specified.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(arg__1, arg__2)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFarg__2 –
PySide6.QtGui.QBrush
Fills the given rectangle with the brush specified.
Alternatively, you can specify a QColor instead of a QBrush ; the QBrush constructor (taking a QColor argument) will automatically create a solid pattern brush.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(r, c)
- Parameters:
c –
GlobalColor
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the specified color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(r, style)
- Parameters:
style –
BrushStyle
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the brush style specified.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(arg__1, color)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectcolor –
PySide6.QtGui.QColor
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the color specified.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(arg__1, arg__2)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectarg__2 –
PySide6.QtGui.QBrush
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the specified brush.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fillRect(r, preset)
- Parameters:
preset –
Preset
This is an overloaded function.
Fills the given rectangle with the specified gradient preset.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.font()#
- Return type:
Returns the currently set font used for drawing text.
See also
setFont()drawText()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fontInfo()#
- Return type:
Returns the font info for the painter if the painter is active. Otherwise, the return value is undefined.
See also
font()isActive()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.fontMetrics()#
- Return type:
Returns the font metrics for the painter if the painter is active. Otherwise, the return value is undefined.
See also
font()isActive()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.hasClipping()#
- Return type:
bool
Returns true if clipping has been set; otherwise returns false.
See also
setClipping()Clipping
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.isActive()#
- Return type:
bool
Returns true if begin() has been called and end() has not yet been called; otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.layoutDirection()#
- Return type:
Returns the layout direction used by the painter when drawing text.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.opacity()#
- Return type:
float
Returns the opacity of the painter. The default value is 1.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.paintEngine()#
- Return type:
Returns the paint engine that the painter is currently operating on if the painter is active; otherwise 0.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.pen()#
- Return type:
Returns the painter’s current pen.
See also
setPen()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.renderHints()#
- Return type:
RenderHints
Returns a flag that specifies the rendering hints that are set for this painter.
See also
setRenderHints()testRenderHint()Rendering Quality
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.resetTransform()#
Resets any transformations that were made using translate() , scale() , shear() , rotate() , setWorldTransform() , setViewport() and setWindow() .
See also
Coordinate Transformations
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.restore()#
Restores the current painter state (pops a saved state off the stack).
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.rotate(a)#
- Parameters:
a – float
Rotates the coordinate system clockwise. The given angle parameter is in degrees.
See also
setWorldTransform()Coordinate Transformations
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.save()#
Saves the current painter state (pushes the state onto a stack). A save() must be followed by a corresponding restore() ; the end() function unwinds the stack.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.scale(sx, sy)#
- Parameters:
sx – float
sy – float
Scales the coordinate system by (sx, sy).
See also
setWorldTransform()Coordinate Transformations
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setBackground(bg)#
- Parameters:
bg –
PySide6.QtGui.QBrush
Sets the background brush of the painter to the given brush.
The background brush is the brush that is filled in when drawing opaque text, stippled lines and bitmaps. The background brush has no effect in transparent background mode (which is the default).
See also
background()setBackgroundMode()Settings
Sets the background mode of the painter to the given mode
TransparentMode (the default) draws stippled lines and text without setting the background pixels. OpaqueMode fills these space with the current background color.
Note that in order to draw a bitmap or pixmap transparently, you must use setMask() .
See also
backgroundMode()setBackground()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setBrush(style)#
- Parameters:
style –
BrushStyle
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the painter’s brush to black color and the specified style.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setBrush(brush)
- Parameters:
brush –
PySide6.QtGui.QBrush
Sets the painter’s brush to the given brush.
The painter’s brush defines how shapes are filled.
See also
brush()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setBrushOrigin(arg__1)#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QPoint
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the brush’s origin to the given position.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setBrushOrigin(arg__1)
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointF
Sets the brush origin to position.
The brush origin specifies the (0, 0) coordinate of the painter’s brush.
Note that while the brushOrigin() was necessary to adopt the parent’s background for a widget in Qt 3, this is no longer the case since the Qt 4 painter doesn’t paint the background unless you explicitly tell it to do so by setting the widget’s autoFillBackground property to true.
See also
brushOrigin()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setBrushOrigin(x, y)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the brush’s origin to point (x, y).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setClipPath(path[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])#
- Parameters:
path –
PySide6.QtGui.QPainterPathop –
ClipOperation
Enables clipping, and sets the clip path for the painter to the given path, with the clip operation.
Note that the clip path is specified in logical (painter) coordinates.
See also
clipPath()clipRegion()Clipping
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setClipRect(arg__1[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectop –
ClipOperation
This is an overloaded function.
Enables clipping, and sets the clip region to the given rectangle using the given clip operation.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setClipRect(x, y, w, h[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
op –
ClipOperation
Enables clipping, and sets the clip region to the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setClipRect(arg__1[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtCore.QRectFop –
ClipOperation
Enables clipping, and sets the clip region to the given rectangle using the given clip operation. The default operation is to replace the current clip rectangle.
Note that the clip rectangle is specified in logical (painter) coordinates.
See also
clipRegion()setClipping()Clipping
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setClipRegion(arg__1[, op=Qt.ReplaceClip])#
- Parameters:
arg__1 –
PySide6.QtGui.QRegionop –
ClipOperation
Sets the clip region to the given region using the specified clip operation. The default clip operation is to replace the current clip region.
Note that the clip region is given in logical coordinates.
See also
clipRegion()setClipRect()Clipping
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setClipping(enable)#
- Parameters:
enable – bool
Enables clipping if enable is true, or disables clipping if enable is false.
