QFormLayout#
The QFormLayout class manages forms of input widgets and their associated labels. More…
Synopsis#
Properties#
fieldGrowthPolicy- The way in which the form’s fields growformAlignment- The alignment of the form layout’s contents within the layout’s geometryhorizontalSpacing- The spacing between widgets that are laid out side by sidelabelAlignment- The horizontal alignment of the labelsrowWrapPolicy- The way in which the form’s rows wrapverticalSpacing- The spacing between widgets that are laid out vertically
Functions#
def
addRow(label, field)def
addRow(layout)def
addRow(labelText, field)def
addRow(labelText, field)def
addRow(label, field)def
addRow(widget)def
fieldGrowthPolicy()def
formAlignment()def
getItemPosition(index)def
getLayoutPosition(layout)def
getWidgetPosition(widget)def
horizontalSpacing()def
insertRow(row, label, field)def
insertRow(row, labelText, field)def
insertRow(row, labelText, field)def
insertRow(row, widget)def
insertRow(row, label, field)def
insertRow(row, layout)def
isRowVisible(layout)def
isRowVisible(widget)def
isRowVisible(row)def
itemAt(row, role)def
labelAlignment()def
labelForField(field)def
labelForField(field)def
removeRow(layout)def
removeRow(widget)def
removeRow(row)def
rowCount()def
rowWrapPolicy()def
setFieldGrowthPolicy(policy)def
setFormAlignment(alignment)def
setHorizontalSpacing(spacing)def
setItem(row, role, item)def
setLabelAlignment(alignment)def
setLayout(row, role, layout)def
setRowVisible(layout, on)def
setRowVisible(widget, on)def
setRowVisible(row, on)def
setRowWrapPolicy(policy)def
setVerticalSpacing(spacing)def
setWidget(row, role, widget)def
takeRow(layout)def
takeRow(widget)def
takeRow(row)def
verticalSpacing()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
QFormLayout is a convenience layout class that lays out its children in a two-column form. The left column consists of labels and the right column consists of “field” widgets (line editors, spin boxes, etc.).
Traditionally, such two-column form layouts were achieved using QGridLayout . QFormLayout is a higher-level alternative that provides the following advantages:
Adherence to the different platform’s look and feel guidelines.
For example, the macOS Aqua and KDE guidelines specify that the labels should be right-aligned, whereas Windows and GNOME applications normally use left-alignment.
Support for wrapping long rows.
For devices with small displays,
QFormLayoutcan be set towrap long rows, or even towrap all rows.Convenient API for creating label–field pairs.
The
addRow()overload that takes aQStringand aQWidget* creates aQLabelbehind the scenes and automatically set up its buddy. We can then write code like this:formLayout = QFormLayout(self) formLayout.addRow(tr("Name:"), nameLineEdit) formLayout.addRow(tr("Email:"), emailLineEdit) formLayout.addRow(tr("Age:"), ageSpinBox)Compare this with the following code, written using
QGridLayout:gridLayout = QGridLayout(self) nameLabel = QLabel(tr("Name:")) nameLabel.setBuddy(nameLineEdit) emailLabel = QLabel(tr("Name:")) emailLabel.setBuddy(emailLineEdit) ageLabel = QLabel(tr("Name:")) ageLabel.setBuddy(ageSpinBox) gridLayout.addWidget(nameLabel, 0, 0) gridLayout.addWidget(nameLineEdit, 0, 1) gridLayout.addWidget(emailLabel, 1, 0) gridLayout.addWidget(emailLineEdit, 1, 1) gridLayout.addWidget(ageLabel, 2, 0) gridLayout.addWidget(ageSpinBox, 2, 1)
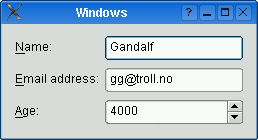
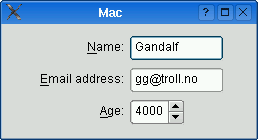
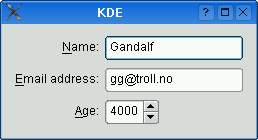
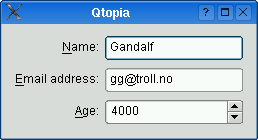
The table below shows the default appearance in different styles.
QCommonStylederived styles (except QPlastiqueStyle)QMacStyle
QPlastiqueStyle
Qt Extended styles
Traditional style used for Windows, GNOME, and earlier versions of KDE. Labels are left aligned, and expanding fields grow to fill the available space. (This normally corresponds to what we would get using a two-column
QGridLayout.)Style based on the macOS Aqua guidelines. Labels are right-aligned, the fields don’t grow beyond their size hint, and the form is horizontally centered.
