ペインターパスの例
ペインターパスの例では、ペインターパスを使用してレンダリング用の複雑な図形を構築する方法を示します。
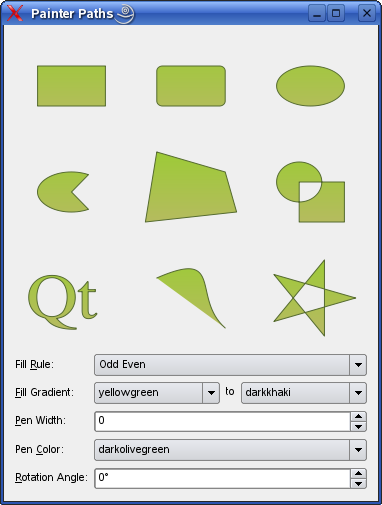
QPainterPath クラスは描画操作のためのコンテナを提供し、グラフィカルな図形を構築して再利用できるようにします。
ペインタパスは、多数のグラフィカルな構成要素(矩形、楕円、直線、曲線など)からなるオブジェクトで、塗りつぶし、アウトライン化、クリッピングに使用できます。通常の描画操作に対するペインタパスの主な利点は、複雑な形状を一度だけ作成すればよく、QPainter::drawPath() の呼び出しだけで何度でも描画できることです。
この例は2つのクラスで構成されています:
RenderAreaクラスは、単一のペインターパスを表示するカスタムウィジェットです。Windowクラスはアプリケーションのメイン・ウィンドウで、RenderAreaウィジェットをいくつか表示し、ユーザーがペインター・パスの塗りつぶし、ペン、色、回転角度を操作できるようにします。
まずWindow クラスについて説明し、次にRenderArea クラスについて説明します。
ウィンドウクラスの定義
Window クラスはQWidget を継承し、いくつかのRenderArea ウィジェットを表示するアプリケーションのメイン・ウィンドウで、ユーザーがペインター・パスの塗りつぶし、ペン、色、回転角度を操作できるようにします。
class Window : public QWidget { Q_OBJECT public: Window(); private slots: void fillRuleChanged(); void fillGradientChanged(); void penColorChanged();
塗りや色に関するユーザー入力に応答するために、3つのプライベート・スロットを宣言します:fillRuleChanged() 、fillGradientChanged() 、penColorChanged() 。
ユーザーがペンの幅と回転角度を変更すると、新しい値はQSpinBox::valueChanged() シグナルを使用してRenderArea ウィジェットに直接渡されます。塗りや色を更新するためにスロットを実装しなければならない理由は、QComboBox が新しい値を引数として渡す同様のシグナルを提供していないからです。したがって、RenderArea ウィジェットを更新する前に、新しい値(または値)を取得する必要があります。
private: void populateWithColors(QComboBox *comboBox); QVariant currentItemData(QComboBox *comboBox);
populateWithColors() は、与えられたQComboBox に Qt が知っている色の名前に対応するアイテムを入力し、currentItemData() は、与えられたQComboBox の現在のアイテムを返します。
QList<RenderArea*> renderAreas; QLabel *fillRuleLabel; QLabel *fillGradientLabel; QLabel *fillToLabel; QLabel *penWidthLabel; QLabel *penColorLabel; QLabel *rotationAngleLabel; QComboBox *fillRuleComboBox; QComboBox *fillColor1ComboBox; QComboBox *fillColor2ComboBox; QSpinBox *penWidthSpinBox; QComboBox *penColorComboBox; QSpinBox *rotationAngleSpinBox; };
そして、メイン・ウィジェットの様々なコンポーネントを宣言します。また、RenderArea ウィジェットの数を指定する便宜定数も宣言します。
ウィンドウ・クラスの実装
Window コンストラクタで、さまざまなペインタ・パスを定義し、グラフィカルな図形をレンダリングする対応するRenderArea ウィジェットを作成します:
Window::Window() { QPainterPath rectPath; rectPath.moveTo(20.0, 30.0); rectPath.lineTo(80.0, 30.0); rectPath.lineTo(80.0, 70.0); rectPath.lineTo(20.0, 70.0); rectPath.closeSubpath();
QPainterPath::moveTo() とQPainterPath::lineTo() 関数を使用して、鋭角の矩形を作成します。
QPainterPath::moveTo() は現在の点を引数として渡された点に移動します。ペインターパスは、いくつかのグラフィカルな構成要素、つまりサブパスで構成されるオブジェクトです。カレントポイントを移動すると、新しいサブパスも開始されます(新しいサブパスが開始されると、それまでのカレントパスは暗黙のうちに閉じられます)。QPainterPath::lineTo() 関数は、現在点から与えられた終点まで直線を追加します。直線が引かれた後、現在点は直線の終点に位置するように更新されます。
まず、現在点を新しいサブパスから移動させ、長方形の3辺を描画する。そして、QPainterPath::closeSubpath ()関数を呼び出し、現在のサブパスの始点に線を引く。現在のサブパスが閉じられると、新しいサブパスが自動的に開始される。新しいパスの現在の点は(0, 0)です。最後の線を描画するためにQPainterPath::lineTo() を呼び出し、QPainterPath::moveTo() 関数を使用して新しいサブパスを明示的に開始することもできます。