See also
hasClipping()Clipping
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setCompositionMode(mode)#
- Parameters:
mode –
CompositionMode
Sets the composition mode to the given mode.
Warning
Only a QPainter operating on a QImage fully supports all composition modes. The RasterOp modes are supported for X11 as described in compositionMode() .
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setFont(f)#
- Parameters:
Sets the painter’s font to the given font.
This font is used by subsequent drawText() functions. The text color is the same as the pen color.
If you set a font that isn’t available, Qt finds a close match. font() will return what you set using setFont() and fontInfo() returns the font actually being used (which may be the same).
See also
font()drawText()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setLayoutDirection(direction)#
- Parameters:
direction –
LayoutDirection
Sets the layout direction used by the painter when drawing text, to the specified direction.
The default is LayoutDirectionAuto , which will implicitly determine the direction from the text drawn.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setOpacity(opacity)#
- Parameters:
opacity – float
Sets the opacity of the painter to opacity. The value should be in the range 0.0 to 1.0, where 0.0 is fully transparent and 1.0 is fully opaque.
Opacity set on the painter will apply to all drawing operations individually.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setPen(pen)#
- Parameters:
pen –
PySide6.QtGui.QPen
Sets the painter’s pen to be the given pen.
The pen defines how to draw lines and outlines, and it also defines the text color.
See also
pen()Settings
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setPen(color)
- Parameters:
color –
PySide6.QtGui.QColor
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the painter’s pen to have style SolidLine , width 1 and the specified color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setPen(style)
- Parameters:
style –
PenStyle
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the painter’s pen to have the given style, width 1 and black color.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setRenderHint(hint[, on=true])#
- Parameters:
hint –
RenderHinton – bool
Sets the given render hint on the painter if on is true; otherwise clears the render hint.
See also
setRenderHints()renderHints()Rendering Quality
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setRenderHints(hints[, on=true])#
- Parameters:
hints –
RenderHintson – bool
Sets the given render hints on the painter if on is true; otherwise clears the render hints.
See also
setRenderHint()renderHints()Rendering Quality
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setTransform(transform[, combine=false])#
- Parameters:
transform –
PySide6.QtGui.QTransformcombine – bool
Sets the world transformation matrix. If combine is true, the specified transform is combined with the current matrix; otherwise it replaces the current matrix.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setViewTransformEnabled(enable)#
- Parameters:
enable – bool
Enables view transformations if enable is true, or disables view transformations if enable is false.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setViewport(viewport)#
- Parameters:
viewport –
PySide6.QtCore.QRect
Sets the painter’s viewport rectangle to the given rectangle, and enables view transformations.
The viewport rectangle is part of the view transformation. The viewport specifies the device coordinate system. Its sister, the window() , specifies the logical coordinate system.
The default viewport rectangle is the same as the device’s rectangle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setViewport(x, y, w, h)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the painter’s viewport rectangle to be the rectangle beginning at (x, y) with the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setWindow(window)#
- Parameters:
window –
PySide6.QtCore.QRect
Sets the painter’s window to the given rectangle, and enables view transformations.
The window rectangle is part of the view transformation. The window specifies the logical coordinate system. Its sister, the viewport() , specifies the device coordinate system.
The default window rectangle is the same as the device’s rectangle.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setWindow(x, y, w, h)
- Parameters:
x – int
y – int
w – int
h – int
This is an overloaded function.
Sets the painter’s window to the rectangle beginning at (x, y) and the given width and height.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setWorldMatrixEnabled(enabled)#
- Parameters:
enabled – bool
Enables transformations if enable is true, or disables transformations if enable is false. The world transformation matrix is not changed.
See also
worldMatrixEnabled()worldTransform()Coordinate Transformations
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.setWorldTransform(matrix[, combine=false])#
- Parameters:
matrix –
PySide6.QtGui.QTransformcombine – bool
Sets the world transformation matrix. If combine is true, the specified matrix is combined with the current matrix; otherwise it replaces the current matrix.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.shear(sh, sv)#
- Parameters:
sh – float
sv – float
Shears the coordinate system by (sh, sv).
See also
setWorldTransform()Coordinate Transformations
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.strokePath(path, pen)#
- Parameters:
path –
PySide6.QtGui.QPainterPathpen –
PySide6.QtGui.QPen
Draws the outline (strokes) the path path with the pen specified by pen
See also
fillPath()Drawing
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.testRenderHint(hint)#
- Parameters:
hint –
RenderHint- Return type:
bool
Returns true if hint is set; otherwise returns false.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.transform()#
- Return type:
Alias for worldTransform() . Returns the world transformation matrix.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.translate(offset)#
- Parameters:
offset –
PySide6.QtCore.QPoint
This is an overloaded function.
Translates the coordinate system by the given offset.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.translate(offset)
- Parameters:
offset –
PySide6.QtCore.QPointF
Translates the coordinate system by the given offset; i.e. the given offset is added to points.
See also
setWorldTransform()Coordinate Transformations
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.translate(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – float
dy – float
This is an overloaded function.
Translates the coordinate system by the vector (dx, dy).
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.viewTransformEnabled()#
- Return type:
bool
Returns true if view transformation is enabled; otherwise returns false.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.viewport()#
- Return type:
Returns the viewport rectangle.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.window()#
- Return type:
Returns the window rectangle.
See also
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.worldMatrixEnabled()#
- Return type:
bool
Returns true if world transformation is enabled; otherwise returns false.
- PySide6.QtGui.QPainter.worldTransform()#
- Return type:
Returns the world transformation matrix.
See also