Recommended style for KDE applications . Similar to MacStyle, except that the form is left-aligned and all fields grow to fill the available space.
Default style for Qt Extended styles. Labels are right-aligned, expanding fields grow to fill the available space, and row wrapping is enabled for long lines.
The form styles can be also be overridden individually by calling setLabelAlignment() , setFormAlignment() , setFieldGrowthPolicy() , and setRowWrapPolicy() . For example, to simulate the form layout appearance of QMacStyle on all platforms, but with left-aligned labels, you could write:
formLayout.setRowWrapPolicy(QFormLayout.DontWrapRows) formLayout.setFieldGrowthPolicy(QFormLayout.FieldsStayAtSizeHint) formLayout.setFormAlignment(Qt.AlignHCenter | Qt.AlignTop) formLayout.setLabelAlignment(Qt.AlignLeft)See also
- class PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout([parent=None])#
- Parameters:
parent –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Constructs a new form layout with the given parent widget.
The layout is set directly as the top-level layout for parent. There can be only one top-level layout for a widget. It is returned by layout() .
See also
Note
Properties can be used directly when from __feature__ import true_property is used or via accessor functions otherwise.
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.fieldGrowthPolicy: FieldGrowthPolicy#
This property holds the way in which the form’s fields grow.
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QMacStyle, the default is FieldsStayAtSizeHint ; for QCommonStyle derived styles (like Plastique and Windows), the default is ExpandingFieldsGrow ; for Qt Extended styles, the default is AllNonFixedFieldsGrow .
If none of the fields can grow and the form is resized, extra space is distributed according to the current form alignment .
See also
- Access functions:
setFieldGrowthPolicy(policy)
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.formAlignment: Alignment#
This property holds the alignment of the form layout’s contents within the layout’s geometry.
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QMacStyle, the default is AlignHCenter | AlignTop ; for the other styles, the default is AlignLeft | AlignTop .
See also
- Access functions:
setFormAlignment(alignment)
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.horizontalSpacing: int#
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out side by side.
By default, if no value is explicitly set, the layout’s horizontal spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
See also
verticalSpacingpixelMetric()PM_LayoutHorizontalSpacing
- Access functions:
setHorizontalSpacing(spacing)
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.labelAlignment: Alignment#
This property holds the horizontal alignment of the labels.
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For QCommonStyle derived styles, except for QPlastiqueStyle, the default is AlignLeft ; for the other styles, the default is AlignRight .
See also
- Access functions:
setLabelAlignment(alignment)
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.rowWrapPolicy: RowWrapPolicy#
This property holds the way in which the form’s rows wrap.
The default value depends on the widget or application style. For Qt Extended styles, the default is WrapLongRows ; for the other styles, the default is DontWrapRows .
If you want to display each label above its associated field (instead of next to it), set this property to WrapAllRows .
See also
- Access functions:
setRowWrapPolicy(policy)
- property PᅟySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.verticalSpacing: int#
This property holds the spacing between widgets that are laid out vertically.
By default, if no value is explicitly set, the layout’s vertical spacing is inherited from the parent layout, or from the style settings for the parent widget.
See also
horizontalSpacingpixelMetric()PM_LayoutHorizontalSpacing
- Access functions:
setVerticalSpacing(spacing)
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.FieldGrowthPolicy#
This enum specifies the different policies that can be used to control the way in which the form’s fields grow.
Constant
Description
QFormLayout.FieldsStayAtSizeHint
The fields never grow beyond their
effective size hint. This is the default for QMacStyle.QFormLayout.ExpandingFieldsGrow
Fields with an horizontal
size policyofExpandingorMinimumExpandingwill grow to fill the available space. The other fields will not grow beyond their effective size hint. This is the default policy for Plastique.QFormLayout.AllNonFixedFieldsGrow
All fields with a size policy that allows them to grow will grow to fill the available space. This is the default policy for most styles.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.RowWrapPolicy#
This enum specifies the different policies that can be used to control the way in which the form’s rows wrap.
Constant
Description
QFormLayout.DontWrapRows
Fields are always laid out next to their label. This is the default policy for all styles except Qt Extended styles.
QFormLayout.WrapLongRows
Labels are given enough horizontal space to fit the widest label, and the rest of the space is given to the fields. If the minimum size of a field pair is wider than the available space, the field is wrapped to the next line. This is the default policy for Qt Extended styles.
QFormLayout.WrapAllRows
Fields are always laid out below their label.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.ItemRole#
This enum specifies the types of widgets (or other layout items) that may appear in a row.