QPainterPath また、QPainterPath::addRect() という便利な関数も用意されており、与えられた矩形を閉じたサブパスとしてパスに追加します。矩形は、 時計回 り の線の集合 と し て追加 さ れます。矩形が追加された後のペインターのパスの現在位置は、矩形の左上隅になります。
QPainterPath roundRectPath; roundRectPath.moveTo(80.0, 35.0); roundRectPath.arcTo(70.0, 30.0, 10.0, 10.0, 0.0, 90.0); roundRectPath.lineTo(25.0, 30.0); roundRectPath.arcTo(20.0, 30.0, 10.0, 10.0, 90.0, 90.0); roundRectPath.lineTo(20.0, 65.0); roundRectPath.arcTo(20.0, 60.0, 10.0, 10.0, 180.0, 90.0); roundRectPath.lineTo(75.0, 70.0); roundRectPath.arcTo(70.0, 60.0, 10.0, 10.0, 270.0, 90.0); roundRectPath.closeSubpath();
次に、角を丸めた矩形を作成します。先ほどと同様に、QPainterPath::moveTo() とQPainterPath::lineTo() 関数を使用して矩形の辺を描画します。角丸を作るには、QPainterPath::arcTo ()関数を使う。
QPainterPath::arcTo() 関数は、指定された矩形(QRect または矩形の座標で指定)を占める円弧を、指定された開始角度から反時計回りに指定された角度だけ伸びるように作成します。角度は度単位で指定します。反時計回りの円弧は,負の角度を用いて指定することができます.この関数は、現在の点と円弧の始点がまだ接続されていない場合、それらを接続します。
QPainterPath ellipsePath; ellipsePath.moveTo(80.0, 50.0); ellipsePath.arcTo(20.0, 30.0, 60.0, 40.0, 0.0, 360.0);
また、QPainterPath::arcTo()関数を使用して楕円のパスを作成します。まず、現在点を移動して新しいパスを開始します。そして、開始角度0.0、360.0度を最後の引数としてQPainterPath::arcTo ()を呼び出し、楕円を作成します。
ここでもQPainterPath は、与えられた外接矩形内に楕円を作成し、それをペインターのパスに追加する便利な関数 (QPainterPath::addEllipse()) を提供しています。現在のサブパスが閉じている場合は、新しいサブパスが開始されます。楕円は時計回りの曲線で構成され、0度(3時の位置)で始まり、0度で終わります。
QPainterPath piePath; piePath.moveTo(50.0, 50.0); piePath.arcTo(20.0, 30.0, 60.0, 40.0, 60.0, 240.0); piePath.closeSubpath();
円グラフのパスを作るときは、前述の関数の組み合わせを使い続ける:まず、現在の点を移動し、新しいサブパスを始める。まず、現在の点を移動し、新しいサブパスを開始する。次に、チャートの中心から円弧までの線と、円弧そのものを作成する。サブパスを閉じるとき、グラフの中心に戻る最後の線を暗黙のうちに作成する。
QPainterPath polygonPath; polygonPath.moveTo(10.0, 80.0); polygonPath.lineTo(20.0, 10.0); polygonPath.lineTo(80.0, 30.0); polygonPath.lineTo(90.0, 70.0); polygonPath.closeSubpath();
多角形の作成は、長方形の作成と同じです。
QPainterPath また、与えられた多角形を新しいサブパスとしてパスに追加するQPainterPath::addPolygon() 便利関数も提供します。多角形が追加された後の現在位置は、多角形の最後の点になります。
QPainterPath groupPath; groupPath.moveTo(60.0, 40.0); groupPath.arcTo(20.0, 20.0, 40.0, 40.0, 0.0, 360.0); groupPath.moveTo(40.0, 40.0); groupPath.lineTo(40.0, 80.0); groupPath.lineTo(80.0, 80.0); groupPath.lineTo(80.0, 40.0); groupPath.closeSubpath();
次に、サブパスのグループからなるパスを作成する:まず、現在点を移動し、QPainterPath::arcTo ()関数を使い、開始角0.0、最後の引数に360度を指定し、楕円パスを作成したときと同じように円を作成します。次に、現在点を再び移動して新しいサブパスを開始し、QPainterPath::lineTo ()関数を使って正方形の3辺を作る。
ここで、QPainterPath::closeSubpath ()関数を呼び出すと、最後の辺が作成される。QPainterPath::closeSubpath()関数は、現在のサブパス、つまり正方形の始点に線を引くことを覚えておいてください。
QPainterPath QPainterPath::addPath() は、この関数を呼び出すパスに、与えられたパスを追加する便利な関数です。
QPainterPath textPath; QFont timesFont("Times", 50); timesFont.setStyleStrategy(QFont::ForceOutline); textPath.addText(10, 70, timesFont, tr("Qt"));
テ キ ス ト パ ス を作成す る 際には、 まずフ ォ ン ト を作成 し ます。こ れは、 フ ォ ン ト マ ッ チ ン グ アルゴ リ ズ ムに対 し て、 ど の種類の フ ォ ン ト を用い る べ き か を指示 し 、 適切なデフ ォ ル ト フ ァ ミ リ を見つけ る よ う に し ます。QFont::ForceOutline はアウトラインフォントの使用を強制します。
テ キ ス ト を作成す る には、QPainterPath::addText () 関数を用います。 こ れは、 与え ら れた テ キ ス ト を、 与え ら れた フ ォ ン ト か ら 作成 さ れた閉 じ たサブパスの集合 と し てパスに追加 し ます。こ のサブパスは、 テ キ ス ト のベース ラ イ ンの左端が指定 し た点に位置す る よ う に配置 さ れます。
QPainterPath bezierPath; bezierPath.moveTo(20, 30); bezierPath.cubicTo(80, 0, 50, 50, 80, 80);
Bezier パ ス を作成す る には、QPainterPath::cubicTo() 関数を用います。 こ れは、 カ レ ン ト 点 と 与えられた終点 と の間に、 与えられた制御点を用いて Bezier 曲線を追加 し ます。曲線が追加されると、現在点は曲線の終点に更新される。
この場合、単純な曲線になるように、サブパスを閉じることを省略する。しかし、曲線の終点からサブパスの始点に戻る論理的な線は残っている。アプリケーションのメイン・ウィンドウで見ることができるように、パスを塗りつぶすと見えるようになる。
QPainterPath starPath; starPath.moveTo(90, 50); for (int i = 1; i < 5; ++i) { starPath.lineTo(50 + 40 * std::cos(0.8 * i * M_PI), 50 + 40 * std::sin(0.8 * i * M_PI)); } starPath.closeSubpath();
最後に作成したパスは、QPainterPath を使って、先に述べたQPainterPath::moveTo(),QPainterPath::lineTo(),QPainterPath::closeSubpath() 関数だけで、かなり複雑な形状を作成できることを示しています。
renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(rectPath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(roundRectPath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(ellipsePath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(piePath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(polygonPath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(groupPath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(textPath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(bezierPath)); renderAreas.push_back(new RenderArea(starPath));
必要なペインターパスをすべて作成したので、それぞれに対応するRenderArea ウィジェットを作成します。最後に、Q_ASSERT ()マクロを使用して、レンダーエリアの数が正しいことを確認します。
fillRuleComboBox = new QComboBox; fillRuleComboBox->addItem(tr("Odd Even"), Qt::OddEvenFill); fillRuleComboBox->addItem(tr("Winding"), Qt::WindingFill); fillRuleLabel = new QLabel(tr("Fill &Rule:")); fillRuleLabel->setBuddy(fillRuleComboBox);
次に、ペインターパスの塗りつぶしルールに関連するウィジェットを作成します。
Qt には 2 つの塗りつぶしルールがあります:Qt::OddEvenFill のルールは、点からシェイプの外側の位置まで水平線を引き、交点の数をカウントすることで、点がシェイプの内側にあるかどうかを判断します。交点の数が奇数であれば、その点はシェイプの内側にある。このルールはデフォルトである。
Qt::WindingFill 規則は、点から図形の外側の位置まで水平線を引くことによって、点が図形の内側にあるかどうかを判定する。そして、各交点における線の方向が上か下かを判断する。巻き数は、各交点の方向を合計して決定される。この数が0でなければ、その点は図形の内側にある。
Qt::WindingFill ルールは、ほとんどの場合、閉じた形状の交点と考えることができる。