Constant
Description
QFormLayout.LabelRole
A label widget.
QFormLayout.FieldRole
A field widget.
QFormLayout.SpanningRole
A widget that spans label and field columns.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.addRow(label, field)#
- Parameters:
label –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidgetfield –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
This is an overloaded function.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.addRow(layout)
- Parameters:
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
This is an overloaded function.
Adds the specified layout at the end of this form layout. The layout spans both columns.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.addRow(labelText, field)
- Parameters:
labelText – str
field –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
This is an overloaded function.
This overload automatically creates a QLabel behind the scenes with labelText as its text. The field is set as the new QLabel ‘s buddy .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.addRow(labelText, field)
- Parameters:
labelText – str
field –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
This is an overloaded function.
This overload automatically creates a QLabel behind the scenes with labelText as its text.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.addRow(label, field)
- Parameters:
label –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidgetfield –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Adds a new row to the bottom of this form layout, with the given label and field.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.addRow(widget)
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
This is an overloaded function.
Adds the specified widget at the end of this form layout. The widget spans both columns.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.fieldGrowthPolicy()#
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property fieldGrowthPolicy .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.formAlignment()#
- Return type:
Alignment
See also
Getter of property formAlignment .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.getItemPosition(index)#
- Parameters:
index – int
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the item at the specified index. If index is out of bounds, *``rowPtr`` is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *``rowPtr`` and the role is stored in *``rolePtr``.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.getLayoutPosition(layout)#
- Parameters:
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the specified child layout. If layout is not in the form layout, *``rowPtr`` is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *``rowPtr`` and the role is stored in *``rolePtr``.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.getWidgetPosition(widget)#
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Retrieves the row and role (column) of the specified widget in the layout. If widget is not in the layout, *``rowPtr`` is set to -1; otherwise the row is stored in *``rowPtr`` and the role is stored in *``rolePtr``.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.horizontalSpacing()#
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property horizontalSpacing .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.insertRow(row, label, field)#
- Parameters:
row – int
label –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidgetfield –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Inserts a new row at position row in this form layout, with the given label and field. If row is out of bounds, the new row is added at the end.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.insertRow(row, labelText, field)
- Parameters:
row – int
labelText – str
field –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
This is an overloaded function.
This overload automatically creates a QLabel behind the scenes with labelText as its text. The field is set as the new QLabel ‘s buddy .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.insertRow(row, labelText, field)
- Parameters:
row – int
labelText – str
field –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
This is an overloaded function.
This overload automatically creates a QLabel behind the scenes with labelText as its text.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.insertRow(row, widget)
- Parameters:
row – int
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
This is an overloaded function.
Inserts the specified widget at position row in this form layout. The widget spans both columns. If row is out of bounds, the widget is added at the end.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.insertRow(row, label, field)
- Parameters:
row – int
label –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidgetfield –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
This is an overloaded function.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.insertRow(row, layout)
- Parameters:
row – int
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
This is an overloaded function.
Inserts the specified layout at position row in this form layout. The layout spans both columns. If row is out of bounds, the widget is added at the end.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.isRowVisible(layout)#
- Parameters:
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout- Return type:
bool
This is an overloaded function.
Returns true if some items in the row corresponding to layout are visible, otherwise returns false.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.isRowVisible(widget)
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget- Return type:
bool
This is an overloaded function.
Returns true if some items in the row corresponding to widget are visible, otherwise returns false.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.isRowVisible(row)
- Parameters:
row – int
- Return type:
bool
Returns true if some items in the row row are visible, otherwise returns false.
Returns the layout item in the given row with the specified role (column). Returns None if there is no such item.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.labelAlignment()#
- Return type:
Alignment
See also
Getter of property labelAlignment .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.labelForField(field)#
- Parameters:
field –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.labelForField(field)
- Parameters:
field –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget- Return type:
Returns the label associated with the given field.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.removeRow(layout)#
- Parameters:
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Deletes the row corresponding to layout from this form layout.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All widgets and nested layouts that occupied this row are deleted. That includes both the field widget(s) and the label, if any. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow() :
flay = ... vbl = QVBoxLayout() flay.insertRow(2, "User:", vbl) # later: flay.removeRow(layout) # vbl == None at this point
If you want to remove the row from the form layout without deleting the inserted layout, use takeRow() instead.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.removeRow(widget)
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Deletes the row corresponding to widget from this form layout.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All widgets and nested layouts that occupied this row are deleted. That includes both the field widget(s) and the label, if any. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow() :
flay = ... le = QLineEdit() flay.insertRow(2, "User:", le) # later: flay.removeRow(le) # le == None at this point
If you want to remove the row from the layout without deleting the widgets, use takeRow() instead.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.removeRow(row)
- Parameters:
row – int
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Deletes row row from this form layout.
row must be non-negative and less than rowCount() .