fillColor1ComboBox = new QComboBox; populateWithColors(fillColor1ComboBox); fillColor1ComboBox->setCurrentIndex(fillColor1ComboBox->findText("mediumslateblue")); fillColor2ComboBox = new QComboBox; populateWithColors(fillColor2ComboBox); fillColor2ComboBox->setCurrentIndex(fillColor2ComboBox->findText("cornsilk")); fillGradientLabel = new QLabel(tr("&Fill Gradient:")); fillGradientLabel->setBuddy(fillColor1ComboBox); fillToLabel = new QLabel(tr("to")); fillToLabel->setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy::Fixed, QSizePolicy::Fixed); penWidthSpinBox = new QSpinBox; penWidthSpinBox->setRange(0, 20); penWidthLabel = new QLabel(tr("&Pen Width:")); penWidthLabel->setBuddy(penWidthSpinBox); penColorComboBox = new QComboBox; populateWithColors(penColorComboBox); penColorComboBox->setCurrentIndex(penColorComboBox->findText("darkslateblue")); penColorLabel = new QLabel(tr("Pen &Color:")); penColorLabel->setBuddy(penColorComboBox); rotationAngleSpinBox = new QSpinBox; rotationAngleSpinBox->setRange(0, 359); rotationAngleSpinBox->setWrapping(true); rotationAngleSpinBox->setSuffix(QLatin1String("\xB0")); rotationAngleLabel = new QLabel(tr("&Rotation Angle:")); rotationAngleLabel->setBuddy(rotationAngleSpinBox);
塗りつぶし、ペン、回転角度に関連する他のウィジェットも作成します。
connect(fillRuleComboBox, &QComboBox::activated, this, &Window::fillRuleChanged); connect(fillColor1ComboBox, &QComboBox::activated, this, &Window::fillGradientChanged); connect(fillColor2ComboBox, &QComboBox::activated, this, &Window::fillGradientChanged); connect(penColorComboBox, &QComboBox::activated, this, &Window::penColorChanged); for (RenderArea *area : std::as_const(renderAreas)) { connect(penWidthSpinBox, &QSpinBox::valueChanged, area, &RenderArea::setPenWidth); connect(rotationAngleSpinBox, &QSpinBox::valueChanged, area, &RenderArea::setRotationAngle); }
コンボボックスactivated() シグナルをWindow クラスの関連スロットに接続し、スピンボックスvalueChanged() シグナルをRenderArea ウィジェットの各スロットに直接接続します。
QGridLayout *topLayout = new QGridLayout; int i = 0; for (RenderArea *area : std::as_const(renderAreas)) { topLayout->addWidget(area, i / 3, i % 3); ++i; } QGridLayout *mainLayout = new QGridLayout; mainLayout->addLayout(topLayout, 0, 0, 1, 4); mainLayout->addWidget(fillRuleLabel, 1, 0); mainLayout->addWidget(fillRuleComboBox, 1, 1, 1, 3); mainLayout->addWidget(fillGradientLabel, 2, 0); mainLayout->addWidget(fillColor1ComboBox, 2, 1); mainLayout->addWidget(fillToLabel, 2, 2); mainLayout->addWidget(fillColor2ComboBox, 2, 3); mainLayout->addWidget(penWidthLabel, 3, 0); mainLayout->addWidget(penWidthSpinBox, 3, 1, 1, 3); mainLayout->addWidget(penColorLabel, 4, 0); mainLayout->addWidget(penColorComboBox, 4, 1, 1, 3); mainLayout->addWidget(rotationAngleLabel, 5, 0); mainLayout->addWidget(rotationAngleSpinBox, 5, 1, 1, 3); setLayout(mainLayout);
RenderArea ウィジェットを別のレイアウトに追加し、残りのウィジェットと共にメインレイアウトに追加します。
fillRuleChanged();
fillGradientChanged();
penColorChanged();
penWidthSpinBox->setValue(2);
setWindowTitle(tr("Painter Paths"));
}最後に、fillRuleChanged() 、fillGradientChanged() 、penColorChanged() スロットを呼び出してRenderArea ウィジェットを初期化し、初期ペン幅とウィンドウ・タイトルを設定します。
void Window::fillRuleChanged() { Qt::FillRule rule = (Qt::FillRule)currentItemData(fillRuleComboBox).toInt(); for (RenderArea *area : std::as_const(renderAreas)) area->setFillRule(rule); } void Window::fillGradientChanged() { QColor color1 = qvariant_cast<QColor>(currentItemData(fillColor1ComboBox)); QColor color2 = qvariant_cast<QColor>(currentItemData(fillColor2ComboBox)); for (RenderArea *area : std::as_const(renderAreas)) area->setFillGradient(color1, color2); } void Window::penColorChanged() { QColor color = qvariant_cast<QColor>(currentItemData(penColorComboBox)); for (RenderArea *area : std::as_const(renderAreas)) area->setPenColor(color); }
プライベート・スロットは、関連するコンボボックスから新しい値を取得し、RenderAreaウィジェットを更新するために実装されています。
まず、privatecurrentItemData() 関数とqvariant_cast() テンプレート関数を使用して、新しい値を決定します。次に、RenderArea ウィジェットの関連スロットを呼び出して、ペインタパスを更新します。
void Window::populateWithColors(QComboBox *comboBox) { const QStringList colorNames = QColor::colorNames(); for (const QString &name : colorNames) comboBox->addItem(name, QColor(name)); }
populateWithColors() 関数は、静的なQColor::colorNames() 関数によって提供された Qt が知っている色の名前に対応するアイテムを、指定されたコンボボックスに入力します。
QVariant Window::currentItemData(QComboBox *comboBox) { return comboBox->itemData(comboBox->currentIndex()); }
currentItemData() 関数は、単に与えられたコンボボックスの現在の項目を返します。
RenderAreaクラスの定義
RenderArea クラスはQWidget を継承し、単一のペインターパスを表示するカスタムウィジェットです。
class RenderArea : public QWidget { Q_OBJECT public: explicit RenderArea(const QPainterPath &path, QWidget *parent = nullptr); QSize minimumSizeHint() const override; QSize sizeHint() const override; public slots: void setFillRule(Qt::FillRule rule); void setFillGradient(const QColor &color1, const QColor &color2); void setPenWidth(int width); void setPenColor(const QColor &color); void setRotationAngle(int degrees); protected: void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) override;
RenderArea ウィジェットに関連するペインタ・パスを更新するいくつかのパブリック・スロットを宣言します。さらに、QWidget::minimumSizeHint() とQWidget::sizeHint() 関数を再実装して、RenderArea ウィジェットをアプリケーション内で適切なサイズにし、QWidget::paintEvent() イベント・ハンドラを再実装して、ペインタ・パスを描画します。
private: QPainterPath path; QColor fillColor1; QColor fillColor2; int penWidth; QColor penColor; int rotationAngle; };
RenderArea クラスの各インスタンスには、QPainterPath 、塗りつぶしの色、ペンの幅、ペンの色、回転角度があります。
RenderAreaクラスの実装
コンストラクタは引数としてQPainterPath を取ります(オプションのQWidget 親に加えて):
RenderArea::RenderArea(const QPainterPath &path, QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent), path(path) { penWidth = 1; rotationAngle = 0; setBackgroundRole(QPalette::Base); }