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All widgets and nested layouts that occupied this row are deleted. That includes both the field widget(s) and the label, if any. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow() :
flay = ... le = QLineEdit() flay.insertRow(2, "User:", le) # later: flay.removeRow(2) # le == None at this point
If you want to remove the row from the layout without deleting the widgets, use takeRow() instead.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.rowCount()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of rows in the form.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.rowWrapPolicy()#
- Return type:
See also
Getter of property rowWrapPolicy .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setFieldGrowthPolicy(policy)#
- Parameters:
policy –
FieldGrowthPolicy
See also
Setter of property fieldGrowthPolicy .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setFormAlignment(alignment)#
- Parameters:
alignment –
Alignment
See also
Setter of property formAlignment .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setHorizontalSpacing(spacing)#
- Parameters:
spacing – int
See also
Setter of property horizontalSpacing .
Sets the item in the given row for the given role to item, extending the layout with empty rows if necessary.
If the cell is already occupied, the item is not inserted and an error message is sent to the console. The item spans both columns.
Warning
Do not use this function to add child layouts or child widget items. Use setLayout() or setWidget() instead.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setLabelAlignment(alignment)#
- Parameters:
alignment –
Alignment
See also
Setter of property labelAlignment .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setLayout(row, role, layout)#
- Parameters:
row – int
role –
ItemRolelayout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout
Sets the sub-layout in the given row for the given role to layout, extending the form layout with empty rows if necessary.
If the cell is already occupied, the layout is not inserted and an error message is sent to the console.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setRowVisible(layout, on)#
- Parameters:
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayouton – bool
This is an overloaded function.
Shows the row corresponding to layout if on is true, otherwise hides the row.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setRowVisible(widget, on)
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidgeton – bool
This is an overloaded function.
Shows the row corresponding to widget if on is true, otherwise hides the row.
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setRowVisible(row, on)
- Parameters:
row – int
on – bool
Shows the row row if on is true, otherwise hides the row.
row must be non-negative and less than rowCount() .
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setRowWrapPolicy(policy)#
- Parameters:
policy –
RowWrapPolicy
See also
Setter of property rowWrapPolicy .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setVerticalSpacing(spacing)#
- Parameters:
spacing – int
See also
Setter of property verticalSpacing .
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.setWidget(row, role, widget)#
- Parameters:
row – int
role –
ItemRolewidget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget
Sets the widget in the given row for the given role to widget, extending the layout with empty rows if necessary.
If the cell is already occupied, the widget is not inserted and an error message is sent to the console.
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.takeRow(layout)#
- Parameters:
layout –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QLayout- Return type:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Removes the specified layout from this form layout.
Note
This function doesn’t delete anything.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
flay = ... vbl = QVBoxLayout() flay.insertRow(2, "User:", vbl) # later: QFormLayout.TakeRowResult result = flay.takeRow(widget)
If you want to remove the row from the form layout and delete the inserted layout, use removeRow() instead.
Returns A structure containing both the widget and corresponding label layout items
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.takeRow(widget)
- Parameters:
widget –
PySide6.QtWidgets.QWidget- Return type:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
This is an overloaded function.
Removes the specified widget from this form layout.
Note
This function doesn’t delete anything.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
flay = ... le = QLineEdit() flay.insertRow(2, "User:", le) # later: QFormLayout.TakeRowResult result = flay.takeRow(widget)
If you want to remove the row from the layout and delete the widgets, use removeRow() instead.
Returns A structure containing both the widget and corresponding label layout items
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.takeRow(row)
- Parameters:
row – int
- Return type:
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Removes the specified row from this form layout.
row must be non-negative and less than rowCount() .
Note
This function doesn’t delete anything.
After this call, rowCount() is decremented by one. All following rows are shifted up one row and the freed vertical space is redistributed amongst the remaining rows.
You can use this function to undo a previous addRow() or insertRow() :
flay = ... le = QLineEdit() flay.insertRow(2, "User:", le) # later: QFormLayout.TakeRowResult result = flay.takeRow(2)
If you want to remove the row from the layout and delete the widgets, use removeRow() instead.
Returns A structure containing both the widget and corresponding label layout items
See also
- PySide6.QtWidgets.QFormLayout.verticalSpacing()#
- Return type:
int
See also
Getter of property verticalSpacing .