コンストラクタでは、QPainterPath パラメータでRenderArea ウィジェットを初期化し、ペン幅と回転角度を初期化します。また、ウィジェットbackground role を設定します。QPalette::Base は通常白です。
QSize RenderArea::minimumSizeHint() const { return QSize(50, 50); } QSize RenderArea::sizeHint() const { return QSize(100, 100); }
次に、QWidget::minimumSizeHint() とQWidget::sizeHint() 関数を再実装して、RenderArea ウィジェットをアプリケーション内で適切なサイズにします。
void RenderArea::setFillRule(Qt::FillRule rule) { path.setFillRule(rule); update(); } void RenderArea::setFillGradient(const QColor &color1, const QColor &color2) { fillColor1 = color1; fillColor2 = color2; update(); } void RenderArea::setPenWidth(int width) { penWidth = width; update(); } void RenderArea::setPenColor(const QColor &color) { penColor = color; update(); } void RenderArea::setRotationAngle(int degrees) { rotationAngle = degrees; update(); }
さまざまなパブリック・スロットは、関連するプロパティを設定することでRenderArea ウィジェットのペインタ・パスを更新し、QWidget::update() 関数を呼び出して、新しいレンダリング設定でウィジェットの再描画を強制します。
QWidget::update() スロットは、即座に再描画を行うのではなく、Qt がメインイベントループに戻ったときに処理するペイントイベントをスケジュールします。
void RenderArea::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *) { QPainter painter(this); painter.setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
ペイントイベントは、ウィジェットの全部または一部を再ペイントする要求です。paintEvent() 関数は、ウィジェットのペイントイベントを受け取るために再実装できるイベントハンドラです。このイベントハンドラを再実装して、RenderArea ウィジェットのペインタパスをレンダリングします。
まず、RenderArea インスタンス用にQPainter を作成し、ペインターのレンダリングヒントを設定します。QPainter::RenderHints は、QPainter にフラグを指定するために使用します。このフラグは、任意のエンジンによって尊重される場合もあれば、尊重されない場合もあります。QPainter::Antialiasing は、エンジンが可能であればプリミティブのエッジをアンチエイリアスにすること、つまり、エッジを滑らかにするために元のピクセルの周囲に追加のピクセルを置くことを示します。
painter.scale(width() / 100.0, height() / 100.0); painter.translate(50.0, 50.0); painter.rotate(-rotationAngle); painter.translate(-50.0, -50.0);
それから、QPainter の座標系をスケーリングして、ペインターパスが適切なサイズでレンダリングされるようにします。つまり、アプリケーションのサイズが変更されたときに、RenderArea ウィジェットとともに大きくなるようにします。RenderArea::sizeHint() QPainter::scale() 関数は、RenderArea ウィジェットの現在の幅と高さを 100 で割った値で座標系をスケーリングします。
さて、ペインターパスが正しいサイズであることを確認したら、座標系を平行移動して、ペインターパスをRenderArea ウィジェットの中心を中心に回転させます。回転させた後、座標系を再び平行移動させることを忘れないようにしなければなりません。
painter.setPen(QPen(penColor, penWidth, Qt::SolidLine, Qt::RoundCap, Qt::RoundJoin)); QLinearGradient gradient(0, 0, 0, 100); gradient.setColorAt(0.0, fillColor1); gradient.setColorAt(1.0, fillColor2); painter.setBrush(gradient); painter.drawPath(path); }
次に、インスタンスのレンダリング環境設定でQPainter のペンを設定します。QLinearGradient を作成し、RenderArea ウィジェットの塗りつぶし色に対応する色を設定します。最後に、QPainter のブラシを設定し(グラデーションは自動的にQBrush に変換されます)、QPainter::drawPath() 関数を使用してRenderArea ウィジェットのペインターパスを描画します。
© 2025 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.

